Method for extracting palladium from alkaline cyanide solution with dodecyldimethyl-2-phenoxyethyl ammonium bromide
A technology of phenoxyethylammonium bromide and dodecyldimethyl, which is applied in the field of extracting palladium, can solve the problems of low selectivity of activated carbon adsorption, difficult recycling of zinc, and low direct recovery rate, etc. The effect of cheap price, fast return on investment, and large profit space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
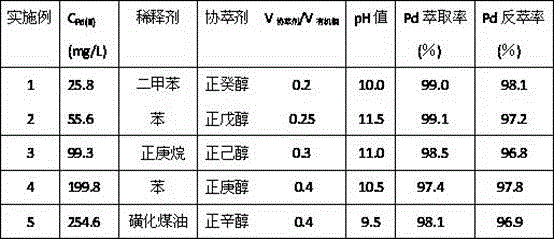
[0036] Get the Pd(CN) whose Pd(II) concentration is 25.8mg / L 4 2- 60 mL of the solution was placed in a separatory funnel, and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 10.0 as the aqueous phase of the extraction system. The organic phase was prepared, wherein the total volume of the organic phase was 20 mL, the organic phase contained 4 mL of n-decyl alcohol, and the remainder was diluent with xylene, and the concentration of DDPB in the organic phase was 0.01 mol / L. Add the organic phase to the water phase (O / A=1:3), mechanically shake for 5 minutes and then stand for stratification. After phase separation, measure the concentration of palladium in the water phase, and obtain the concentration of palladium in the organic phase by subtraction. Take the organic phase loaded with palladium, put it into another separatory funnel, add NH with a concentration of 0.1mol / L according to the ratio of the aqueous phase to the organic phase (A / O) 1:2 4 SCN back-extraction, after 5 minute...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Get the Pd(CN) whose Pd(II) concentration is 55.6mg / L 4 2- 40 mL of the solution was placed in a separatory funnel, and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 11.5 as the aqueous phase of the extraction system. The organic phase was prepared, wherein the total volume of the organic phase was 20 mL, the organic phase contained 5 mL of n-amyl alcohol, the balance was benzene as a diluent, and the concentration of DDPB in the organic phase was 0.01 mol / L. Add the organic phase to the water phase (O / A=1:2), mechanically shake for 4 minutes and then stand for stratification. After phase separation, measure the concentration of palladium in the water phase, and obtain the concentration of palladium in the organic phase by subtraction. Take the organic phase loaded with palladium, put it into another separatory funnel, add NH with a concentration of 0.1mol / L according to the ratio of the aqueous phase to the organic phase (A / O) 1:2 4 SCN back-extraction, after 5 minutes of m...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Get the Pd(CN) whose Pd(II) concentration is 99.3mg / L 4 2- 20 mL of the solution was placed in a separatory funnel, and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 11.0 as the aqueous phase of the extraction system. Prepare the organic phase, wherein the total volume of the organic phase is 20 mL, the organic phase contains 6 mL of n-hexanol, and the balance uses n-heptane as a diluent, and the concentration of DDPB in the organic phase is 0.01 mol / L. Add the organic phase to the water phase (O / A=1:1), mechanically shake for 5 minutes and then stand for stratification. After phase separation, measure the concentration of palladium in the water phase, and obtain the concentration of palladium in the organic phase by subtraction. Take the organic phase loaded with palladium, put it into another separatory funnel, add 0.1mol / LNH according to the ratio of water phase and organic phase (A / O) 1:1 4 SCN back-extraction, after 5 minutes of mixed phases, let it stand for stratifica...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| extraction efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com