Method for preparing biomass conductive charcoal electromagnetic shielding material
An electromagnetic shielding material and biomass technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, carbon compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and limited resources, and achieve low manufacturing costs, large resources, and improved utilization grades. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
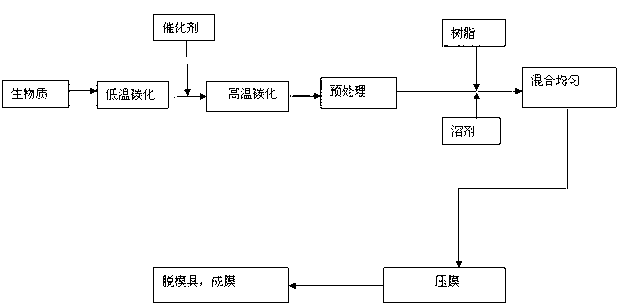
[0030] The first step is to use iron ferric oxide as the main catalyst, calcium carbide as the catalytic auxiliary agent, and mix the main catalyst and the auxiliary catalyst according to the mass ratio of 1:0.5 to form a catalyst;
[0031] In the second step, after removing the impurities in the rice straw, the rice straw is crushed and screened into granular particles with a particle size of 1mm, and sent into the carbonization furnace, heated to 480°C at a heating rate of 1°C / min for low-temperature carbonization, and the temperature is maintained at 0.5 h, cooling;
[0032] In the third step, the biomass conductive carbon obtained by low-temperature carbonization is taken out from the furnace, and the biomass conductive carbon and the catalyst are mixed evenly in a mass ratio of 50:1;
[0033] In the fourth step, the biomass conductive carbon mixed with the catalyst is used as a raw material for high-temperature carbonization, and it is sent into a carbonization furnace, h...
Embodiment 2
[0039] In the first step, nickel acetate is used as the main catalyst, calcium carbide is used as the catalyst promoter, and the catalyst is configured by mixing the main catalyst and the promoter according to the mass ratio of 1:4;
[0040] In the second step, after the impurities in the straw are removed, the wheat straw is crushed and screened into granular particles with a particle size of 15mm, and sent into the carbonization furnace, heated to 520°C at a heating rate of 30°C / min for low-temperature carbonization, and maintained at this temperature Temperature 10h, cooling;
[0041] In the third step, the biomass conductive carbon obtained by low-temperature carbonization is taken out from the furnace, and the biomass conductive carbon and the catalyst are mixed evenly in a ratio of 200:1 by mass;
[0042] In the fourth step, the biomass conductive carbon mixed with the catalyst is used as a raw material for high-temperature carbonization, and it is sent into a carbonizat...
Embodiment 3
[0048] In the first step, iron oxide is used as the main catalyst, calcium oxide is used as the catalyst promoter, and the catalyst is configured by mixing the main catalyst and the promoter according to the mass ratio of 1:2;
[0049] In the second step, after removing the impurities in the corn stalks, crush the corn stalks and screen the granular particles with a particle size of 8mm, send them into the carbonization furnace, heat them to 500°C at a heating rate of 15°C / min for low-temperature carbonization, and maintain this temperature 5h cooling;
[0050] In the third step, the biomass conductive carbon obtained by low-temperature carbonization is taken out from the furnace, and the biomass conductive carbon and the catalyst are mixed evenly in a ratio of 100:1 by mass;
[0051] In the fourth step, the biomass conductive carbon mixed with the catalyst is used as a raw material for high-temperature carbonization, and it is sent into a carbonization furnace, heated to 900°...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com