Method for production of low carbon olefins from synthetic gas via low carbon alkanes
A technology for the production of low-carbon olefins and carbon alkanes, which is applied in the field of low-carbon olefins, can solve the problems of relatively large influence of olefin prices and low selectivity of low-carbon olefins, and achieve the effects of reducing equipment investment, less by-products, and reducing operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] One-stage reaction composite catalyst preparation:
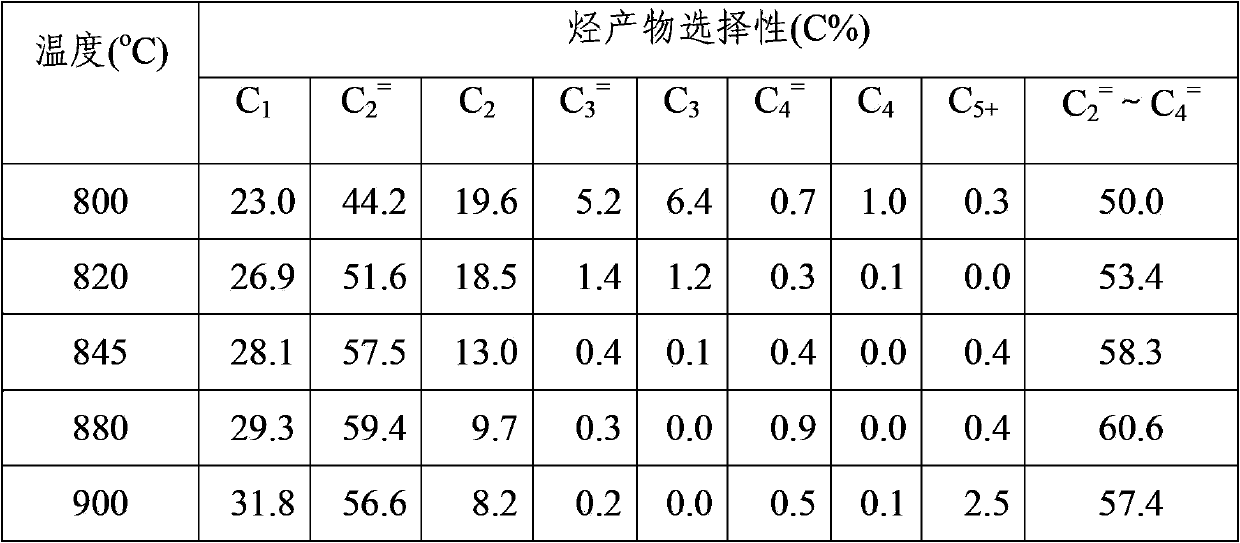
[0048] Weigh 15g SAPO-34 molecular sieve and disperse it in 200ml deionized water, dissolve 3.75ml of PdCl 2 The solution (metal Pd content 20mg / ml) was slowly added dropwise onto the molecular sieve, exchanged in a water bath at 60°C for 8h, then filtered and washed, dried at 120°C, and roasted at 520°C for 6h to obtain 0.5%Pd / SAPO -34. Catalyst Cu-ZnO-Al 2 o 3 (Cu-Zn-Al) and 0.5%Pd / SAPO-34, respectively pressed into tablets, broken into 20-40 mesh. Get 0.8g (1ml) mixed catalyst, carry out particle mixing with Cu-Zn-Al:0.5%Pd / SAPO-34=1:3 mass ratio, H 2 Reduction at 250°C for 5h under atmosphere, H 2 The flow rate is 10ml / min. The temperature is raised to 325°C, and synthesis gas (H 2 + CO + 4% N by volume 2 ), pressurized to 2.0MPa, total gas flow rate 1000ml / h, H 2 / CO=2. The CO conversion rate is 77%, and the hydrocarbon composition in the product after the first stage of reaction is:
[0049] CH 4 5....
Embodiment 2
[0055] One-stage process is carried out according to the conditions given in Example 1 to produce low-carbon alkanes from syngas, the CO conversion rate is 77%, and the hydrocarbon composition in the one-stage reaction product is:
[0056] CH 4 5.2%, C 2 h 6 23.6%, C 3 h 8 49.9%, C 4 h 10 16.1%, C 5 +5.2%.
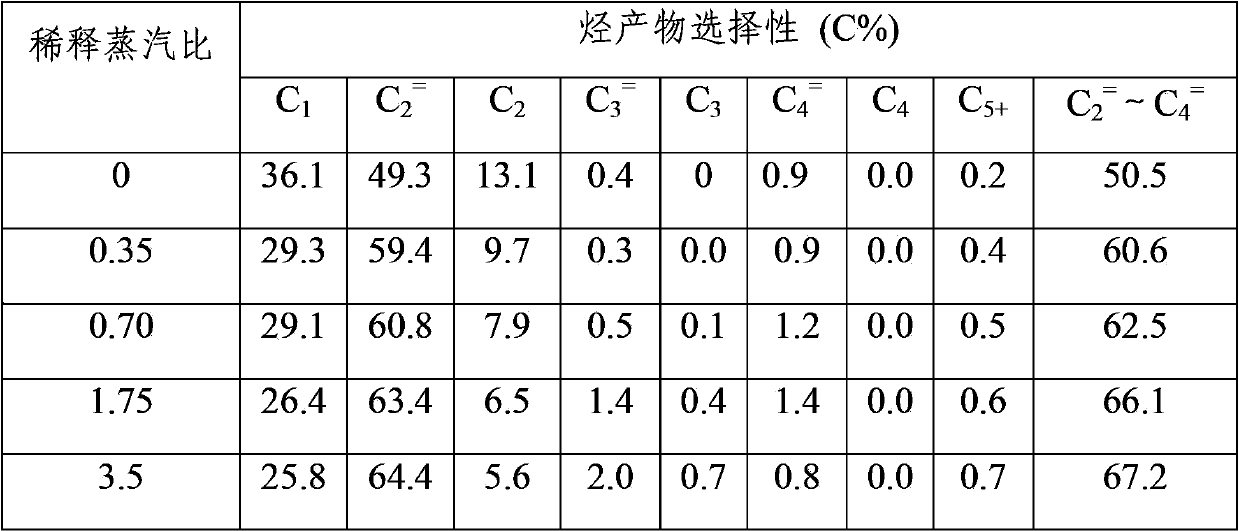
[0057] The obtained product is directly introduced into the second-stage reactor for steam thermal cracking reaction. The volume ratio of the dilution steam to the feed gas in the second stage is 0.35. Table 2 shows the test results of pyrolysis of light alkanes to light olefins at different cracking temperatures.
[0058] Table 2 Effect of the same dilution steam ratio at different temperatures
[0059]
Embodiment 3
[0061] One-stage process is carried out according to the conditions given in Example 1 to produce low-carbon alkanes from syngas, the CO conversion rate is 77%, and the hydrocarbon composition in the one-stage reaction product is:
[0062] CH 4 5.2%, C 2 h 6 23.6%, C 3 h 8 49.9%, C 4 h 10 16.1%, C 5 +5.2%.
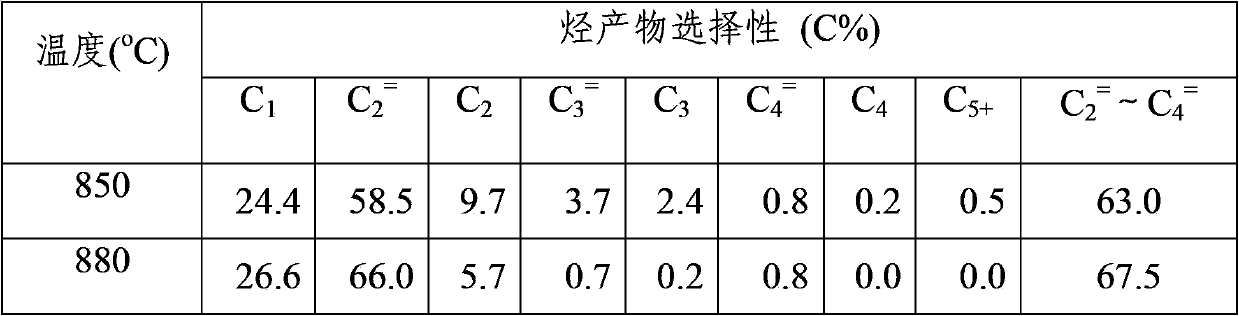
[0063] The resulting product is directly introduced into the second-stage reactor for thermal cracking reaction. The dilution steam of the second stage process is changed to N 2 , diluted N 2 The volume ratio of raw material gas to the second stage is 2. Table 3 shows the test results of the thermal cracking of light alkanes to light olefins at different cracking temperatures.
[0064] Table 3 The same N at different temperatures 2 Effect of Dilution Ratio
[0065]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com