Preparation method and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron-beta zeolite new composite nano material
A technology of composite nanomaterials and nano-zero-valent iron, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, ion-exchange water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of easy agglomeration and poor diffusion performance, and achieve popularization and The effect of promotion, low cost, and uniformity improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
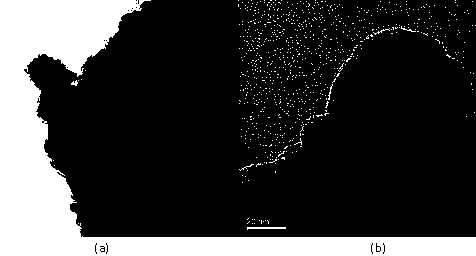
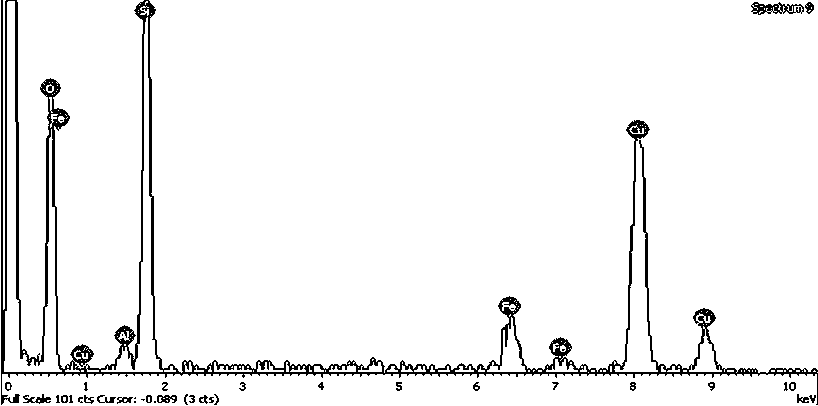
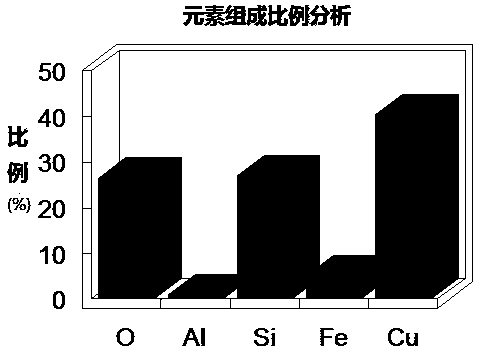
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Dissolve 1.622 g of anhydrous ferric chloride in 100 mL of deionized water and stir thoroughly; weigh 1 g of β zeolite dissolved in 5 mL of deionized water for 5 minutes, add the ferric chloride aqueous solution, and use a mechanical stirring device to Stir at rpm for 16 hours; divide the mixed solution into 50 mL centrifuge tubes and centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 2 minutes; pour the supernatant into the storage device for later use, take the bottom centrifuged solid and dissolve it in 100 mL of deionized water and fully agitate to disperse; weigh 2 g of sodium borohydride (China National Pharmaceutical Analytical Pure,> 96%), dissolved in 100 mL of deionized water, and after it is fully dissolved, add it dropwise to the dispersed solution of iron ions and β zeolite with a peristaltic pump speed of 2.0 on the 16th pump tube. The whole process is accompanied by 600 revolutions. / Min mechanical stirring; after the dripping, continue to stir the reaction for 30 minutes to make ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] In this preparation, the concentrations of three iron ions (0.1 M, 0.2 M, 0.3 M) were set and the amount of β zeolite was kept unchanged, in order to compare the difference in the performance of materials prepared with different ratios of iron ions and β zeolite. Except for the initial iron ion concentration, the remaining steps are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3: Nano zero-valent iron-β zeolite to remove antimony-containing wastewater
[0031] The antimony-containing wastewater here uses potassium antimony tartrate as the source of the contaminant antimony, and different concentrations of antimony-containing wastewater are obtained by diluting a 1 g / L antimony stock solution. In the process of studying the adsorption isotherm, the initial concentration of antimony was 20, 60, 100, 140, 180, 220 mg / L, the reaction temperature was 25, 35, 45 ℃, and the reaction time was 3 hours. The dosage of -β zeolite is 1 g / L, the reaction device is a 50 mL brown bottle, the solution volume is 40 mL, the reaction is carried out in a shaker, and the rotation speed is 200 rpm. During the kinetic study, the initial concentration of antimony was 20 mg / L, the dosages of nano-zerovalent iron-β zeolite were 1, 2, 3 g / L, and 1 g / L β zeolite was used as In contrast, the reaction vessel is a three-necked flask, the solution volume is 200 mL, ni...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com