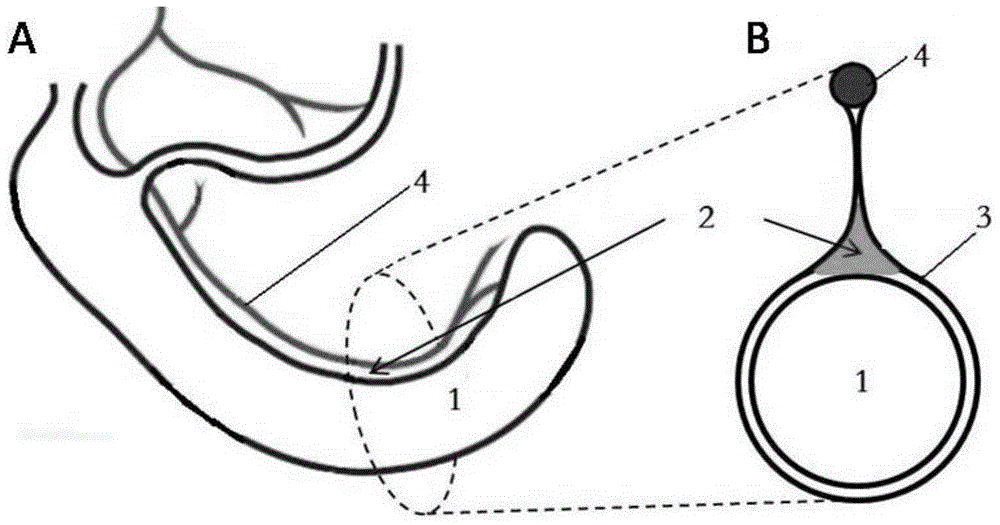
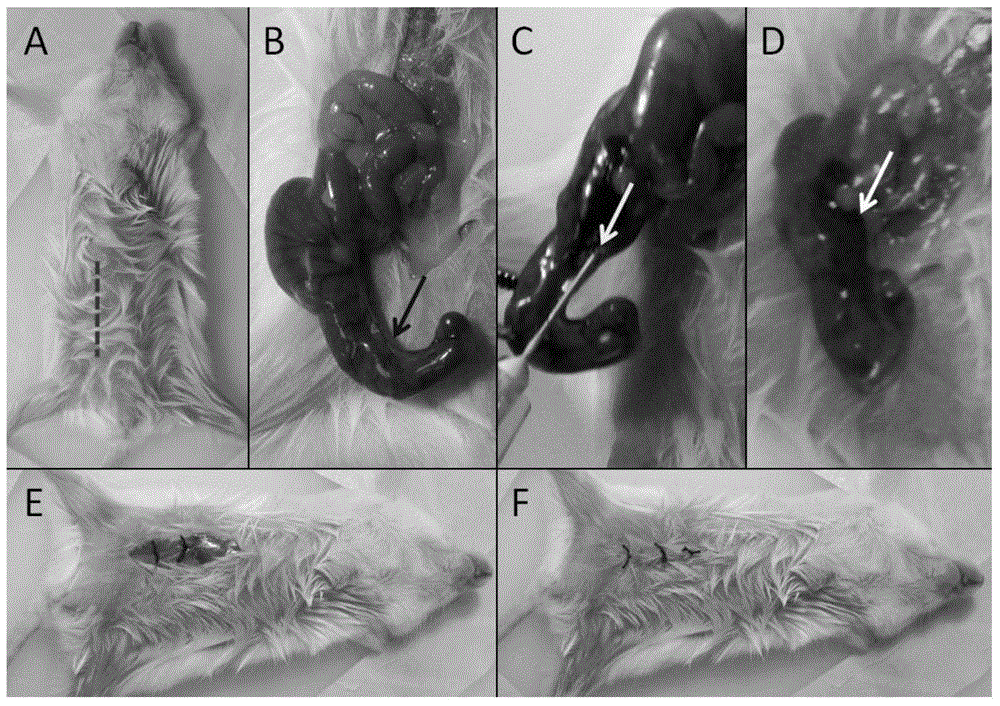
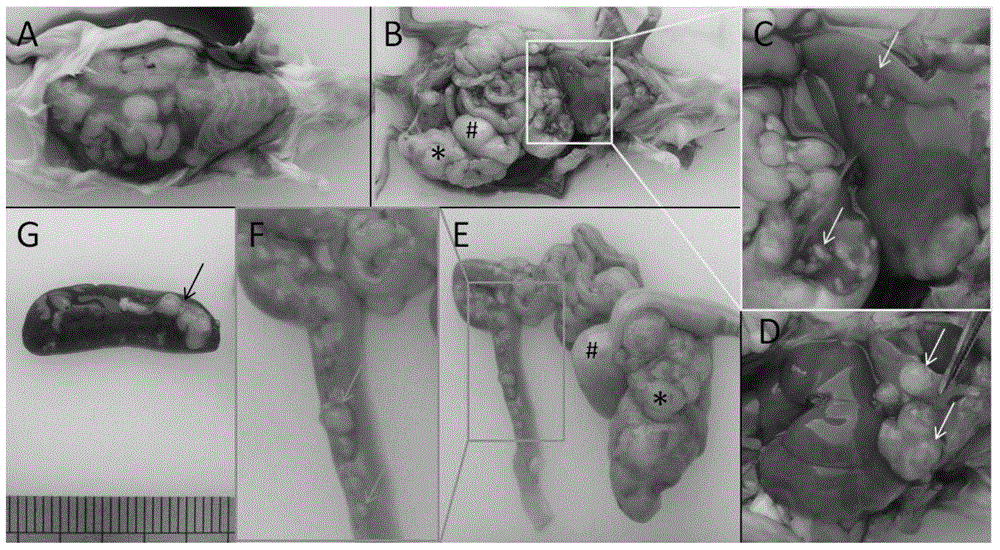
Orthotopic implantation module of mouse colorectal cancer built by mesocaecum triangle and method of orthotopic implantation module
A technology for mesocecal and colon cancer, applied in medical science, veterinary instruments, veterinary surgery, etc., can solve the problems of long cycle and instability of colon cancer models, and achieve high incidence of liver metastases, easy control, and blood supply. rich effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: Method for preparing an orthotopic tumor-bearing model of colon cancer in mice via the mesenteric triangle of the cecum
[0050] 1.1 Preparation of CT26.WT cell suspension
[0051] For routine cell culture, CT26.WT cells were inoculated in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C and 5% CO 2 Cultured in a cell culture incubator. Take cells in the exponential growth phase, digest with 0.25% trypsin containing 0.02% EDTA, mechanically pipette into a cell suspension, filter through a 200-mesh screen, centrifuge at 1000rpm for 8min, discard the supernatant, wash twice with PBS, and add the cell pellet Resuspend in appropriate amount of normal saline, trypan blue staining to determine cell viability>95%, adjust cell concentration to 2.5×10 7 / ml, and stored in ice bath for future use.
[0052] 1.2 After the mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate (0.05ml / g), they were placed in a supine position, and the limb...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2: Ultrasonic examination of colon cancer in mice
[0057] 2.1 Method
[0058] Twenty-five days after the operation, high-frequency ultrasound was used to observe whether there were abnormal echo areas at the inoculation site of the cecum, and the echo type, shape and size of the abnormal mass were recorded.
[0059] 2.2 Results
[0060] High-frequency ultrasound was used to observe the cecal inoculation site, and a hypoechoic mass shadow appeared in the abdominal cavity, with a maximum diameter ranging from 6.1 to 14.5 mm and an average of (9.1±0.4) mm. The test results were as follows: Figure 4 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3: MRI examination of mouse colon cancer
[0062] 3.1 Method
[0063] Mice with orthotopic colon cancer tumors were anesthetized with isoflurane gas and fixed on a scanning table, using a 38mm rat body coil. . MR imaging adopts 7.0T Micro-MRI (Pharma Scan, Bruker, Germany, provided by Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Functional Imaging, Southeast University). The imaging sequence and parameters are as follows: MSME-T2WI sequence: TR 2400ms, TE 16.1ms, layer The thickness is 2mm, the FOV is 3.0cm×3.0cm, the matrix is 256×256, and the imaging time is about 3 minutes and 20 seconds.
[0064] 3.2 Results
[0065] T2WI images showed that there was an oval-shaped slightly high-intensity mass of about 1.7×0.8cm in the cecum of the mouse, the signal was uneven, and small flake-like slightly low-intensity shadows were seen inside, and the boundary of the lesion was not clear ( Figure 5 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor formation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com