Method for detecting pesticide residues through paper-based visualized molecular imprinting biosensor
A biosensor and molecular imprinting technology, applied in the field of quantitative analysis and detection of pesticide residues, can solve the problems of unfavorable on-site detection, limited application and development, and expensive instruments, so as to get rid of the limitation of energy requirements, facilitate popularization and application, and reduce detection costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Detection of Glucose in Serum
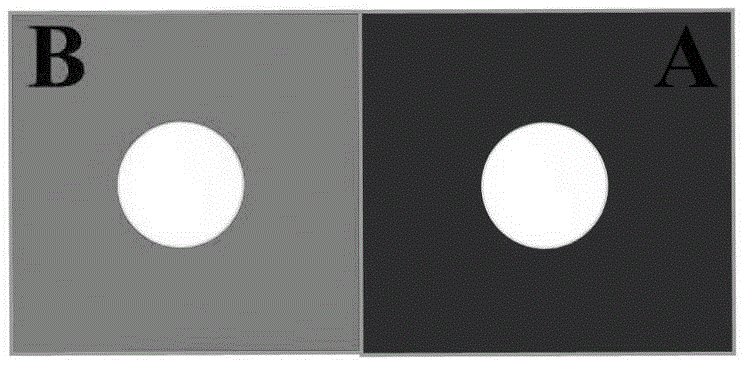
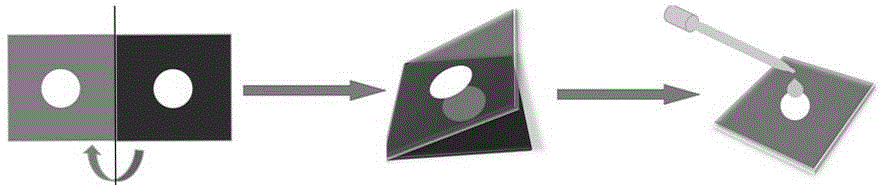
[0035] (1) Use Adobe Illustrator CS4 software to design the microfluidic paper chip on the computer, as attached figure 1 As shown, the microfluidic paper chip includes two wax-printed hydrophobic regions, A and B, with a single unit size of 15×15mm. A hydrophilic region is used for in situ synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers, and B hydrophilic region is used for Fixed 3,3 ’ ,5,5 ’ - Tetramethylbenzidine, the diameter of the hydrophilic area is 6 mm;
[0036] (2) To prepare synthetic zinc ferrite, first synthesize ZnO, add 80mL of secondary water into a three-necked flask and heat to 80°C, then add 0.8mmol of ZnCl 2 and 4 mmol of NaBH 4 Stir for 2 hours, wash by centrifugation, and dry at 60°C for later use; synthesis of zinc ferrite: 0.097g FeCl 3 , 0.053g of ascorbic acid and 0.024g of ZnO prepared above were mixed and added to 1mL of hydrazine hydrate for 30s of ultrasonic mixing, stirred for 30min, transferred ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com