High-yield engineering strain kmust-SQS for ganoderic acid
A technology for engineering strains and ganoderma acid, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and metabolic engineering, can solve the problem of low production of ganoderma acid, and achieve the effects of saving labor, shortening production cycle, and wide application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
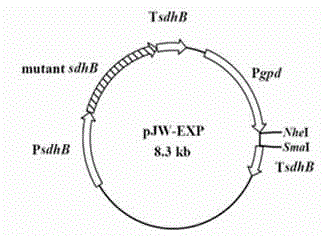
[0049] Embodiment 1: Construction of pJW-EXP vector
[0050] 1. Extraction of Ganoderma lucidum genomic DNA
[0051] Weigh about 0.2 g of mycelium of freeze-dried wild-type Ganoderma lucidum (CCGMC 5.0616), grind it into powder in liquid nitrogen, and transfer the powder into 1.5 mL of CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) preheated at 65 °C ) in the extraction buffer, incubate at 65°C for 30 minutes, then centrifuge at 10,000 g for 20 minutes at 4°C, add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) mixture to the supernatant, and shake gently for 30 minutes Centrifuge at 10,000 g for 20 min at 4°C; transfer the supernatant into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, add 2 / 3 volume of isopropanol pre-cooled at -20°C, shake gently for 5 min, and remove with a glass rod After extracting the DNA, wash 2-3 times with 75% ethanol, dry at room temperature, dissolve in an appropriate amount of TE containing 20 μg / mL RNase, digest the RNA at 37 °C for 30 min, and then obtain the genomic D...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment 2: Construction of pJW-EXP-tSQS vector
[0077] Genomic DNA of Ganoderma lucidum was used as a template, and primers
[0078] SQS-Nhe-F: 5'-GCTAGCATGGGCGCGACGTCTATGCT-3'
[0079] SQS-Sma-R: 5'-GGGCCCTCACCCGAAAAAGTGGATGAGGAC-3'
[0080] Perform PCR to obtain the SQS gene; the PCR conditions are: 95°C for 10 min, 95°C for 30 s, 61°C for 30 s, 72°C for 2 min for 10 s, and 72°C for 10 min (see image 3 ).
[0081] 2. Insert the SQS gene into the pJW-EXP vector
[0082] The pJW-EXP vector was double-digested with SmaI and NheI, and the digested fragment was recovered. Using T4 ligase at 16°C, the SQS gene was inserted between the NheI and SmaI of the pJW-EXP vector to obtain pJW-EXP- tSQS vector (see Figure 4 ).
Embodiment 3
[0083] Example 3: Transformation of pJW-EXP-tSQS into wild-type Ganoderma lucidum cells by PEG-mediated protoplast fusion
[0084] 1. Preparation and transformation of Ganoderma lucidum protoplasts
[0085] The wild-type Ganoderma lucidum mycelium was first prepared into protoplasts with lysozyme, and then the Ganoderma lucidum protoplasts were suspended in 100 μL of STC (0.55 M sorbitol, 10 mM CaCl 2 , 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.5), then add 1 μg of plasmid DNA and PTC buffer (60% PEG4000 (W / V), 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.5 , 50 mM CaCl 2 ); incubate on ice for 10 min, then add 1 mL of PTC buffer to mix well and incubate at room temperature for 20 min; use 10 mL of melted CYM solid medium to mix the transformed protoplasts, and add carboxin to make carboxin The final concentration is 2 mg / L; several single colonies can grow after culturing at 30°C for 10 days.
[0086] 2. Subculture on plates containing carboxin resistance
[0087] Transfer a single colony to a CYM pla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com