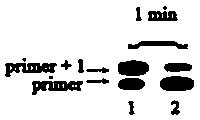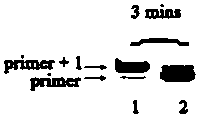Method for positioning and quantitatively detecting 6-methylaminopurine in DNA and RNA
A methylaminopurine, quantitative detection technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology and nucleic acid chemistry, can solve the problems of high cost, inability to locate methylation sites, low efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of short pretreatment time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Design of the system to be tested
[0031] (1) Design two types of DNA template strands, one of which is ordinary DNA with adenine (DNA-A), its sequence is 5'-CCCACCCTATAGAGTCGTA-3'; the other is modified with 6-methylaminopurine DNA (DNA-m 6 A), whose sequence is 5'-CCCm 6 ACCCTATAGAGTCGTA-3', the primer strand is 5'-GTGCATGTGGCAG-3'.
[0032] (2) Design two types of RNA template strands, one of which is an ordinary RNA with adenine (RNA-A), and its sequence is 5'-CCCACCCUAUAGAGUCGUA-3'; the other is an RNA with N 6 -Methyladenine-modified RNA (RNA-m 6 A), whose sequence is 5'-CCCm 6 ACCCUAUAGAGUCGUA-3', the primer strand is 5'-GTGCATGTGGCAG-3'.
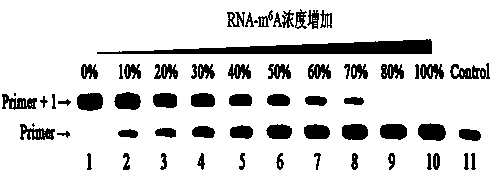
[0033] (3) Prepare 10 groups containing different concentrations of RNA-A and RNA-m 6 A sample of mixed template strands, where RNA-A and RNA-m 6 The concentration ratio of A is 10:0, 9:1, 8:2, 7:3, 6:4, 5:5, 4:6, 3:7, 2:8 and 0:10 in sequence.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Performing a DNA replication reaction
[0035] (1) Prepare a buffer solution containing 10 mM tris hydrochloride, 50 mM ammonium sulfate, 10 mM potassium chloride, 100 mM magnesium sulfate and 100 mM polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether; Add the following substances to the buffer solution in μL to make it final concentration: Bst 0.5 U for polymerase, 400 μM for 5-hydroxymethyldeoxyuridine triphosphate (5-hmdUTP), and 200 nM for primer strand;
[0036] (2) Add the designed two types of DNA template strands respectively, the total concentration is 300 nM, at 50 o Incubate in a water bath of C for 60 min;
[0037] (3) Add 500 μL quencher (volume fraction of formamide is 80%, disodium edetate concentration is 200 mM, pH=8.0) to the reaction system, 80 o C for 20 min, then naturally cooled to room temperature;
[0038] (4) The reaction solution was subjected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (denaturing polyacrylamide gel with a volume fraction of 12%) ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: Carry out RNA reverse transcription reaction
[0040] (1) Prepare a buffer solution containing 2 mM tris hydrochloride, 10 mM ammonium sulfate, 1 mM potassium chloride, 20 mM magnesium sulfate and 20 mM polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether; Add the following substances to the buffer solution in μL to make it final concentration: Bst 0.2 U for polymerase, 0.2 U for RNase inhibitor, 100 μM for 5-fluorouracil deoxynucleotide (5-F-dUTP), and 200 nM for primer strand;
[0041] (2) Add the two types of RNA template strands designed respectively, the total concentration is 500 nM, at 70 o Incubate in a water bath of C for 20 min;
[0042] (3) Add 500 μL quencher (volume fraction of formamide is 80%, disodium edetate concentration is 200 mM, pH=8.0) into the reaction system, 100 o C for 10 min, then naturally cooled to room temperature;
[0043] (4) Electrophoresis the reaction solution on polyacrylamide gel (denaturing polyacrylamide gel with a volume fract...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com