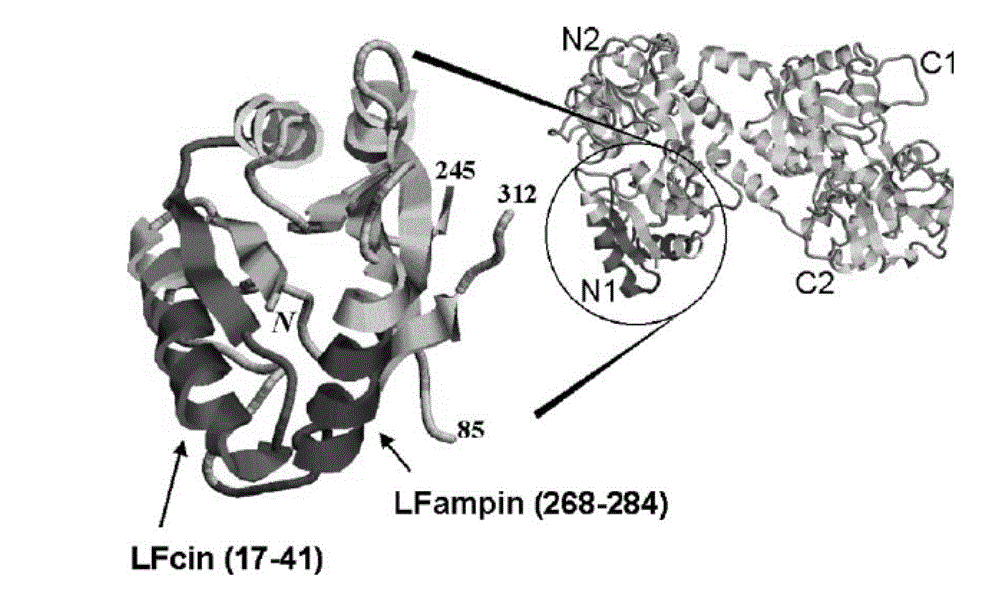
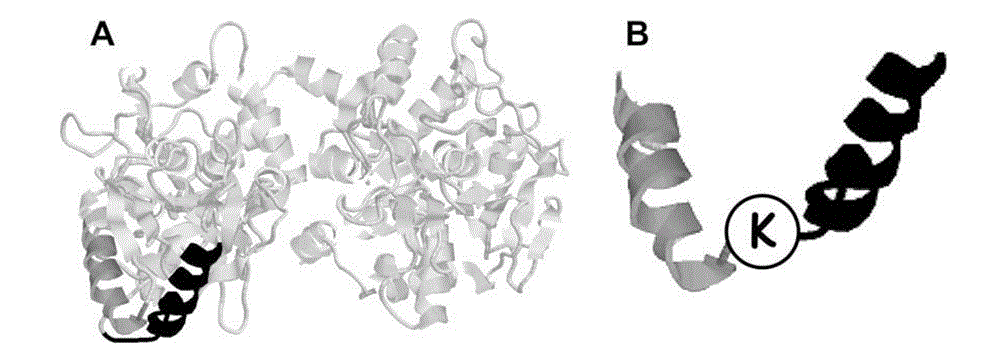
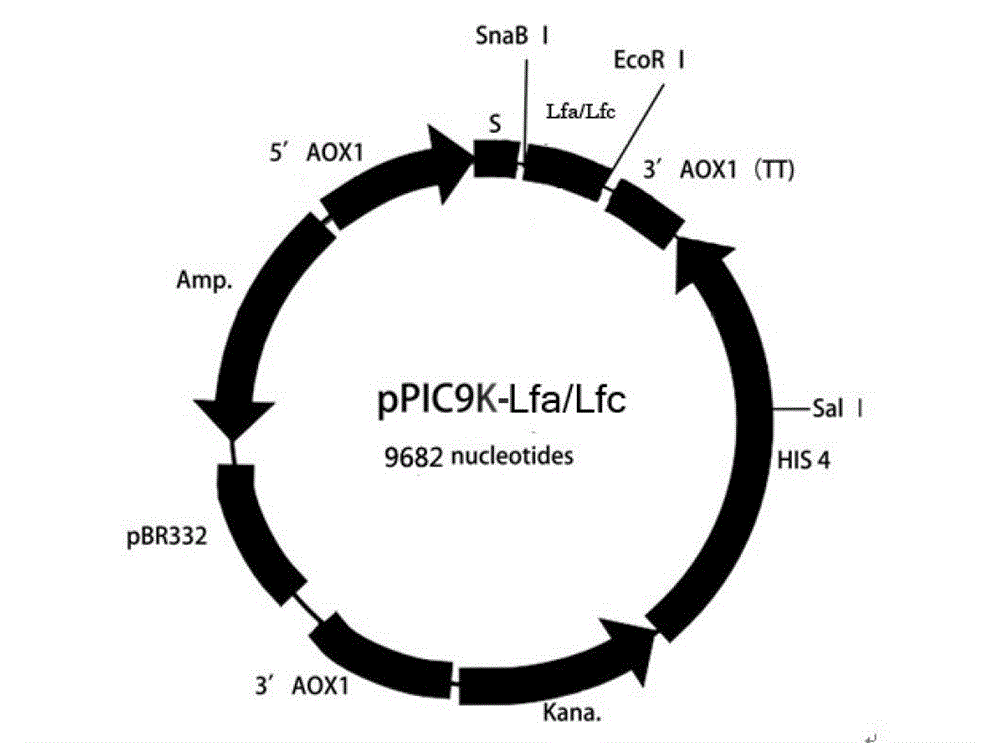
Antibacterial recombination polypeptide and expression vector thereof
A technology for recombinant polypeptides and vectors, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as unsuitable for large-scale production, cumbersome production process, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] The acquisition and identification of embodiment 1 recombinant plasmid pGE-Lfa / Lfc
[0082] Pick a single clone from the puncture bacteria, inoculate it into 5ml LB liquid medium containing 100ug / ml Amp, at 37°C, 220r / min, shake culture for 12-16h, OD value ≈ 0.6; small dose according to SDS alkaline lysis method Extract the recombinant plasmid pGE-Lfa / Lfc containing the antibacterial recombinant polypeptide Lfa-AA-Lfc gene fragment, use restriction endonuclease Hind Ⅲ to digest the recombinant plasmid pGE-Lfa / Lfc, and use 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis to detect .
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2 Connection and Transformation of the Gene of the Antibacterial Recombinant Polypeptide Lfa-AA-Lfc and the Secreted Expression Vector pPIC9K
[0084] The gene sequence of the synthetic antibacterial recombinant polypeptide Lfa-AA-Lfc was used as a template, and P1 and P2 were used as upstream and downstream primers for PCR amplification. Anneal for 30s, extend for 30s at 72°C, 30 cycles, and finally extend for 3min at 72°C to obtain PCR amplification products; PCR amplification products were identified by agarose gel electrophoresis, ligated with pGEM-T Easy Vector, and transformed into Escherichia coli C600 Competent cells; Recombinant plasmid TE-Lfa-AA-Lfc was digested with restriction endonuclease EcoR Ⅰ, the antibacterial recombinant polypeptide Lfa-AA-Lfc gene fragment was recovered, filled in with Klenow Fragment enzyme; secreted by Pichia pastoris The type expression vector pPIC9K was recovered by restriction endonuclease SnaB Ⅰ digestion, and the two re...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3 Linearization of recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-Lfa-AA-Lfc
[0087] The recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-Lfa-AA-Lfc was digested with the restriction endonuclease Sal I. After the digestion reaction, the linearized recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-Lfa-AA-Lfc was recovered with a Biospin gel recovery kit, and 0.8 % agarose gel electrophoresis to estimate the concentration of recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-Lfa-AA-Lfc.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com