Chemical preparation method of L-ribose
A chemical and ribose technology, applied in the field of chemical preparation of L-ribose, can solve the problems of complicated post-processing, many steps, and many by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
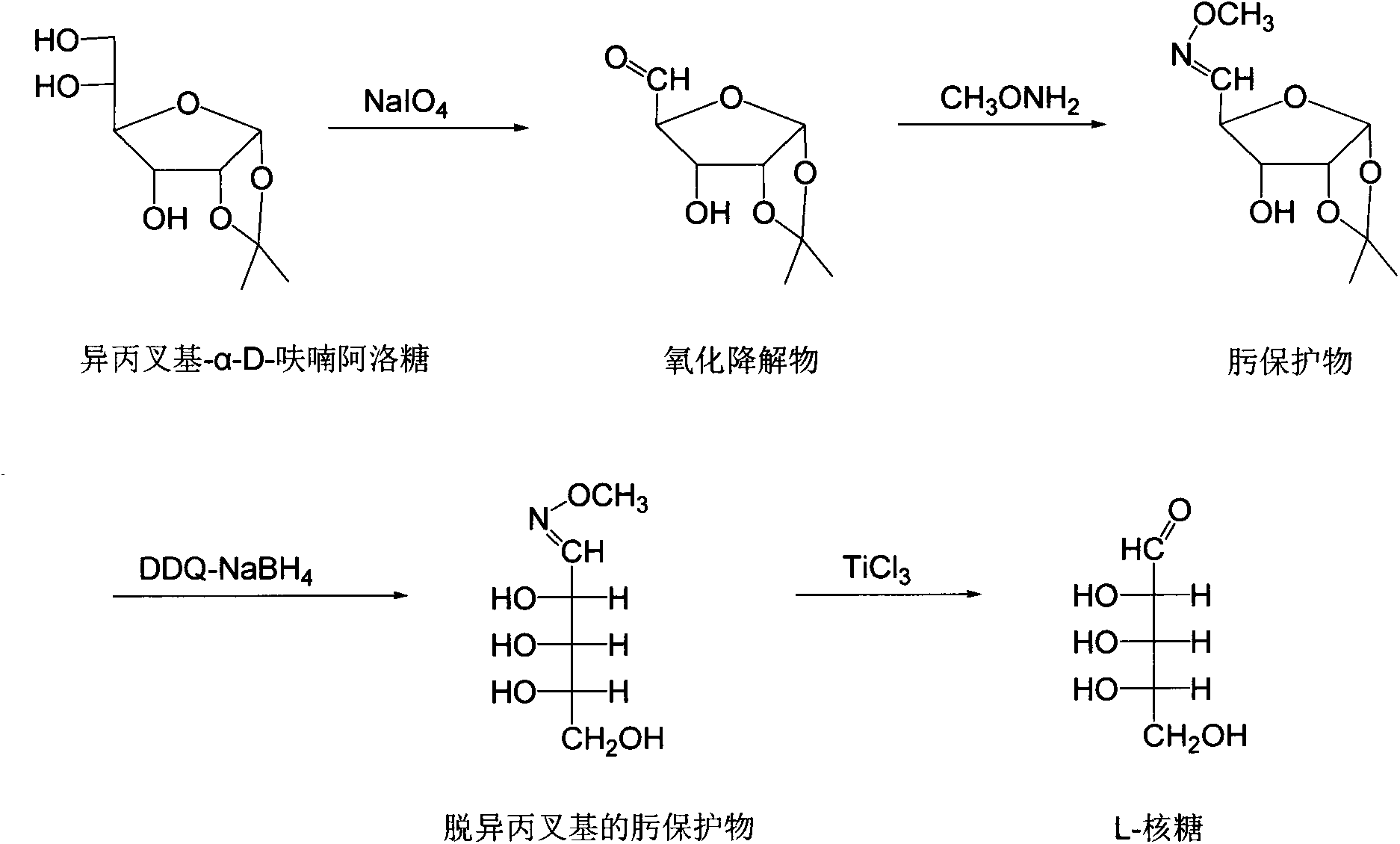
[0015] Example 1: Oxidative degradation of propylidene-α-D-allofuranose
[0016] Add 6.6g of propylidene-α-D-allofuranose, 3g of sodium bicarbonate and 300ml of distilled water into a 500ml four-necked bottle equipped with a thermometer and mechanical stirring, control the temperature at 20-25°C, and add 15g of high After the addition of sodium iodate, the reaction was continued at this temperature for 100 min, followed by TLC (developing solvent: ethyl acetate:methanol=4:1). Concentrate the reaction solution under reduced pressure (not exceeding 40°C), then extract the concentrate with 200ml×4 ethyl acetate, combine the ethyl acetate solution, dry with 100g anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter and concentrate to obtain the oxidative degradation product.
Embodiment 2
[0017] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of oxime protectant
[0018] Add 20ml of chromatographically pure methanol and 2.3g of methoxyamine into a 50ml three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, condenser and electromagnetic stirring, heat and reflux for 10min, and dropwise add a solution of oxidative degradation products (2g of oxidative degradation products+10ml of chromatographically pure Methanol), heated to reflux for 2 hours after dropping, deionized the reaction solution with 001×7 resin (hydrogen ion form) and 201×7 resin (acetate ion form) respectively, then concentrated under reduced pressure, and reconcentrated the concentrate with ether Crystallization can give light yellow needle-like crystals, which are oxime protected substances.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Embodiment 3: the removal of isopropylidene group in the oxime protectant
[0020] Add 1g of oxime protection, 30ml of acetonitrile-water solution (9:1), 0.5g of dichlorodicyanobenzoquinone into a 50ml four-neck flask equipped with a thermometer and electromagnetic stirring, react at 80°C for 4h, concentrate under reduced pressure, and use Dissolve the concentrate in 30ml of water, decolorize with 1g×2 activated carbon, and filter.
[0021] Add the above-mentioned decolorizing solution to a 50ml three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer and electromagnetic stirring, add sodium borohydride solution (0.2g sodium borohydride+5ml water) under stirring at room temperature, and follow the reaction by TLC (developing agent is chloroform:methanol:water=85 : 30: 2), after the reaction is complete, the deionization method is the same as in Example 2, and then concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain a light yellow solid, which is the deisopropylidene protected oxime.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com