Method for production of ethanol by continuous fermentation of immobilized yeast cells
A technology for immobilizing yeast and yeast cells is applied in the field of continuous fermentation of immobilized yeast cells to produce ethanol and continuous fermentation to produce ethanol. Facilitate automated production, high mechanical strength, and reduced equipment volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Using glucose as raw material to carry out single-stage continuous fermentation of immobilized yeast cells
[0037] Fermentation medium components: glucose 200g / L, peptone 7g / L, yeast extract 4g / L, ammonium sulfate 4g / L, phosphate 4g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.1g / L, zinc sulfate heptahydrate 0.1g / L L.
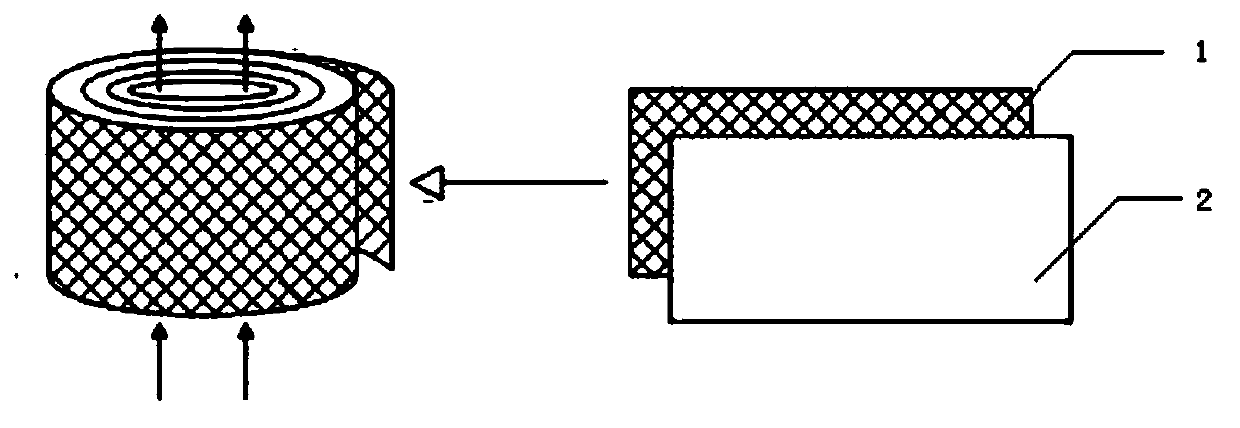
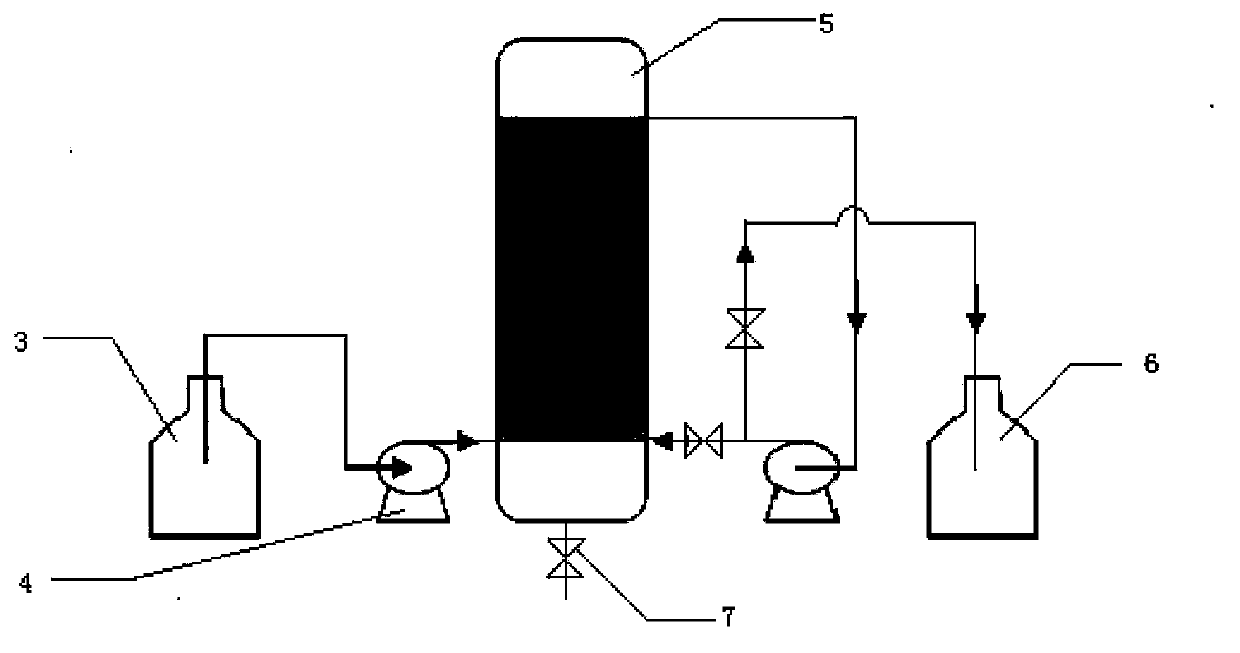
[0038] First, cut activated carbon fiber cotton 1 and steel wire mesh 2 into shapes of the same size, spread them flat on the steel mesh, and roll them into a cylinder (see figure 1 ), the fibrous material layers need to be kept loose and uniform, and loaded into the reactor 5 with a height-to-diameter ratio of 4 (see figure 2 ). Add the cultured strains (logarithmic phase) to the feed tank 3, and the seed liquid flows in from the bottom of the reactor 5 through the left pump 4 at a flow rate of 10L / h. When the seed liquid is full of the reactor, turn off the left pump 4. Turn on the right side pump and the middle valve, and circulate for a fixed pe...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2 carries out single-stage continuous fermentation of immobilized yeast cells with cassava raw material
[0040] Cassava hydrolyzate fermentation medium components: cassava saccharification liquid (glucose concentration 245g / L), urea 0.2g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.2g / L.
[0041] At first, plant fiber (cotton cloth) 1 and steel wire mesh are fixed in the reactor 5 that height and diameter ratio are 5 by the operating method of embodiment 1 (see figure 2 ); then add the cultured strains (logarithmic phase) into the feed tank 3, the seed liquid flows in from the bottom of the reactor 5 through the left pump 4 at a flow rate of 15L / h, until the seed liquid is full of the reactor, Close the left side pump 4, open the right side pump and the middle valve, and circulate for a certain period of time until the bacterium concentration in the feed tank 3 liquid hardly declines any more. Drain the waste liquid, add the cassava hydrolyzate fermentation medium, still flow i...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3 Using glucose as raw material to carry out 5-stage continuous fermentation of immobilized yeast cells
[0043] Fermentation medium components: glucose 250g / L, peptone 5g / L, yeast extract 3g / L, ammonium sulfate 4g / L, phosphate 3g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.05g / L, zinc sulfate heptahydrate 0.05g / L L.
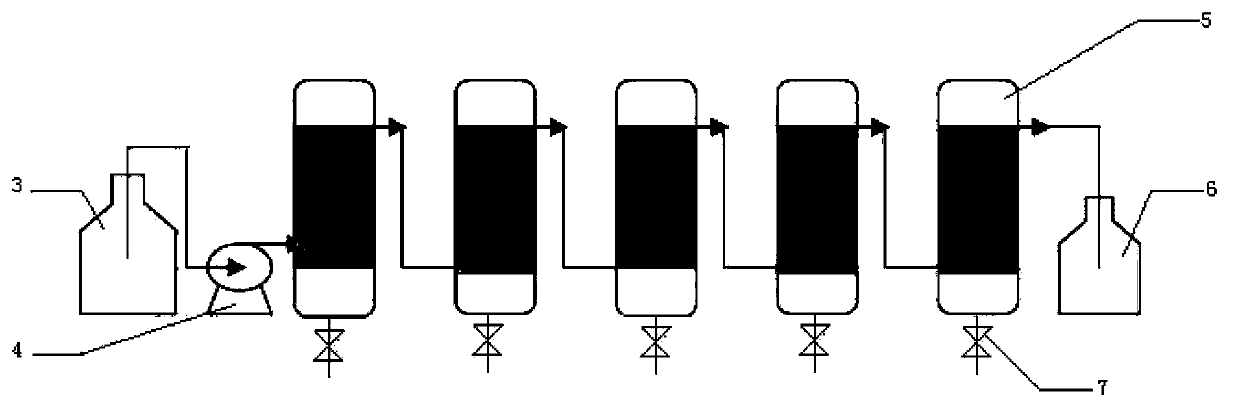
[0044] First, bamboo fibers are soaked in glyoxal solution for 4 hours. After cleaning and drying, they are rolled into a bucket with steel mesh and loaded into five reactors 5 connected in series with a height-to-diameter ratio of 4 (see image 3 ). Next, add the cultured bacteria (logarithmic phase) into the feed tank 3, flow in from the bottom of the first reactor 5 with a flow rate of 15L / h through the pump 4, and then flow out from the upper end of the last reactor 5 To the feeding tank 3, the cycle is fixed for a certain period of time until the OD value of the bacteria in the feeding tank 3 is less than 1. Drain the waste liquid, add fresh ferment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com