Method for recovering feldspar from molybdenum separation tailings
A technology of molybdenum tailings and feldspar, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, flotation, wet separation, etc., can solve problems such as molybdenum tailings cannot be used as resources, and achieve the effect of reducing tailings stockpiles and significant environmental benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
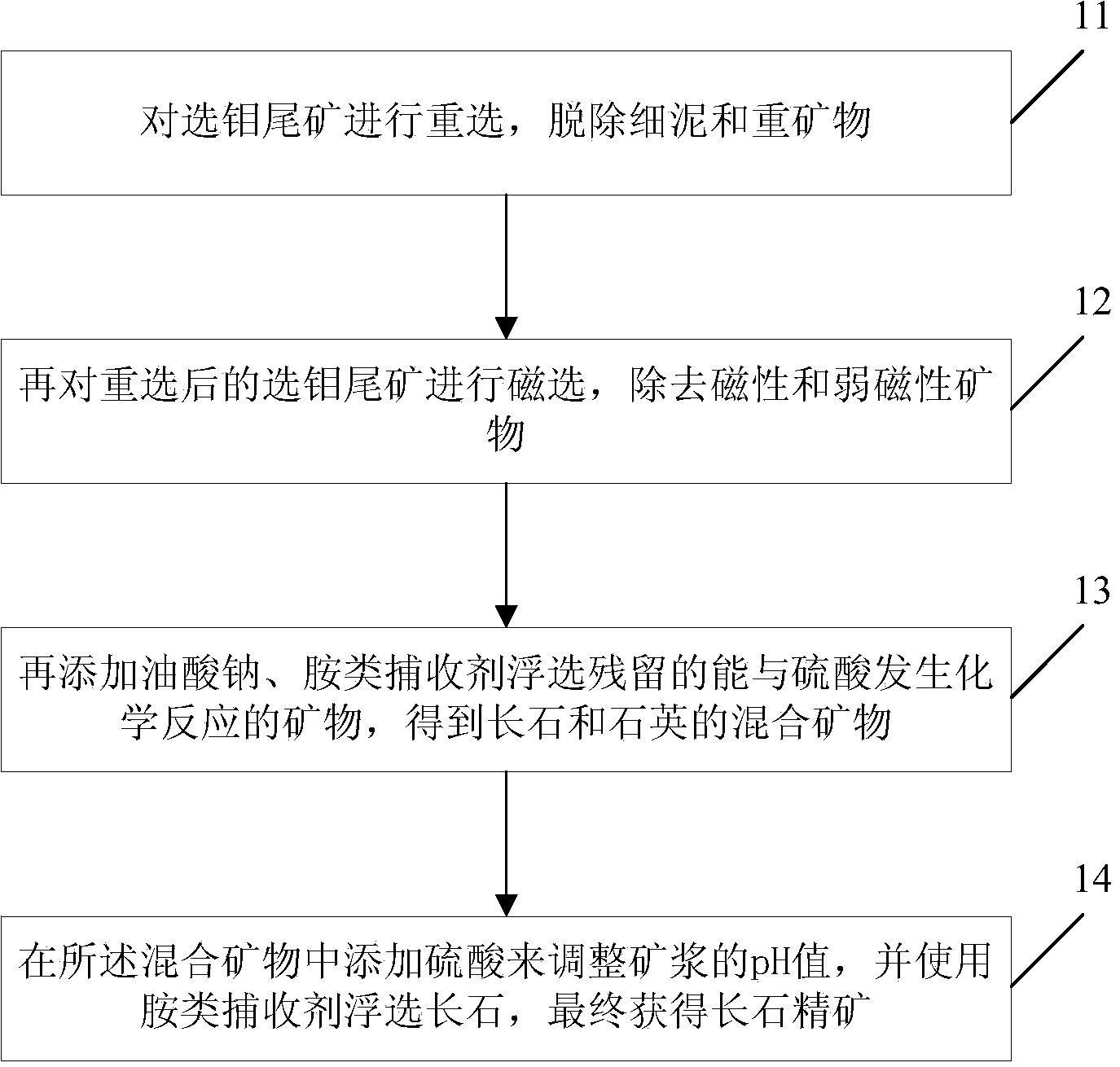
[0031] The metal minerals in the molybdenum tailings of a molybdenum mine in Heilongjiang are mainly pyrite, sphalerite, pyrrhotite, galena, arsenopyrite, ilmenite, limonite, mica, magnetite, rutile, red Iron ore, etc.; non-metallic minerals are mainly feldspar, quartz, calcite, muscovite, sericite, illite, kaolinite, and a small amount of titanite, apatite, etc.
[0032] Adopt the technical process described in the above method embodiment to finally obtain the feldspar concentrate production rate of 28.48%, K 2 O grade is 11.54%, Na 2 O grade is 2.51%, K 2 O recovery was 47.73%; Na 2 The recovery rate of O is 40.30%, and the feldspar concentrate meets the quality standard of potassium feldspar for potash fertilizer and the quality standard of potash feldspar for ceramic industry.
example 2
[0034] The metal minerals in the molybdenum tailings of a molybdenum mine in Inner Mongolia are mainly pyrite, magnetite, ilmenite, rutile, siderite, hematite, limonite and other minerals, and the non-metallic minerals are mainly potassium feldspar and clinoplasty Feldspar, quartz, biotite, chlorite, calcite, apatite, muscovite, dolomite, barite, pyroxene, talc, zircon, etc., K 2 O grade is 4.28%, Na 2 O grade is 2.77%.
[0035] Adopt the technological process described in the above-mentioned method embodiment to finally obtain feldspar concentrate productive rate 18.62%, in the concentrate, K 2 The O grade is 8.62%, and the recovery rate is 37.88%; Na 2 The O grade is 4.39%, the recovery rate is 29.90%; the TFe content in the feldspar concentrate is 0.42%.
[0036] In summary, the above-mentioned process for recovering feldspar from molybdenum tailings includes the following advantages:
[0037] 1) The process has strong adaptability, and is applicable to all molybdenum b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com