Method for cyclic treatment of heavy metal ion wastewater by utilizing modified fly ash
A technology for heavy metal ion and recycling treatment, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems affecting normal production, secondary pollution, low cost, etc., and achieve easy recycling and reuse , avoid secondary pollution, low price effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
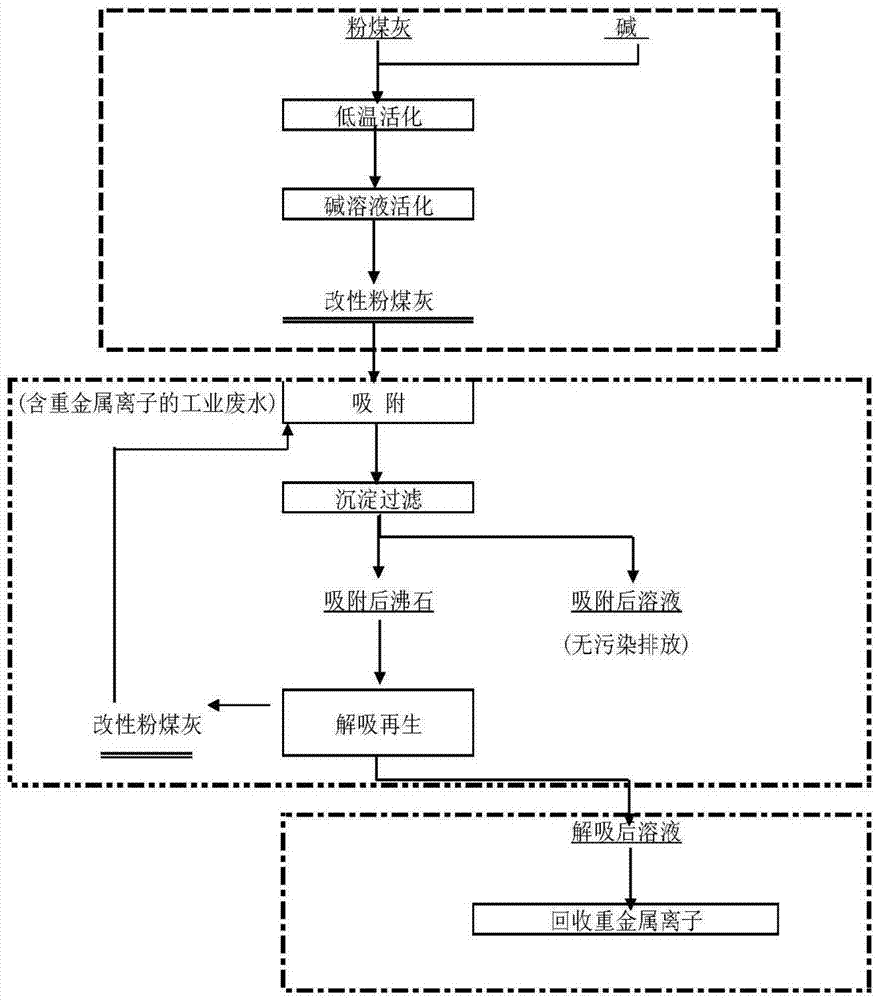
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Treatment of Cu in wastewater before and after fly ash modification 2+ Ion contrast test.
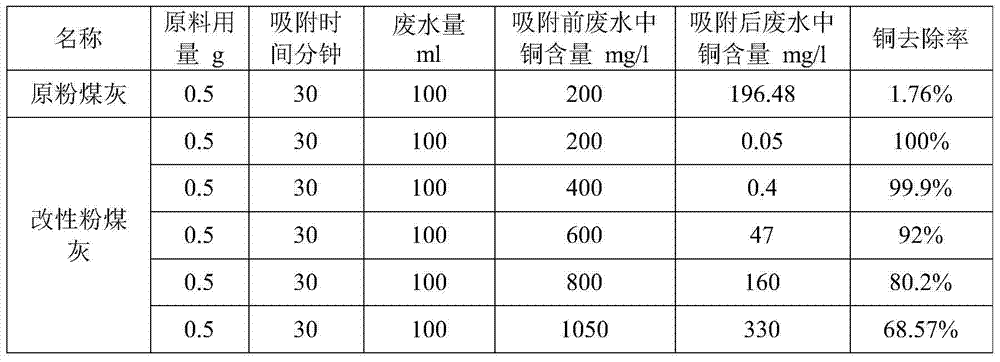
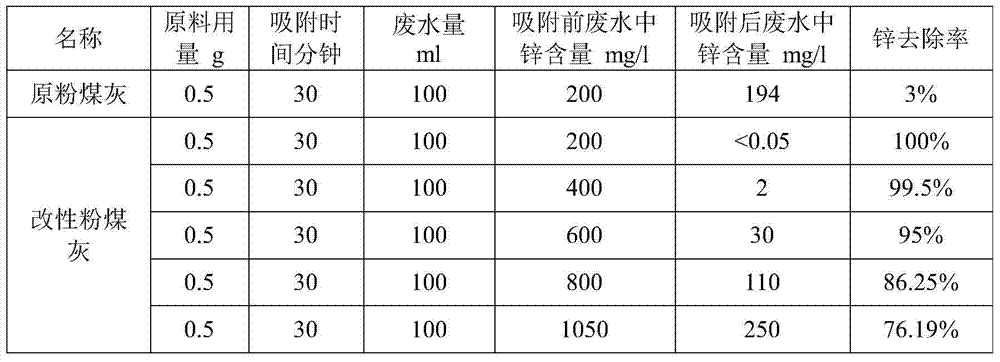
[0031] Get the fly ash of Shanxi Power Plant to modify according to the method of the present invention, then measure the adsorption performance of the fly ash before and after modification to copper, zinc, cadmium ion wastewater, the results are shown in Table 1-3. It can be seen from Table 1-3 that the modified fly ash has several times higher adsorption capacity for heavy metal ions.
[0032] Table 1 Determination of the adsorption performance of fly ash on copper ion wastewater before and after modification
[0033]
[0034] Table 2 Determination of adsorption performance of fly ash to zinc ion wastewater before and after modification
[0035]
[0036] Table 3 Determination of adsorption performance of fly ash to cadmium ion wastewater before and after modification
[0037]
Embodiment 2
[0039] Circular Treatment of High Concentration Cu with Modified Fly Ash 2+ Wastewater Test 1.
[0040] Take 5g of modified fly ash and put it into 2.5l containing Cu 2+ Wastewater (Cu 2+ content of 800mg / l), stirred at room temperature for 1-3h, precipitated and separated; then put the precipitated isolate into 50ml regeneration solution (5% concentration of sodium hexametaphosphate + ammonium chloride solution), at 20-80℃ Then regenerate for 1-3 hours, then filter, wash and dry; the test results of 10 such cycles are shown in Table 4.
[0041] Copper ions in the regeneration solution can be enriched to more than 6.7g / l, which facilitates the next step of copper recovery; after more than 6 cycles, the copper content in the regeneration solution is basically maintained at 10.6g / l, which is mainly due to the fact that after 6 cycles , the copper content of zeolite is close to saturation.
[0042] Table 4 Determination of the circulation adsorption performance of modified fl...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Deep purification of low concentration Cu by modified fly ash 2+ Wastewater Test 2.
[0046] Take 5g of modified fly ash and put it into 2.5l containing Cu 2+ Wastewater (Cu 2+ content of 200mg / l), stir at room temperature for 1-3h, and precipitate and separate; then put the precipitated isolate into 10ml regeneration solution (5% concentration of sodium sulfate + ammonium chloride solution), and regenerate at 20-80°C 1-3h, and then filtered, washed and dried; the test results of 10 such cycles are shown in Table 5.
[0047] Cu in the treated wastewater 2+ The ion content is 0.05mg / l, and the removal rate is greater than 99%. Recycling meets the emission requirements for copper ions (<0.5mg / l) in the national "Pollutant Discharge Standards for Urban Sewage Treatment Plants" (GB18918-2002).
[0048] Table 5 Determination of the deep purification of copper ion wastewater by modified fly ash
[0049] cycle adsorption
[0050] 7th time
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com