Method for separating and purifying paclitaxel from taxus chinensis branches and leaves or bark
A technique for separating and purifying branches and leaves of Taxus chinensis, which is applied in the field of natural medicine extraction, can solve the problems of low efficiency, difficulty in large-scale production, complicated operation and the like, and achieves the effects of simple operation, high-efficiency separation and good repeatability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
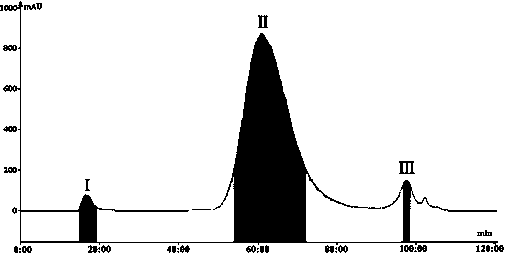
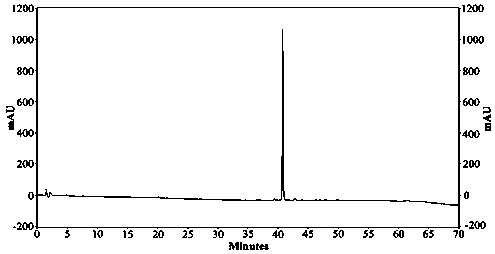
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] 1. Treatment of yew branches and leaves
[0064] (1) Crush yew branches and leaves and pass through a 24-mesh sieve. Take 500 g of powder and add methanol at a ratio of 1:10 (g / mL), soak for 5 h, ultrasonically extract for 1 h, and filter to obtain the filtrate. The residue is calculated as 1: Add methanol at a ratio of 10 (g / mL) and repeat the extraction for 1 h, repeat once, and combine the filtrates.
[0065] (2) The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure below 60°C to obtain the extract (48.75 g). The obtained extract was ultrasonically dispersed in water, extracted 3 times with petroleum ether (1:1, v / v); the water layer was obtained after standing and separated, and the water layer was extracted 3 times with ethyl acetate (1:1, v / v ), the ethyl acetate layer was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain ethyl acetate extract (3.36 g).
[0066] 2. Basic alumina column chromatography
[0067] (1) Take the ethyl acetate extract obtained in...
Embodiment 2
[0084] 1. Treatment of yew bark
[0085] (1) Take yew tree bark and crush it and pass it through a 24-mesh sieve. Take 500 g of the powder and add methanol at a ratio of 1:10 (g / mL), soak for 5 h, reflux for 1 h, and filter to obtain the filtrate. : Add methanol at a ratio of 10 (g / mL) and repeat the extraction for 1 h, repeat once, and combine the filtrates.
[0086] (2) The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure below 60°C to obtain the extract (40.62 g). The obtained extract was ultrasonically dispersed in water, extracted 3 times with petroleum ether (1:1, v / v); the water layer was obtained after standing and separated, and the water layer was extracted 3 times with ethyl acetate (1:1, v / v ), the ethyl acetate layer was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain ethyl acetate extract (4.26 g).
[0087] 2. Basic alumina column chromatography
[0088] (1) Take the ethyl acetate extract obtained in step 1, add an appropriate amount of dichloromethan...
Embodiment 3
[0105] 1. Treatment of yew branches and leaves
[0106] (1) Take yew branches and leaves and pass through a 24-mesh sieve. Take 500 g of powder and add methanol at a ratio of 1:5 (g / mL), soak for 5 hours, reflux for 1 hour, and filter to obtain the filtrate. The residue is calculated as 1: Add methanol at a ratio of 5 (g / mL) and repeat the extraction for 1 h, repeat twice, and combine the filtrates.
[0107] (2) The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure below 60°C to obtain the extract (45.85 g). The obtained extract was ultrasonically dispersed in water, extracted twice with petroleum ether (1:0.5, v / v); the water layer was obtained after standing and separated, and the water layer was extracted twice with ethyl acetate (1:0.5, v / v ), the ethyl acetate layer was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain ethyl acetate extract (3.18 g).
[0108] 2. Basic alumina column chromatography
[0109] (1) Take the ethyl acetate extract obtained in step 1, ad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com