Production method of plant-charcoal fabrics
The technology of a composite fabric and a production method is applied in the production field of vegetable charcoal composite fabrics, which can solve the problems of fabric air permeability and antibacterial properties that need to be improved, and achieve good electrical conductivity and deodorization functions, strong hygroscopicity, and antistatic function promotion. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The plant raw material used in this embodiment is corncob.
[0037] Send the plant material into a microwave vacuum tank, vacuumize until the vacuum degree is -0.02MPa, and then perform microwave treatment, the microwave frequency is 300MHz, and the microwave treatment time is 1min;
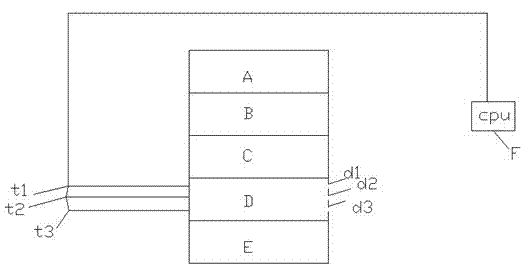
[0038] The plant raw materials obtained through pretreatment are dried, pre-carbonized, carbonized, calcined, and cooled in sequence. The temperature at each temperature measurement point is 150°C in drying area A, 275°C in pre-carbonization area B, and 450°C in carbonization area C. Observation during warming figure 1 The zone D shown is the temperature of different positions in the combustion zone. When the temperature of a certain place in the combustion zone, such as d2, is too low, open the small hole in that place, introduce air and burn it nearby, so as to raise the temperature in this place and control the bamboo to move down. The temperature of the combustion zone experienced in ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The plant material used in this example is bamboo chips (about 40 cm long).
[0046] Put the plant material into the microwave vacuum tank, vacuumize until the vacuum degree is -0.001MPa, and then carry out microwave treatment, the microwave frequency is 950MHz, and the microwave treatment time is 3min;
[0047]The plant raw materials obtained through pretreatment are dried, pre-carbonized, carbonized, calcined, and cooled in sequence. The temperature at each temperature measurement point is 150°C in drying area A, 275°C in pre-carbonization area B, and 450°C in carbonization area C. Observation during warming figure 1 The zone D shown is the temperature of different positions in the combustion zone. When the temperature of a certain place in the combustion zone, such as d2, is too low, open the small hole in that place, introduce air and burn it nearby, so as to raise the temperature in this place and control the bamboo to move down. The temperature of the combustion ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The plant raw material used in this embodiment is pine tree, and the pine tree is first cut after the skin impurities are removed, and the length is controlled to be no more than 15 cm.
[0055] Put the plant raw material into the microwave vacuum tank, vacuumize until the vacuum degree is -0.01MPa, and then carry out microwave treatment, the microwave frequency is 550MHz, and the microwave treatment time is 2min;
[0056] The pre-treated plant raw materials are dried, pre-carbonized, carbonized, calcined, and cooled in sequence. The temperature at each temperature measurement point is 180°C in the drying area A, 325°C in the pre-carbonization area B, and 530°C in the carbonization area C. Observation during warming figure 1 The zone D shown is the temperature of different positions in the combustion zone. When the temperature of a certain place in the combustion zone, such as d2, is too low, open the small hole in that place, introduce air and burn it nearby, so as to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com