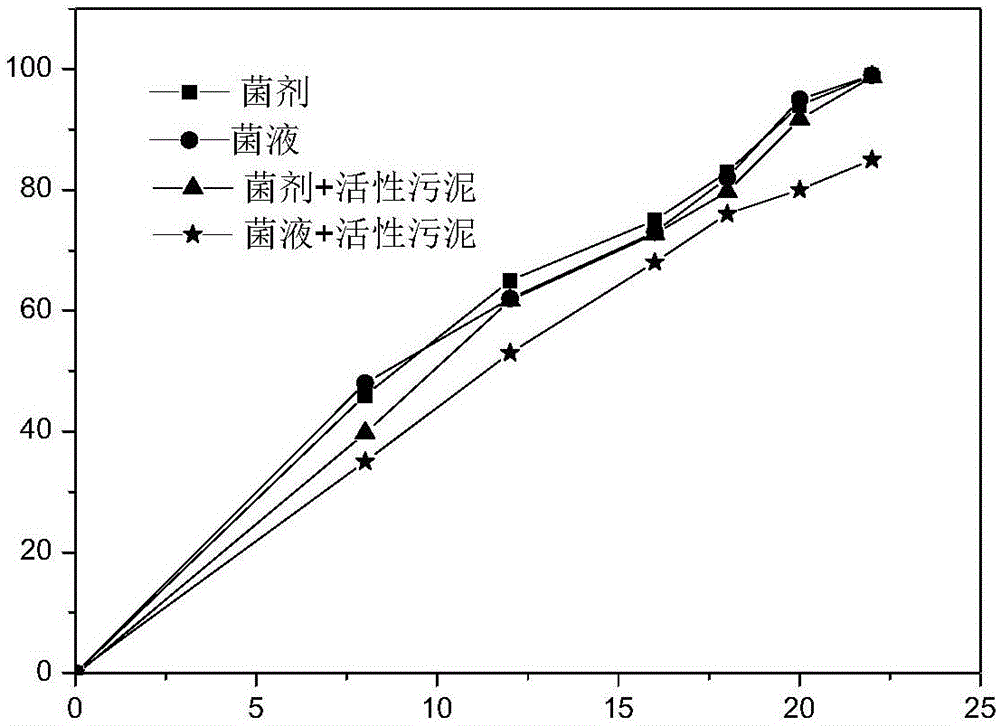
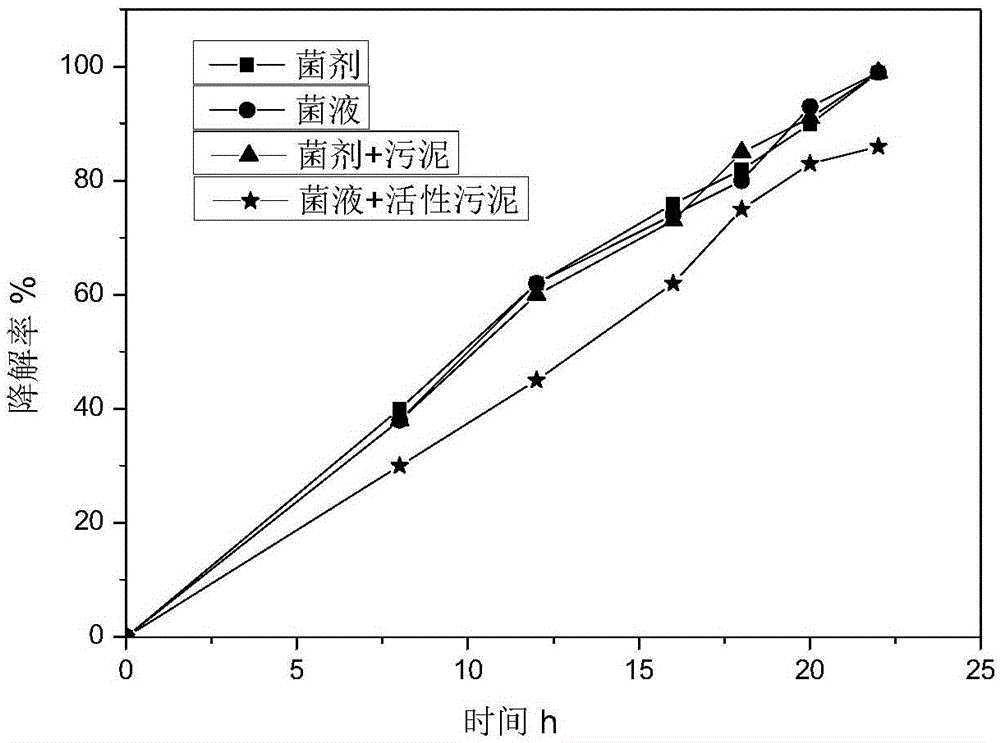
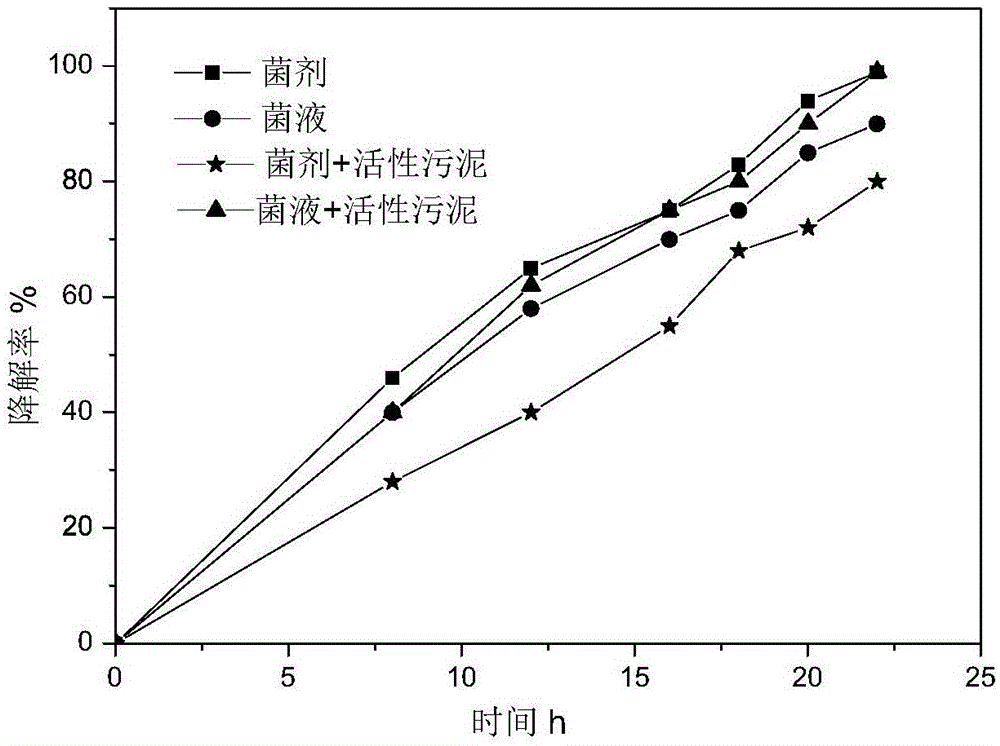
Rhodococcus strain C3, microbial agent containing rhodococcus strain C3, and applications of rhodococcus strain C3 and microbial agent
A technology of microbial agents and strains, applied in the field of bioaugmentation of environmental pollutants, can solve the problems of unstable treatment effect, long sludge domestication time, poor impact resistance, etc., and achieve good solid-liquid separation effect and high-purity strains Efficient and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: the acquisition and identification of rhodococcus strain C3 bacterial strain
[0030] 1. Acquisition of strains
[0031] The strain originated from the activated sludge of the coking plant wastewater biological treatment system. Draw 2 ml of sludge samples into 200 ml of fresh enrichment medium with a phenol concentration of 200 mg / L according to 1% inoculum amount, and culture on a shaking table (30° C., 200 r / min). After the enrichment bottle is turbid, take 2ml of the culture solution and transfer it to a liquid medium with a phenol concentration of 400mg / L for cultivation. By analogy, gradually increase the phenol concentration to 1000mg / L. The cells enriched in the enrichment medium with a phenol concentration of 1000 mg / L were transferred to an inorganic salt medium with a phenol concentration of 1000 mg / L for acclimation. The strains using phenol as the sole carbon and energy source were isolated and screened on the separation medium plate by dil...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: Rhodococcus strain RhodococcusC3 is to the degradation of pyridine and o-cresol in inorganic salt medium
[0039] Pick a single colony of Rhodococcus strain C3 and put it in 3ml LB liquid medium, culture it with shaking at 30°C and 200r / min for 24 hours to obtain a fresh bacterial solution. Pyridine and o-cresol were added to the inorganic salt medium respectively, and the final concentrations of pyridine and o-cresol were respectively 100 mg / L. The degradation results are shown in Table 1.
[0040] substrate pyridine o-cresol Degradation rate% 100 100
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Degradation of phenol, pyridine and o-cresol in coking wastewater of Rhodococcus strain C3
[0042] Measure 100ml of coking wastewater, the concentration of phenol is 350±5mg / L; add pyridine and o-cresol to make the concentration respectively 100±5mg / L, insert 2ml of fresh bacterial liquid, mix well, place at 30℃, 200r / Min shaker culture, 5 days later (120h) samples were taken to determine the degradation rate of the compound. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0043] substrate phenol pyridine o-cresol Degradation rate% 100 >90 >90
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com