Preparation method of core-shell structure magnetic nano-molecular imprinting polymer for separating starch polysaccharides
A magnetic nanoparticle, core-shell structure technology, applied in the direction of alkali metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve the problem of long adsorption time, low maximum saturated adsorption capacity, and low recycling rate and other problems, to achieve the effect of short adsorption time, high adsorption efficiency and high reuse rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
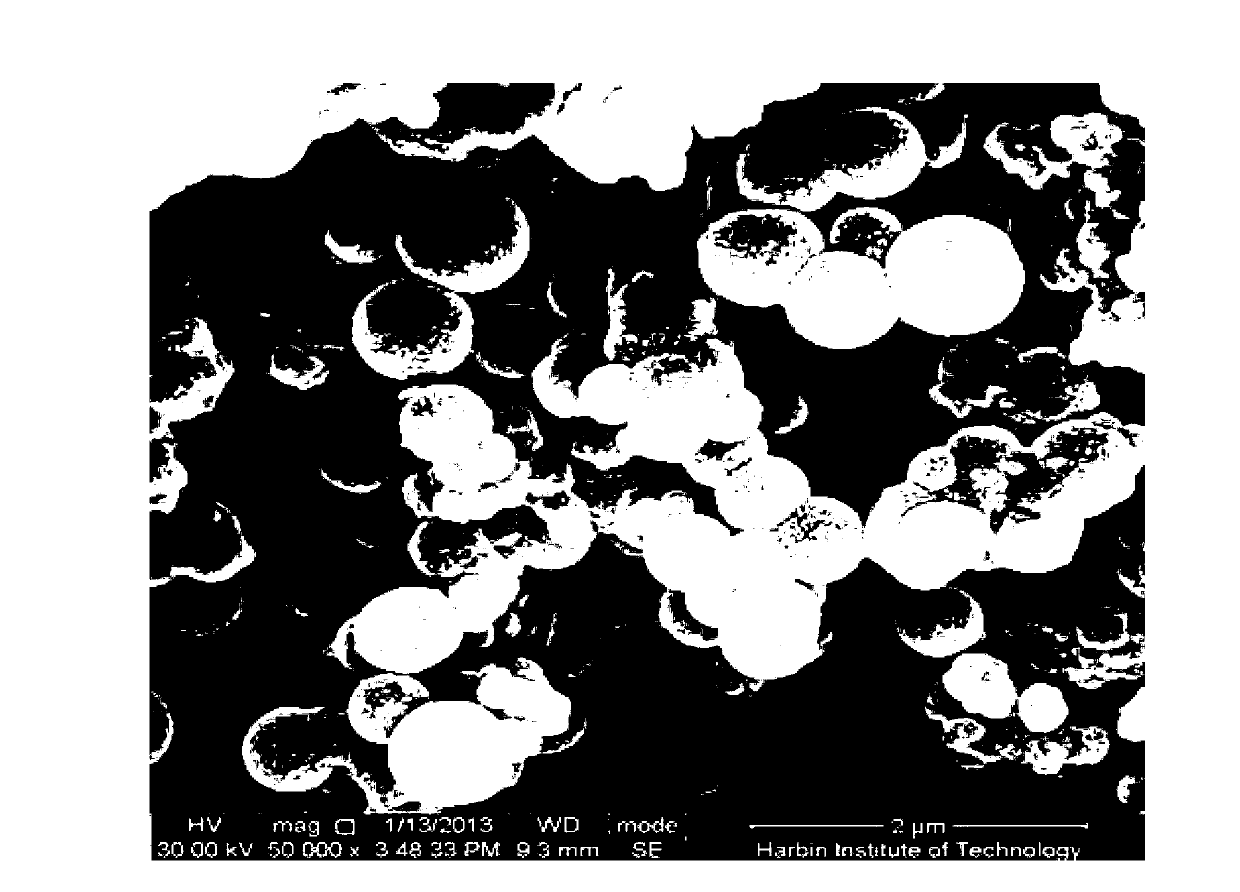
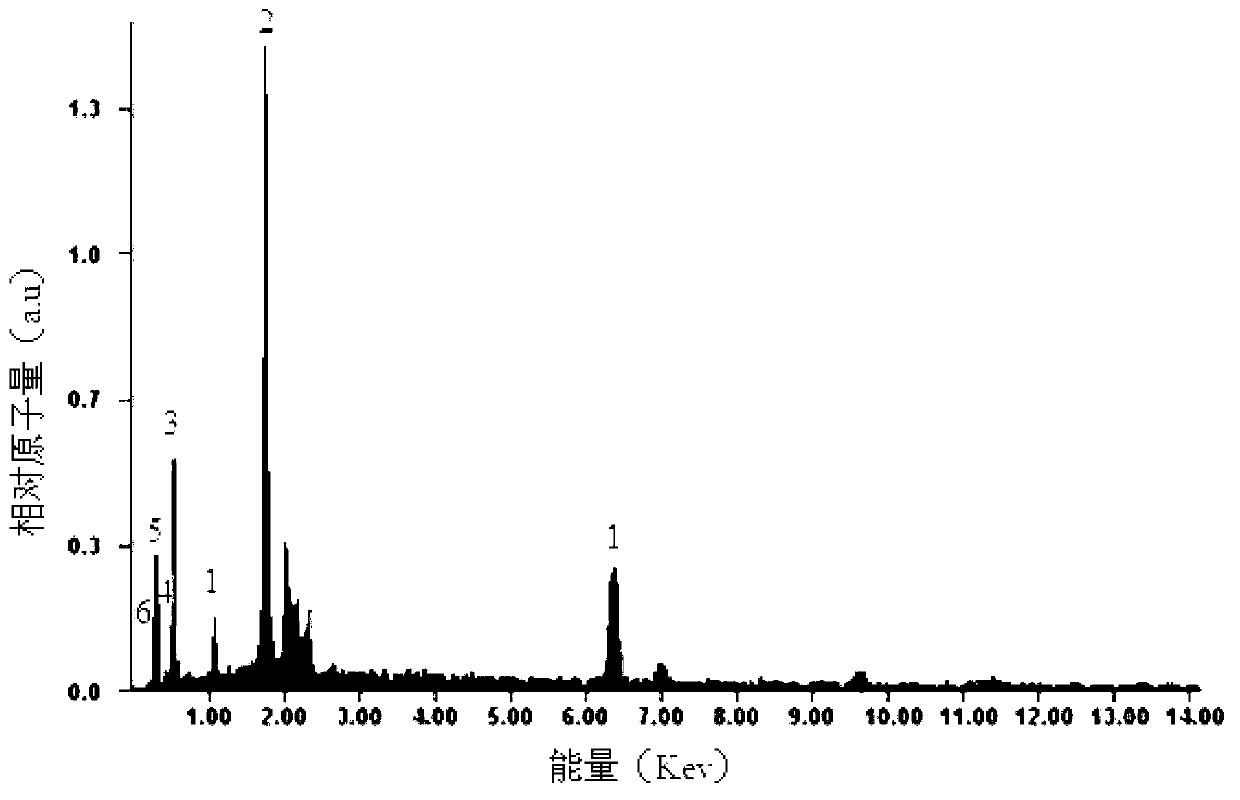
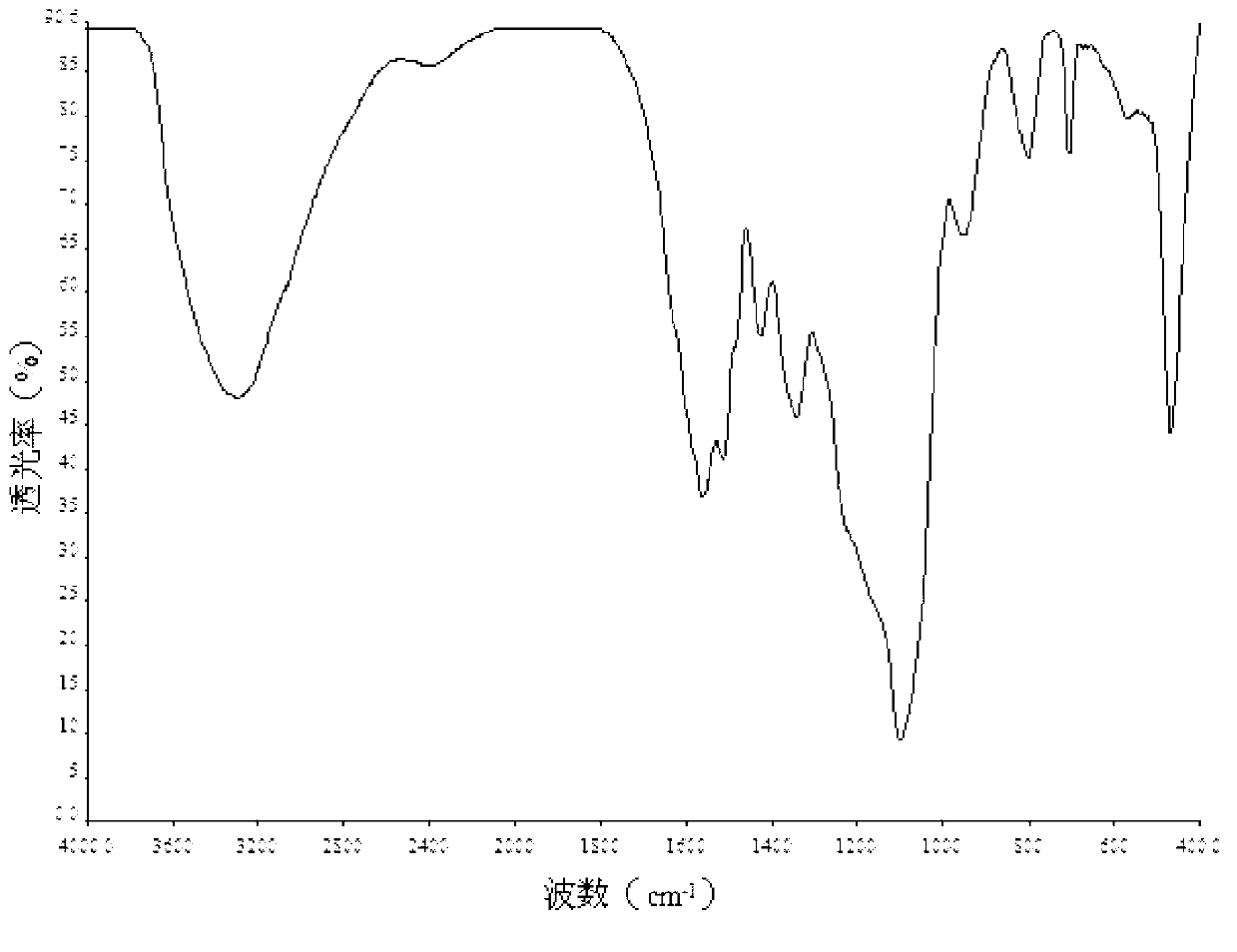
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0019] Specific embodiment one: The preparation method of the core-shell structure magnetic nano-molecularly imprinted polymer of the separation starch polysaccharide of the present embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0020] 1. Preparation of Fe 3 o 4 Magnetic nanoparticles: by FeCl 2 4H 2 O and FeCl 3 ·6H 2 The mass ratio of O is 1: (1.75 ~ 2), according to the Fe in the solution 3+ Concentration of 0.05 ~ 0.07g / mL, FeCl 2 4H 2 O and FeCl 3 ·6H 2O was respectively dissolved in deionized water deoxidized by nitrogen gas, ultrasonicated for 15-25 minutes, then mechanically stirred at a stirring speed of 700-900 rpm under the protection of nitrogen until the substances in the solution were completely dissolved, and then heated to 80-90°C and then added ammonia water Adjust the pH value to 9-10, continue to react for 20-40 minutes, and use NdFeB magnets for magnetic separation and sedimentation after cooling. After pouring out the upper liquid, ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0025] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: in step one, according to the Fe in the solution 3+ The concentration is 0.06g / mL, the FeCl 2 4H 2 O and FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O is respectively dissolved in deionized water deoxygenated with nitrogen, and other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0026] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that the stirring speed in step 1 is 800 rpm, stir until the substance in the solution is completely dissolved, and then heat to 85°C. Other steps and parameters are the same as in specific embodiment 1 or 2. Two same.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Maximum saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com