Method for culturing nitrogen fixation spirulina by using kitchen wastewater
A technology for kitchen wastewater and spirulina, which is applied in the fields of environmental engineering and microalgae cultivation, can solve problems such as unsustainable development, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs, reducing use, and simple preparation methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: the seed preservation culture of spirulina
[0031]The spirulina Spirulina platensis used in this example was purchased from the Freshwater Algae Species Bank of the Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, numbered FACHB-901. Before the reactor wastewater culture, the seed preservation culture of Spirulina platensis was carried out: the seed preservation culture was carried out in a 1L glass Erlenmeyer flask containing 600mL of sterilized culture solution, and the medium was the improved Zarrouk medium. See Tables 1 and 2 for ingredients, configuration and usage (add 2mL of A5 solution per L of culture medium). The incubator was set with a light of 3000Lux, a light-to-dark ratio of 16 / 8, and the temperature of the incubator was controlled at 30±1°C. The conservation culture lasts for 8 to 10 days.
[0032] Table 1 Components of the modified Zarrouk medium
[0033]
[0034] Table 2 Trace element stock solution A5
[0035]
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: Utilize the microalgae culture medium prepared by kitchen waste water to cultivate spirulina
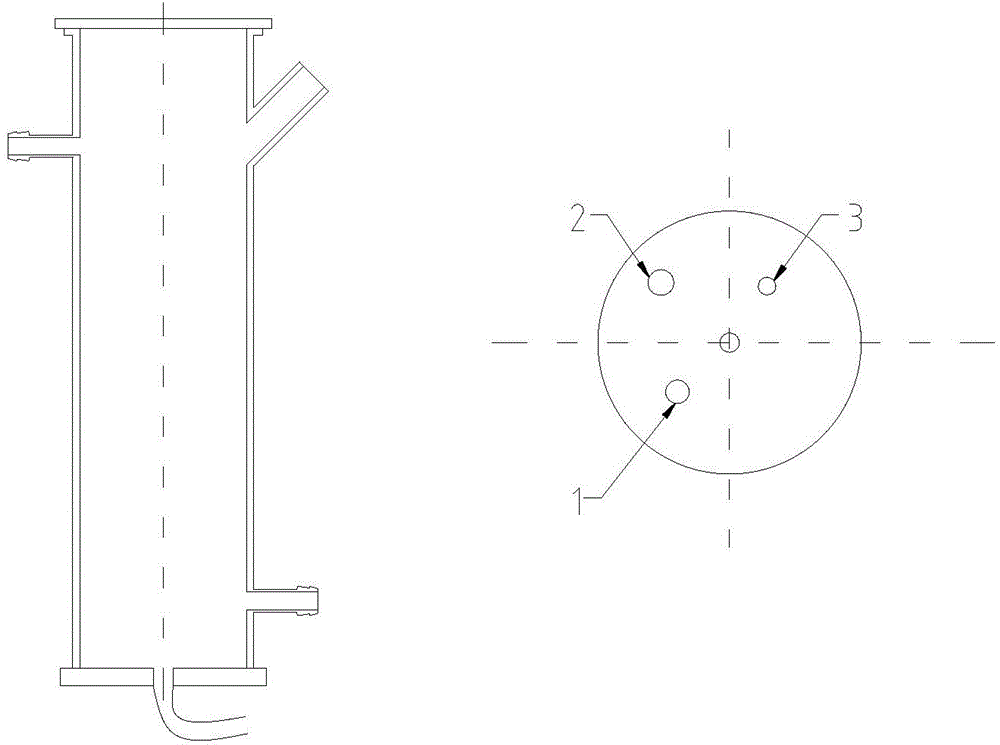
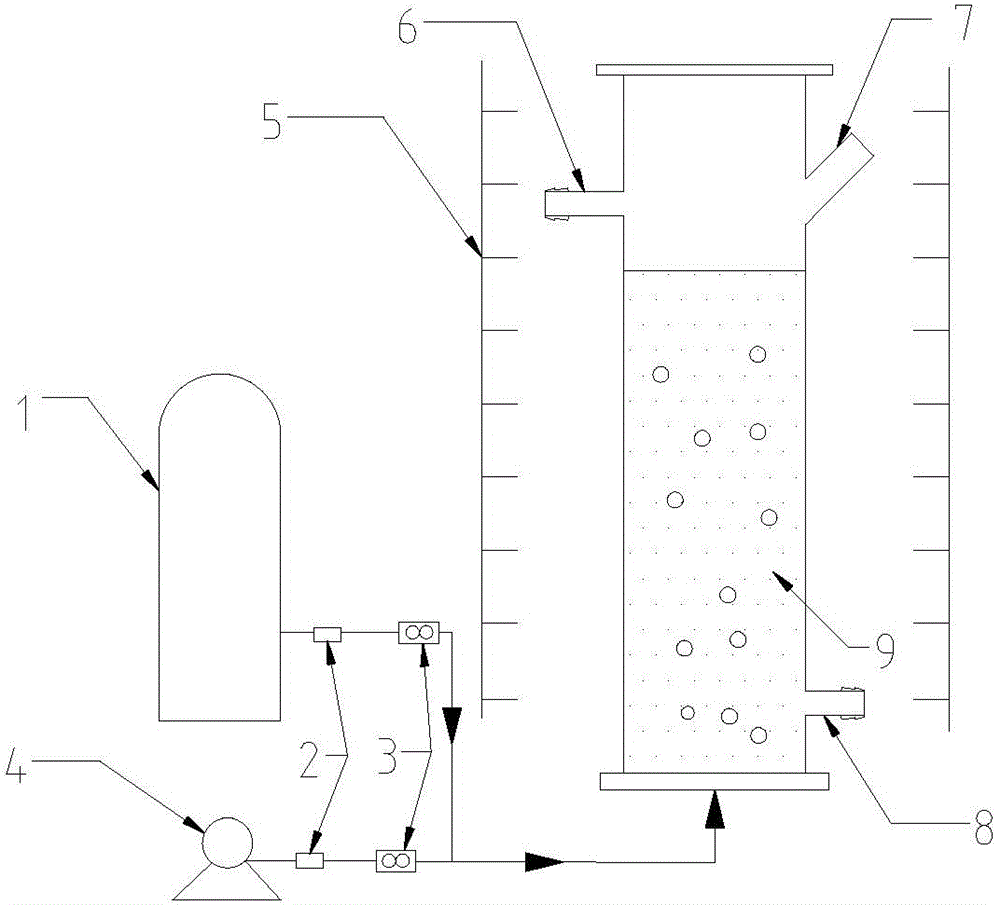
[0037] Inoculate the algal liquid in the logarithmic phase into the photobioreactor (such as figure 1 , figure 2 shown).
[0038] Trace elements (same as the type of trace elements in the trace element stock solution A5 of Zarrouk medium) were added to kitchen waste water to prepare microalgae culture medium, and batch culture of Spirulina platensis was carried out. Microalgae culture can replace nitrogen and phosphorus chemical reagents (NaNO 3 and K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 0) As the source of nitrogen and phosphorus required for the growth of Spirulinaplatensis. The culture conditions were as follows: CO was fed intermittently at a rate of 0.22vvm 2 , the light is 3000Lux, the light-to-dark ratio is 16 / 8, and the temperature of the incubator is controlled at 30±1°C.
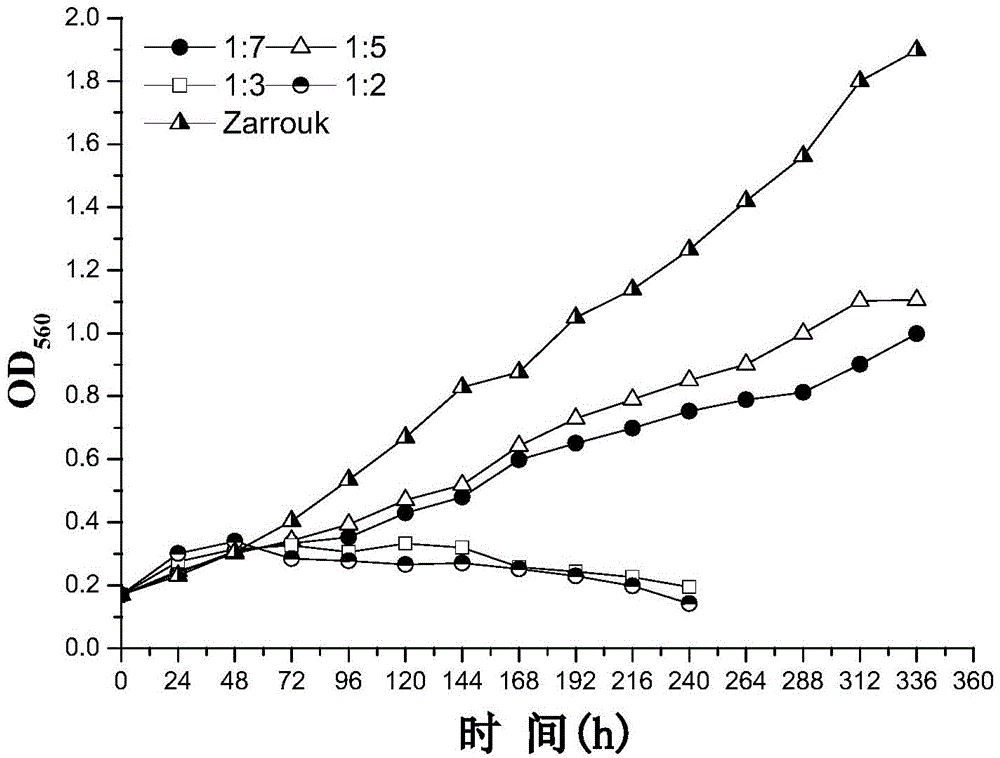
[0039] The culture medium prepared by diluting different multiples of kitchen wastewater (TN co...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Changes of N and P elements in the culture medium during microalgae cultivation
[0042] Use tap water to dilute unsterilized kitchen wastewater until the TN concentration is about 170mg / L, add the trace element solution in Table 2 to make a microalgae culture medium, and conduct a pilot test in a 10L reactor to cultivate carbon-fixing helix algae.
[0043] During periodic operation, 50mL samples were taken multiple times to determine the content of chlorophyll a, and 50mL algae liquid was filtered with a 0.45μm filter membrane to determine the TN and NO contained in it. 3 - -N, NO 2 - -N, NH 4 + -N, TP concentration. After the sampling, the pre-diluted kitchen waste water was added back. Inject CO intermittently during cycle operation 2 , as a carbon source to provide Spirulina with carbon elements necessary for photosynthesis.
[0044] The result is as Figure 4 As shown, the OD of Spirulina 560 Enter logarithmic growth phase after 48h lag period...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com