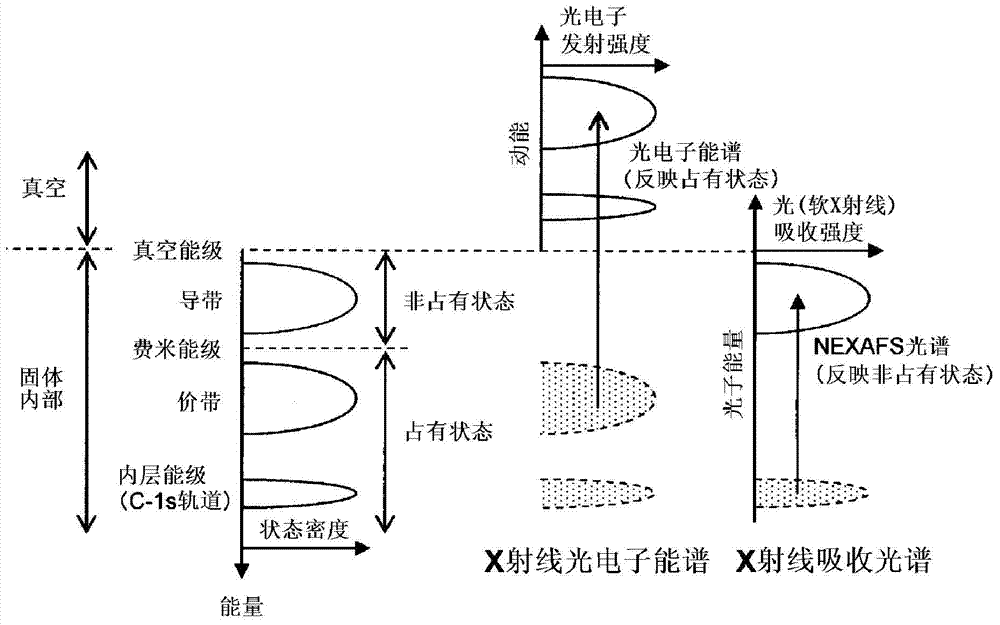
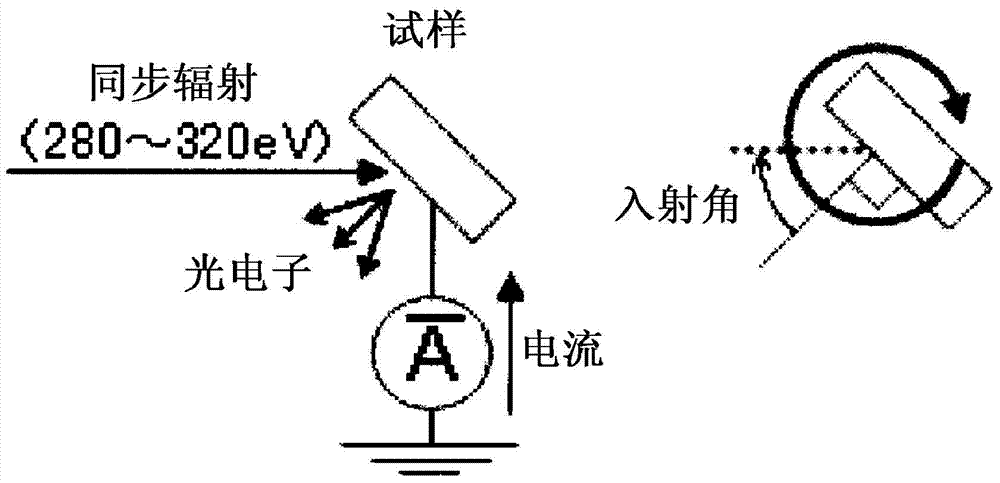
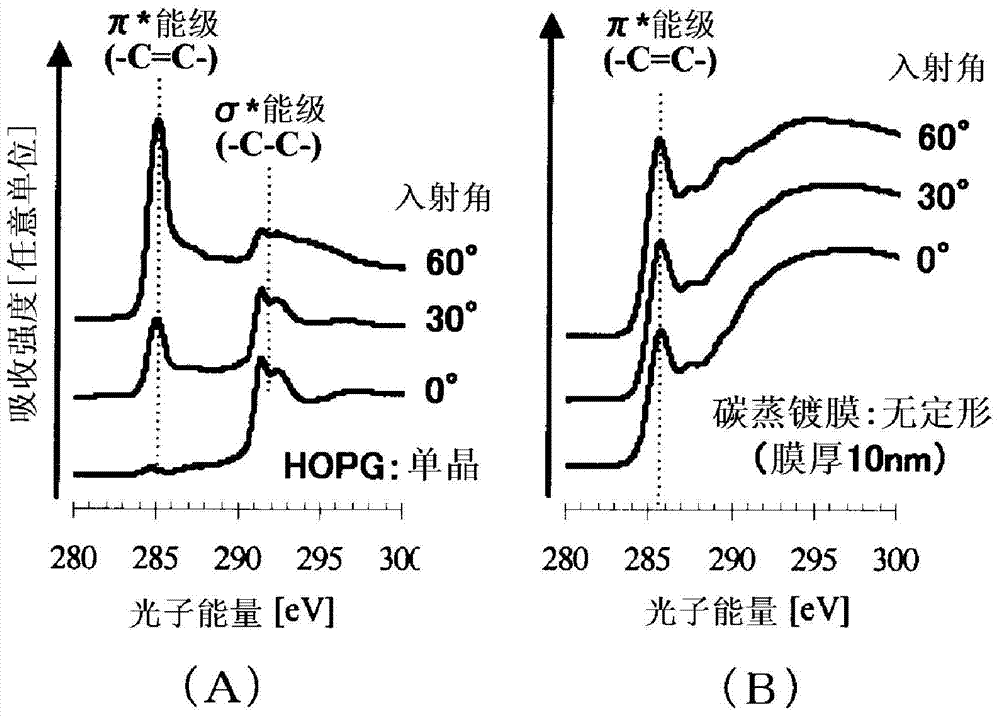
Modified natural graphite particles
A technology of natural graphite and particles, applied in the direction of graphite, structural parts, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of falling off of negative electrode mixture, decrease of bonding strength between negative electrode active material and current collector, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~4 and comparative example 1~4
[0127] (1) Manufacture of modified natural graphite particles
[0128] For raw material natural graphite particles (flaky graphite produced in China, the absolute specific gravity is 2.26g / cm 3 ), the spheroidization process was performed using a pulverization device (ACM pulverizer, ACM-10A) manufactured by HOSOKAWA MICRON CORPORATION. Repeat treatment 15 times. Then the fine powder is removed by wind classification. The spheroidization treatment was carried out at appropriately different grinding rotation speeds and classification rotation speeds to obtain four types of spheroidized graphite particles having different particle sizes as shown in Comparative Examples 1 to 4 in Table 1.
[0129] With respect to these graphite particles, a portion of each was further subjected to smoothing treatment using a Mechano Fusion system (AMS-Lab) manufactured by HOSOKAWA MICRON CORPORATION. The processing conditions are as follows.
[0130] Input amount: 600g
[0131] Gap between r...
Embodiment 5 and comparative example 5
[0167] Coal-based pitch powder with an average particle diameter of 15 μm was mixed with the graphite particles obtained in Example 2 and Comparative Example 2 in an amount of 20% by mass relative to the graphite particles, and the mixture was subjected to nitrogen flow at 1000° C. for 1 hour. After heat treatment, carbon-attached graphite particles with turbostratic carbon attached to the surface are obtained. The average particle diameter, specific surface area, tap density, and linseed oil absorption of the obtained carbon-attached graphite particles were determined in the same manner as in Examples 1 to 4. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0168] The anode active material containing the thus obtained carbon-attached graphite particles and PVdF were mixed at a mass ratio of 95:5 to prepare an anode mixture. Using these negative electrode mixtures, negative electrode plates were prepared in the same manner as in Examples 1-4. The results of measuring the peel strength of...
Embodiment 6 and comparative example 6
[0173] Coal-based pitch powder with an average particle size of 15 μm was mixed with the graphite particles obtained in Example 3 and Comparative Example 3 in an amount of 2% by mass relative to the graphite particles, and heat-treated at 1000° C. for 1 hour in a nitrogen stream. , to obtain carbon-attached graphite particles with turbostratic carbon attached to the surface. The average particle diameter, specific surface area, tap density, and linseed oil absorption of the obtained carbon-attached graphite particles were determined in the same manner as in Examples 1 to 4. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0174] A negative electrode mixture was prepared by mixing the negative electrode active material containing the thus obtained carbon-attached graphite particles, SBR, and CMC at a mass ratio of 98:1:1. Using these negative electrode mixtures, negative electrode plates were prepared in the same manner as in Examples 1-4. The results of measuring the peel strength of the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com