Method for treating p-aminodiphenylamine production device wastewater
A technology for p-aminodiphenylamine and production equipment, which is applied in the fields of natural water treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of unreached COD content, cumbersome recovery of formic acid, and high cost of sewage pretreatment. , to achieve the effect of high processing load, short water retention time, and solving the problems of discharge and treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
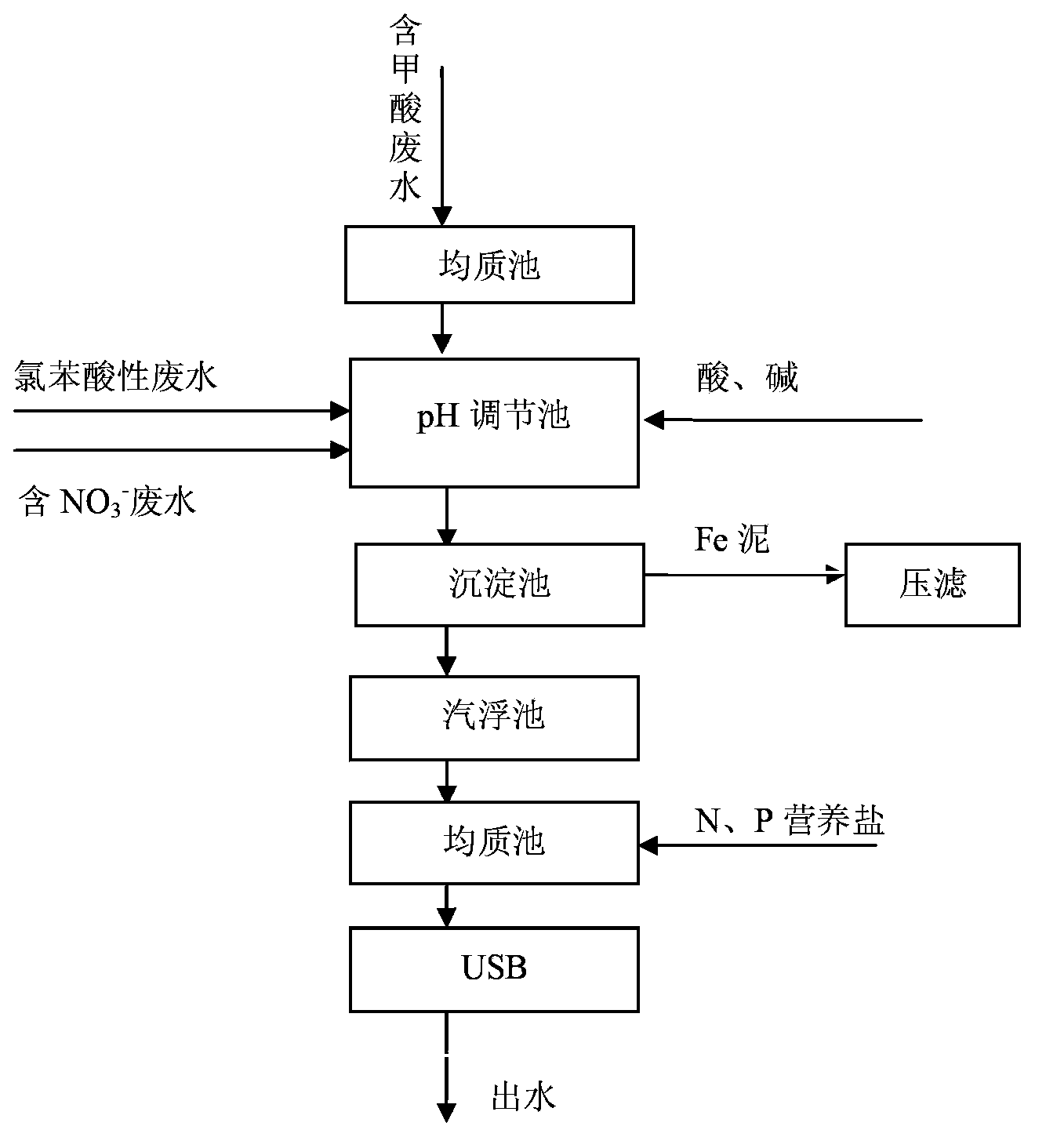
[0046] Wastewater from a p-aminodiphenylamine production unit in a chemical plant: influent COD is 55000mg / L, TOC is 31920mg / L, formic acid concentration is 156950mg / L, after homogenization and containing NO 3 - Mix catalyst wastewater, add a certain amount of chlorobenzene acidic wastewater, and add a certain amount of dilution water to dilute the wastewater containing p-aminodiphenylamine to 50 times, and the Fe content is 40mg / L; add a certain amount of HNO as needed 3 To supplement a certain amount of NO 3 - , NO 3 - The final concentration is 948mg / L, so that the C / N in the wastewater is maintained at about 2.98, and dilute HCl is added to adjust the pH of the influent to 6.00, and the mixed wastewater flows into the next operation unit by itself;
[0047] Then the Fe(OH) in the wastewater 3 It settles completely in the sedimentation tank, and the sedimentation time is about 1 hour. The Fe sludge at the bottom of the sedimentation tank is sent to the filter press roo...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The waste water flow rate of a p-aminodiphenylamine production unit in a chemical plant is 144t / d, and the pollutant indicators before entering the process are: influent COD is 82000mg / L, TOC is 45195mg / L, and formic acid concentration is 242750mg / L. After quality and containing NO 3 - Mix catalyst wastewater, add a certain amount of chlorobenzene acidic wastewater, and add a certain amount of dilution water to dilute the wastewater containing p-aminodiphenylamine to 50 times, and the Fe content is 50mg / L; add a certain amount of HNO as needed 3 To supplement a certain amount of NO 3 - , NO 3 - The final concentration is 2000mg / L, so that the C / N in the wastewater is maintained at about 1.98, and dilute HCl is added to adjust the pH of the influent to 7.50, and the mixed wastewater flows into the next operation unit by itself;
[0054] Then the Fe(OH) in the wastewater 3 It settles completely in the sedimentation tank, and the sedimentation time is about 0.7h. The...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The waste water flow rate of a p-aminodiphenylamine production unit in a chemical plant is 120t / d, and the pollutant indicators before entering the process are: influent COD is 48500mg / L, TOC is 30470mg / L, and formic acid concentration is 144190mg / L. After quality and containing NO 3 -Mix catalyst wastewater, add a certain amount of chlorobenzene acidic wastewater, and add a certain amount of dilution water to dilute the wastewater containing p-aminodiphenylamine to 50 times, and the Fe content is 20mg / L; add a certain amount of HNO as needed 3 To supplement a certain amount of NO 3 - , NO 3 - The final concentration is 1061.3mg / L, so that the C / N in the wastewater is maintained at about 2.54, and dilute HCl is added to adjust the pH of the influent to 9.0, and the mixed wastewater flows into the next operation unit by itself;
[0061] Then the Fe(OH) in the wastewater 3 It settles completely in the sedimentation tank, and the sedimentation time is about 1.2h. The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com