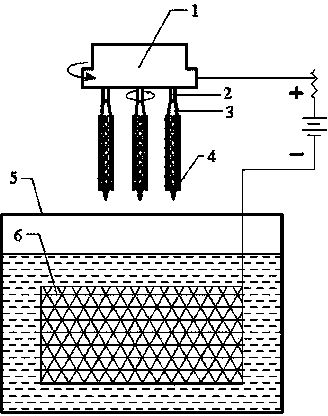
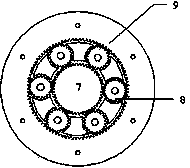
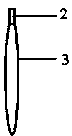Electrochemical treatment method suitable for magnesium alloy interventional device and auxiliary equipment
A processing method and auxiliary equipment technology, applied in the direction of electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of unstable polishing results, complicated operation, and the content of polishing liquid, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient clamping, high smoothness, and bright surface quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: Electrolytic polishing of magnesium zinc yttrium neodymium alloy vascular stent
[0027] An electrochemical treatment method suitable for magnesium alloy interventional devices, including surface pretreatment and electrolytic polishing, the pretreatment is: ultrasonically cleaning the magnesium zinc yttrium neodymium alloy stent in a pretreatment aqueous solution at 50 ° C for 15 minutes, and then Then place it in absolute ethanol for ultrasonic cleaning for 10 minutes; 1 L of pretreatment aqueous solution is composed of: 30 g of sodium phosphate, 20 g of sodium hydroxide, 80 g of sodium silicate, and the balance is distilled water. The power of the ultrasonic cleaner is 50Hz. The electrolytic polishing is as follows: the pretreated magnesium zinc yttrium neodymium alloy vascular stent is clamped and then placed in the electrolyte, and electrolytic polishing is carried out at room temperature; the cathode material is an annular mesh stainless steel elect...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: Electropolishing of magnesium-zinc-calcium bone plate or bone nail
[0032]An electrochemical treatment method suitable for magnesium alloy interventional devices, including surface pretreatment and electrolytic polishing, the pretreatment is: ultrasonically cleaning magnesium-zinc-calcium bone plates or bone nails in a pretreatment aqueous solution at 60°C for 10 minutes, Then place it in absolute ethanol for ultrasonic cleaning for 10 minutes; 1 L of pretreatment aqueous solution is composed of: 20 g of sodium phosphate, 30 g of sodium hydroxide, 60 g of sodium silicate, and the balance is distilled water. The power of the ultrasonic cleaner is 50Hz. The electrolytic polishing is as follows: the surface pretreated magnesium-zinc-calcium bone plate or bone nail is clamped and then placed in the electrolyte, and electrolytic polishing is carried out at room temperature; the cathode material is an annular mesh stainless steel electrode, and the polishing ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: Electrolytic polishing to AZ31 alloy wire
[0037] An electrochemical treatment method suitable for magnesium alloy interventional devices, including surface pretreatment and electrolytic polishing, the pretreatment is: AZ31 alloy wire is ultrasonically cleaned at 70°C for 5 minutes in a pretreatment aqueous solution, and then placed in Ultrasonic cleaning in absolute ethanol for 15 minutes; 1 L of pretreatment aqueous solution is composed of: 45 g of sodium phosphate, 10 g of sodium hydroxide, 30 g of sodium silicate, and distilled water as the balance. The power of the ultrasonic cleaner is 50Hz. The electrolytic polishing is as follows: clamp the AZ31 alloy wire that has been pretreated on the surface, place it in the electrolyte, and perform electrolytic polishing at room temperature; the cathode material is an annular mesh stainless steel electrode, the polishing voltage is 20V, and the polishing current It is 0.10A, the electrode distance is 60mm,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com