Application of ginkgol C17:1 in treatment of liver cancer
A kind of ginkgo phenol, technology for treating liver cancer, applied in the field of biomedicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: Preparation and analysis of ginkgolic acid homologues
[0040] Preparation of Ginkgolic Acid Homologs Weigh 100 g of dried Ginkgo biloba testa and crush it, ultrasonically extract 5 times the amount of petroleum ether three times, each time for 2 hours, combine the extracts, filter under reduced pressure, evaporate the solvent to obtain a petroleum ether extract. Dissolve the extract in a small amount of petroleum ether and apply it to a silica gel column (Φ3.2×40cm), elute with petroleum ether: ether: formic acid = 89:11:1 (v / v / v), and perform thin-layer chromatography Fluorescence at 254 nm was detected, and the ginkgolic acid fraction was collected; the column was repeated several times. Finally, the ginkgolic acid components were washed with water until neutral, and the eluent was evaporated to obtain a homologous mixture of ginkgolic acids.
[0041] HPLC Analysis of Ginkgolic Acid HomologsVarian high performance liquid chromatography, SinoC...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: Preparation and analysis of ginkgo biloba homologues
[0044] Preparation of Ginkgol Homologs by Decarboxylation Mix 1.0 g of ginkgolic acid homologs and 0.02 g of NaOH in a flask, stir at 135-140°C until no bubbles are generated, cool the mixture to room temperature, and extract with petroleum ether. Filtration and concentration gave a dark brown oil.
[0045] After the dark brown oil was dissolved in ethyl acetate, the sample was loaded on a silica gel column (a glass column with a diameter of 3.2×40 cm), and the mixed solution of chloroform and chloroform:methanol (the ratio gradually changed from 9:1 to 5:5, V / V) elution, detected by thin-layer chromatography at 254nm fluorescence, collected ginkgo phenol fractions, concentrated to dryness; repeated column once, to obtain the ginkgo phenol homologous mixture.
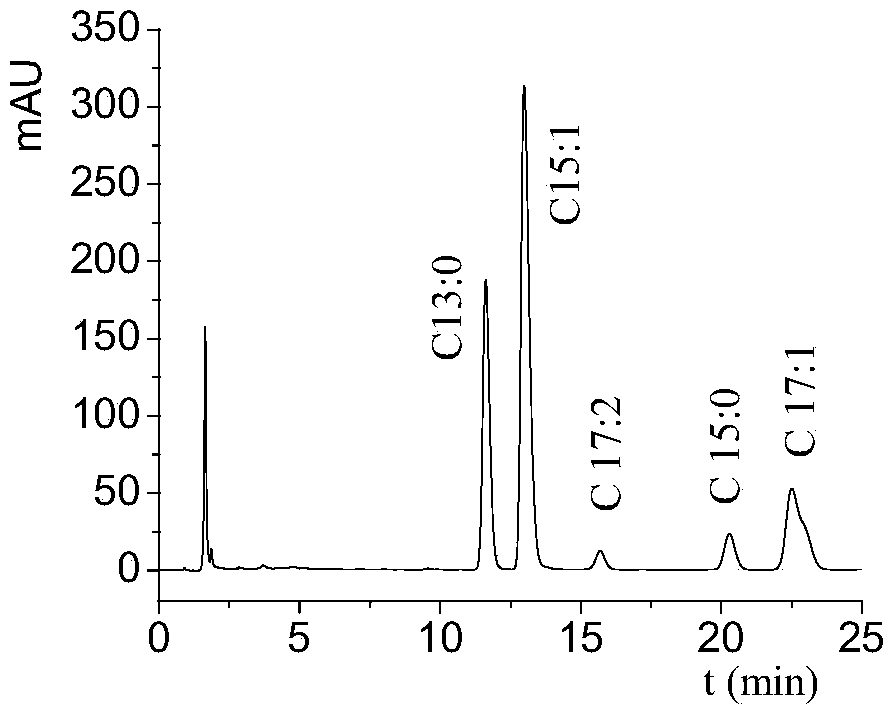
[0046] HPLC Analysis of Ginkgo Biloba Homologs The mobile phase was methanol: water = 92:8 (v / v); the flow rate was 1 mL / min; the ult...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Preparation and identification of Ginkgo biloba C17:1
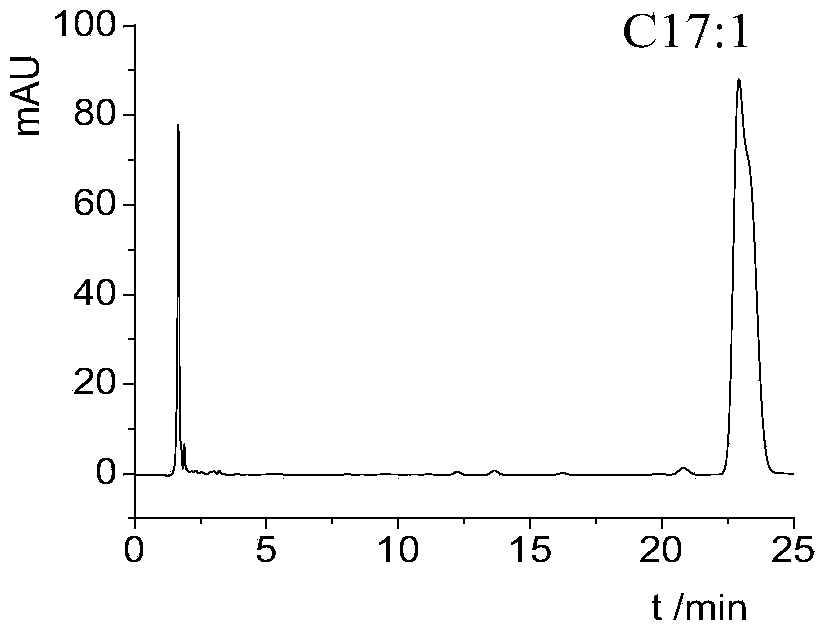
[0048] Preparation of Ginkgo biloba C17:1 Ginkgo biloba homologues were dissolved in tetrahydrofuran: methanol = 1:1 to form a solution, and ginkgo biloba monomers were separated on an HPLC semi-preparative column ZORBAX SB-C18 (250 × 9.4 mm, 15 μm), and the mobile phase was methanol: water = 90 :10, flow rate 3.0 mL / min; UV detector detects the absorption peak at 275 nm, collects the fraction of Ginkgool C17:1, and repeats once to obtain Ginkgool C17:1 monomer.
[0049] HPLC Analysis of Ginkgo biloba C17:1 Analyze the separated ginkgool C17:1 (analysis conditions are the same as the analysis of ginkgool homologues), and its HPLC analysis chart is shown in figure 2 , figure 2 The peak of ginkgool C17:1 is mainly seen in the concentration, and the peaks of other ginkgool homologues are very small. The purity of ginkgool C17:1 obtained by using the area normalization method is more than 90%. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com