Method for co-producing ethanol, acetone and butanol by lignocellulose biomass
A lignocellulose and biomass technology, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of industrial decay of acetone and butanol fermentation, and achieve the increase of organic solvents, the enhancement of blasting effect, and the saving of energy. effect of investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings and embodiments.
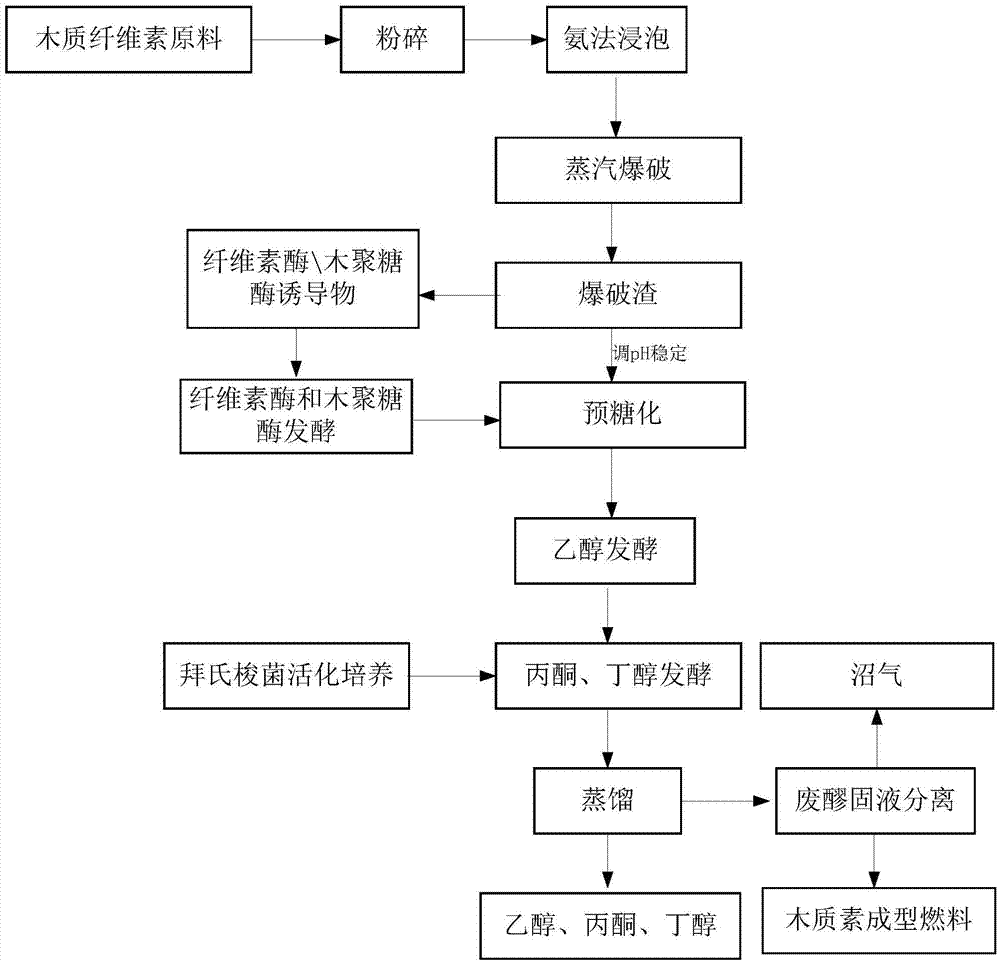
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for co-producing ethanol, acetone and butanol from corn stover specifically includes the following steps:
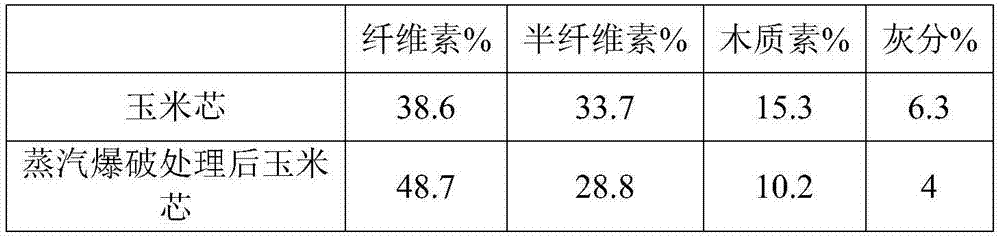
[0045] 1. Cut corn stalks to 3cm, put them in 3 times the mass of 10% (w / w) ammonia solution, soak at room temperature for 3 hours, filter to separate the solid and liquid, and use the liquid to soak the next batch of materials; place the solid in the blasting machine (QBS-200B, Hebi Zhengdao Bioenergy Co., Ltd., Henan), 2.5MPa hold pressure for 60s, instantaneous depressurization sprays out blasting slag; the blasting slag is placed in 4 times the mass of water, and the pH is adjusted to 5.5 with sulfuric acid.
[0046] 2. Activation and fermentation of cellulase from Penicillium oxalicum
[0047] (1) Strain activation: Penicillium oxalicum was grown on a PDA plate at 30°C for 7 days, and then a single colony was picked and...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for co-producing ethanol, acetone and butanol from corn stover specifically includes the following steps:
[0075] 1. Cut corn stalks to 5cm, place 4 times the mass in 15% (w / w) ammonia solution, soak at room temperature for 30 minutes, filter to separate the solid and liquid, and use the liquid to soak the next batch of materials; place the solid in the blasting machine (QBS-200B, Hebi Zhengdao Bio-Energy Company, Henan), 1.8MPa hold pressure for 350s, instantaneously reduce the pressure and spray out the blasting slag; the blasting slag is placed in 3 times the mass of water, and the pH is adjusted to 5 with sulfuric acid.
[0076] 2. Activation and fermentation of cellulase from Penicillium oxalicum
[0077] (1) Strain activation: Penicillium oxalicum was grown on a PDA plate at 30°C for 7 days, and then a single colony was picked and streaked on agar containing PDA (potato powder: 5.0g / L, glucose: 20.0g / L , Agar: 15.0g / L, chloramphenic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com