Substrate with transparent conductive oxide film
A transparent substrate and oxide film technology, applied in semiconductor devices, circuits, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve problems such as low conversion efficiency and short-circuit current reduction, and achieve the effects of suppressing reflection, suppressing contact resistance, and improving photoelectric conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0129] Hereinafter, although an Example demonstrates this invention in detail, this invention is not limited to these Examples.
[0130] In the examples, a film-coated substrate was fabricated according to the procedure shown below, and the photoelectric conversion characteristics of a module formed of a thin-film photoelectric conversion element fabricated using the film-coated substrate were evaluated.
[0131] However, among Examples 1 to 7 shown below, Examples 1 to 4 are examples, and Examples 5 to 7 are comparative examples.
example 1
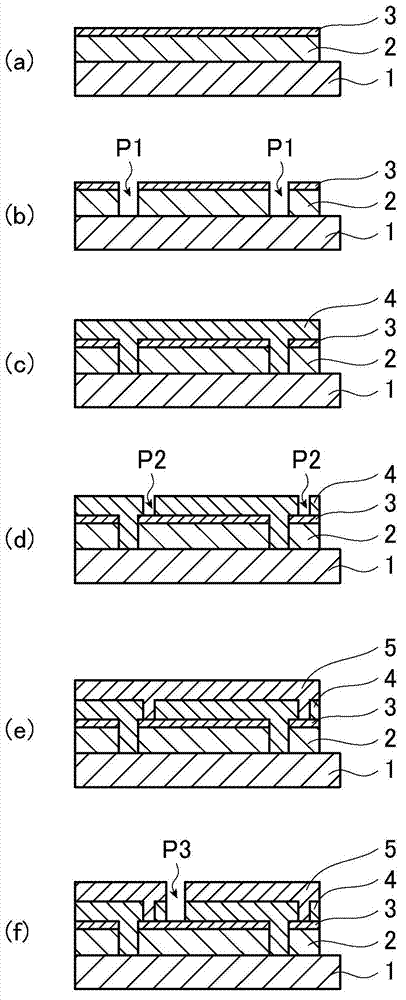
[0133] As a substrate, a soda lime silicate glass substrate (300mm×300mm×3.9mm) with an antireflection film laminated with a titanium oxide layer (thickness 10nm) and a silicon oxide layer (thickness 30nm) was used. A fluorine-doped tin oxide film was formed as the first film by an atmospheric pressure CVD method. The procedure for forming a fluorine-doped tin oxide film by atmospheric pressure CVD is as follows.
[0134] The temperature of the substrate was raised to 550° C. with an electric heater, and a source gas containing tin tetrachloride, water vapor, and hydrogen fluoride as raw materials was purged from a nozzle to form a first film as a fluorine-doped tin oxide film with a thickness of 700 nm.
[0135] The sheet resistance of the formed first film was measured by the DC 4-probe method, and as a result, the sheet resistance was 9Ω / □. In addition, when the molar ratio F / Sn of the first film was measured by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS), the molar ratio F / Sn ...
example 2~ example 7
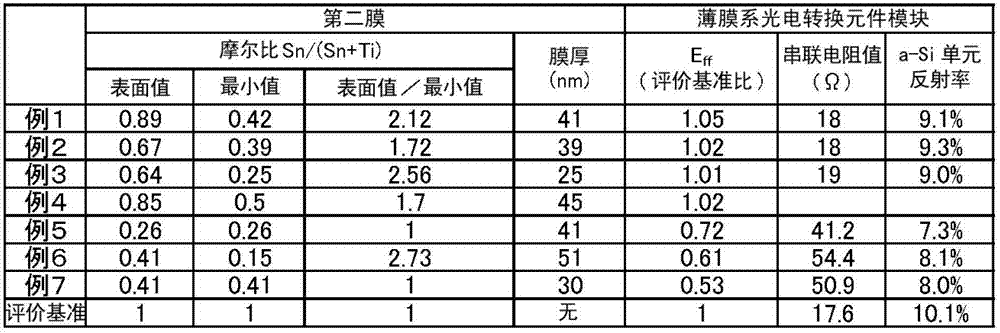
[0162] The same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out except that the raw material composition and supply amount of the raw material mixed gas were adjusted so that the film thickness of the second film and the molar ratio Sn / (Sn+Ti) were the values shown in the following table. The results are shown in the following tables. Blank columns in the table indicate no measurement data.
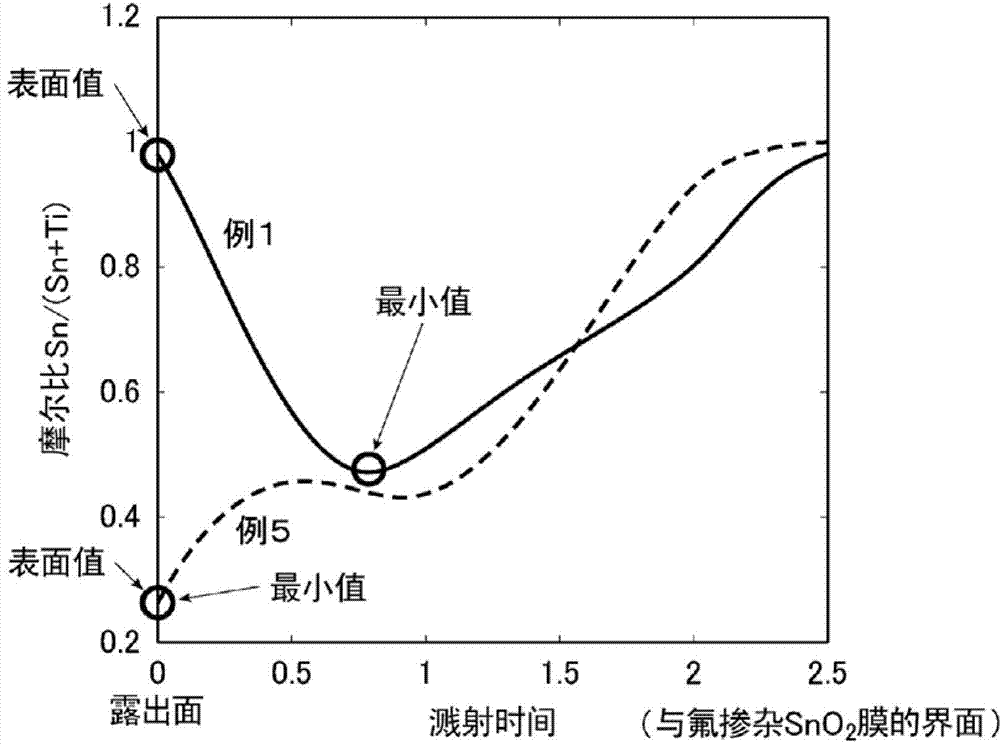
[0163] Here, regarding Examples 2 to 4 and 6, the surface value of the molar ratio Sn / (Sn+Ti) existing on the surface of the second film similarly to Example 1 is the molar ratio Sn / (Sn+Ti) within the total film thickness of the second film The maximum value of Sn+Ti) and the minimum value of the molar ratio Sn / (Sn+Ti) exist inside the second film. On the other hand, example 5 such as figure 1 As shown, there is a minimum of the molar ratio Sn / (Sn+Ti) at the surface of the second film. Fig. 7 also has the minimum value of the molar ratio Sn / (Sn+Ti) at the surface of the second film as in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com