Method for fixed-point introduction of non-natural amino acid to protein
An unnatural amino acid and protein technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of long time consumption, environmental pollution, low yield, etc., and achieve high modification efficiency, The effect of less environmental pollution and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
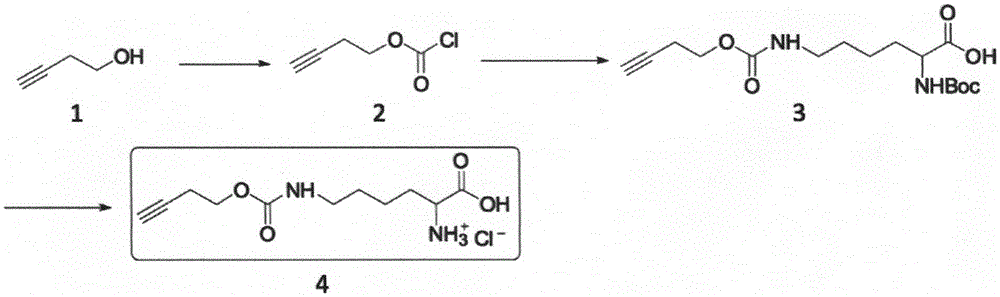
[0030] On the one hand, the present invention relates to a kind of Ne-butynyloxycarbyl-lysine chemical synthesis method, generates 3-alkyne-1-butanol chloroformate by activating 3-alkyne-1-butanol, and then React with Nα-protected lysine, and finally deprotect to obtain Ne-butynyloxycarbyl-lysine.
[0031] In another aspect, the present invention relates to a DNA sequence encoding recombinant wild-type lysyl synthetase;
[0032] In one embodiment, the DNA sequence encoding recombinant wild-type lysyl synthetase of the present invention is SEQ ID NO: 1:
[0033]ATGCCATAGCATTTTTATCCATAAGATTAGCGGATCCTACCTGACGCTTTTTATCGCAACTCTCTACTGTTTCTCCATACCCGTTTTTTTGGGCTAACAGGAGGAATTAGATCTATGGATAAAAAACCACTAAACACTCTGATATCTGCAACCGGGCTCTGGATGTCCAGGACCGGAACAATTCATAAAATAAAACACCACGAAGTCTCTCGAAGCAAAATCTATATTGAAATGGCATGCGGAGACCACCTTGTTGTAAACAACTCCAGGAGCAGCAGGACTGCAAGAGCGCTCAGGCACCACAAATACAGGAAGACCTGCAAACGCTGCAGGGTTTCGGATGAGGATCTCAATAAGTTCCTCACAAAGGCAAACGAAGACCAGACAAGCGTAAAAGTCAAGGTCGTTTCTGCCCCTACCAGAA...
Embodiment 1
[0047] Ne-butyneoxycarbyl-lysine chemical synthesis pathway
[0048] Synthetic routes such as figure 2 As indicated, the specific description is as follows:
[0049] Dissolve triphosgene (29.7 g, 100 mmol) in 200 ml of ether, add 0.5 g of activated carbon, and stir at room temperature for 1 hour. After the phosgene is completely decomposed, cool down to 0° C., and carefully add 3-alkyne-1-butanol ( figure 2 Compound 1, 14.0g, 200mmol). After the addition was complete, continue to stir and react for 16 hours. After TLC (PE:EA=4:1, Rf=0.6) could not detect 3-alkyne-1-butanol, the activated carbon was filtered off, and the residue was colorless after spin-drying the solvent at low temperature. Oily 3-alkyne-1-butanol chloroformate ( figure 2 Compound 2 in , 26 g), with a yield greater than 90%, was used for the next reaction without purification.
[0050] Dissolve sodium hydroxide ((8g, 200mmol) in 400ml water, then add sodium bicarbonate (67.2g, 800mmol), and stir until c...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Mutation treatment of target protein gene
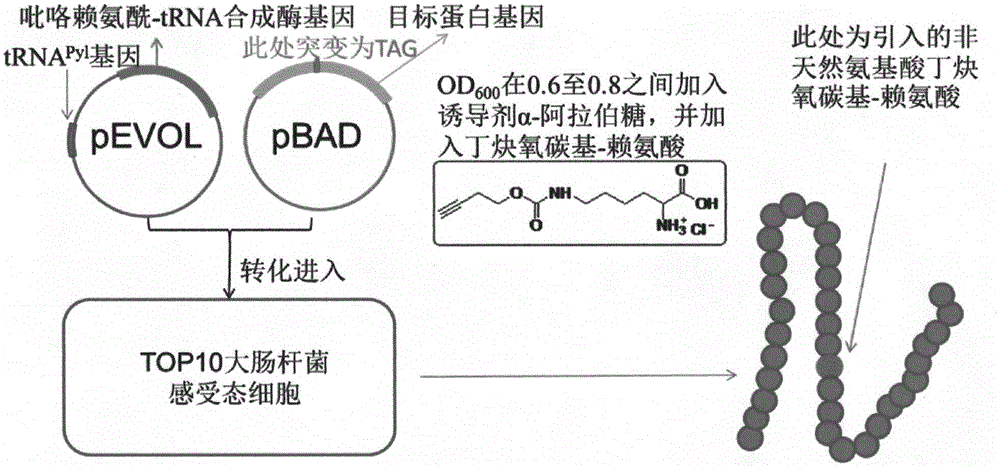
[0056]Using the method of site-directed mutagenesis known to those skilled in the art, the base sequence of the site of the target protein to be introduced with unnatural amino acid is replaced with the primer of TAG, and the triplet of the site of the target protein that needs to be introduced with unnatural amino acid is made by PCR. The body base sequence is mutated to TAG. In the inventor's practice, the inventor selected hPTH (1-34) with superfolder green fluorescent protein (sfGFP) as a fusion tag and GLP-1 (6-36) with sfGFP as a fusion tag as target protein. Among them, the DNA sequences corresponding to the 18th, 22nd and 26th amino acids of hPTH (1-34) were mutated into TAG respectively; the DNA sequences corresponding to the 20th, 21st and 22nd amino acids of GLP-1 (6-36) were mutated into TAG respectively .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com