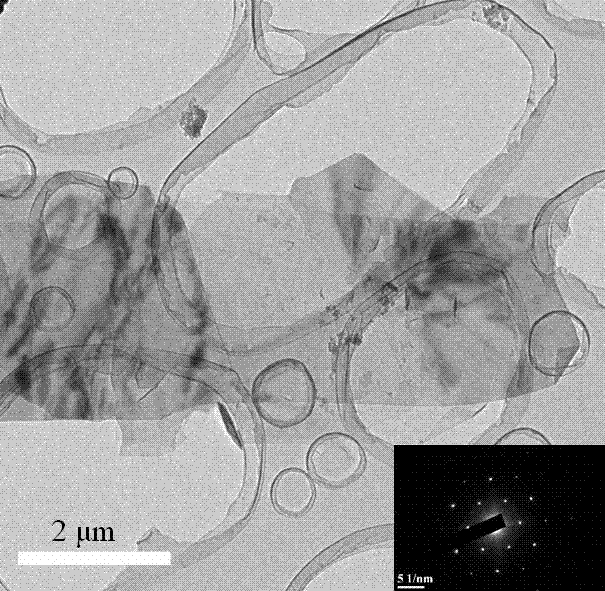
Preparation method of graphene
A graphene and graphene dispersion technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of large-scale preparation limitations, achieve the effects of reducing production costs, mild reaction conditions, and good large-scale industrial applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) Slowly add 1g of potassium permanganate to 100ml of concentrated sulfuric acid to form an acidic solution. Add 1 g of graphite raw material into the acidic solution, stir at 30° C. for 2 h, filter the obtained mixed solution, wash with water, and dry at 50° C. for 10 h to obtain acid-treated raw graphite.
[0030] (2) Add 5g of sodium hydroxide to 100ml of water to form an active substance solution. Then, the raw graphite obtained by the acid treatment is added into the active substance solution to obtain the active substance solution of the raw graphite.
[0031] (3) The active material solution of raw graphite was ultrasonically treated by a 500 W, 20 kHz probe at 20 °C for 2 h to obtain the active material solution of graphene.
[0032] (4) The graphene active substance solution obtained in step (3) is filtered, washed with water, and then dried at 50° C. for 10 hours to obtain graphene powder.
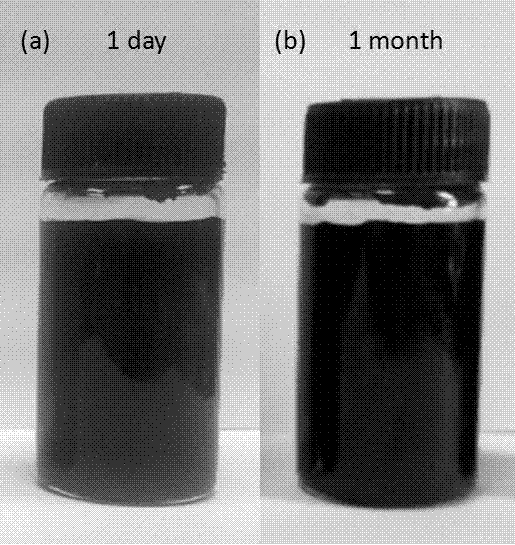
[0033] The graphene prepared by the above method is dispersed in ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Slowly add 1g of potassium permanganate to 10ml of concentrated sulfuric acid to form an acidic solution. Add 1 g of graphite raw material into the acidic solution, stir at 30° C. for 2 h, filter the obtained mixed solution, wash with water, and dry at 50° C. for 10 h to obtain acid-treated raw graphite.
[0036] (2) Add 5g of sodium hydroxide to 100ml of water to form an active substance solution. Then, the raw graphite obtained by the acid treatment is added into the active substance solution to obtain the active substance solution of the raw graphite.
[0037] (3) The active material solution of raw graphite was ultrasonically treated by a 500 W, 20 kHz probe at 20 °C for 2 h to obtain the active material solution of graphene.
[0038] (4) The graphene active substance solution obtained in step (3) is filtered, washed with water, and then dried at 50° C. for 10 hours to obtain graphene powder.
[0039] The graphene prepared by the above method is dispersed in N...
Embodiment 3
[0041] (1) Slowly add 1g of potassium permanganate to 100ml of concentrated sulfuric acid to form an acidic solution. Add 1 g of graphite raw material into the acidic solution, stir at 30° C. for 2 h, filter the obtained mixed solution, wash with water, and dry at 50° C. for 10 h to obtain acid-treated raw graphite.
[0042] (2) Add 1g of sodium hydroxide to 20ml of water to form an active substance solution. Then, the raw graphite obtained by the acid treatment is added into the active substance solution to obtain the active substance solution of the raw graphite.
[0043] (3) The active material solution of raw graphite was ultrasonically treated by a 500 W, 20 kHz probe at 20 °C for 2 h to obtain the active material solution of graphene.
[0044] (4) The graphene active substance solution obtained in step (3) is filtered, washed with water, and then dried at 50° C. for 10 hours to obtain graphene powder.
[0045] The graphene prepared by the above method is dispersed in N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com