Novel Mg-doped NBT (Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3)-based lead-free dielectric ceramic material and preparation method thereof
A bismuth sodium titanate-based, dielectric ceramic technology, which is applied in the field of ceramics, can solve problems such as not being able to meet big data, and achieve low dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, and various performance improvements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0032] Embodiment one: NaBi (Ti 0.98 Mg 0.02 ) 6 o 14 Piezoelectric ceramic preparation
[0033] Chemical formula:
[0034] Using Na 2 CO 3 , TiO 2 and Bi 2 o 3 Three kinds of raw material powders, the reactants are cooled to room temperature in a desiccator, and dried, and Na 2 CO 3 The mass is 2.10856g, TiO 2 The mass is 18.62653g, Bi 2 o 3 The mass is 9.07311g, and the mass of MgO is 0.19179g. The sample is processed and prepared by traditional solid-phase method. The specific procedure was as follows: the powders were mixed in ethanol and ball milled with stabilized zirconia grind for 24 hours and dried. The dried powder was calcined twice at 900°C and 950°C for 4 hours. After each calcining, the powder was ball-milled for 12 hours, and then the powder was re-ground and shaped into granules, and the green body was used to A uniaxial steel mold is pressed into a sheet, pressed into a disc size (area 0.6951cm, diameter 0.941cm, thickness 0.168cm) and cold is...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment two: measure the dielectric properties of the piezoelectric ceramic material sample of the present invention
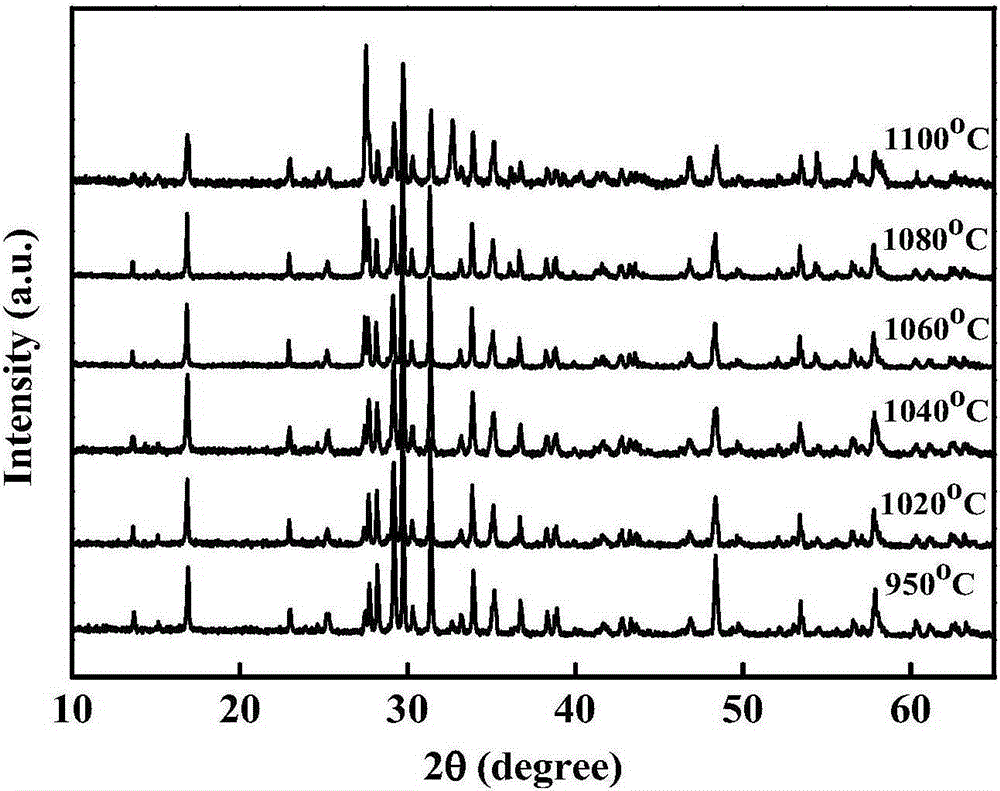
[0040] (1) from figure 1 Diffraction analysis shows that the ceramic sheet obtained by the experimental reaction is a single phase, which is consistent with the theoretical material, except that the sintering temperature is 1100 ° C.
[0041] (2) Relative permittivity measurement data
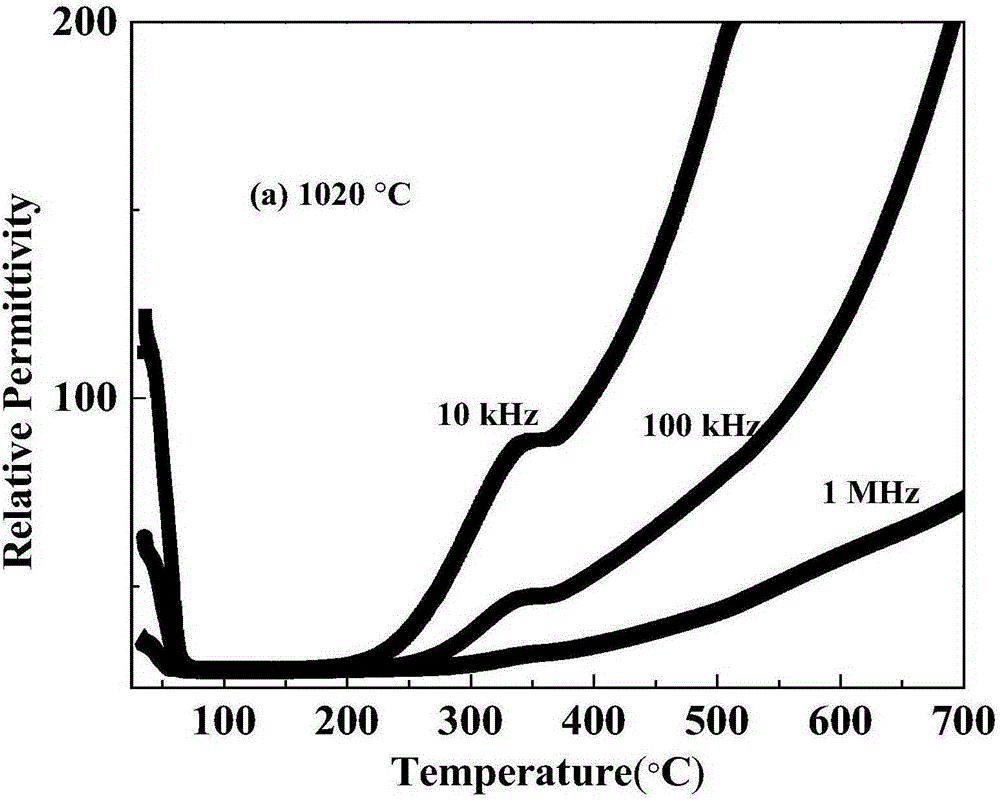
[0042] figure 2 Indicates that NaBi(Ti 0.98 Mg 0.02 ) 6 o 14 Pre-fired twice at 900°C and 950°C, and calcined at 1020°C, the measured relative permittivity varies with the temperature of the material environment. The relative permittivity of the ceramic rises and then falls at lower temperatures, and then after Flat zone, then moderate rise. As the frequency increases, its relative permittivity decreases.
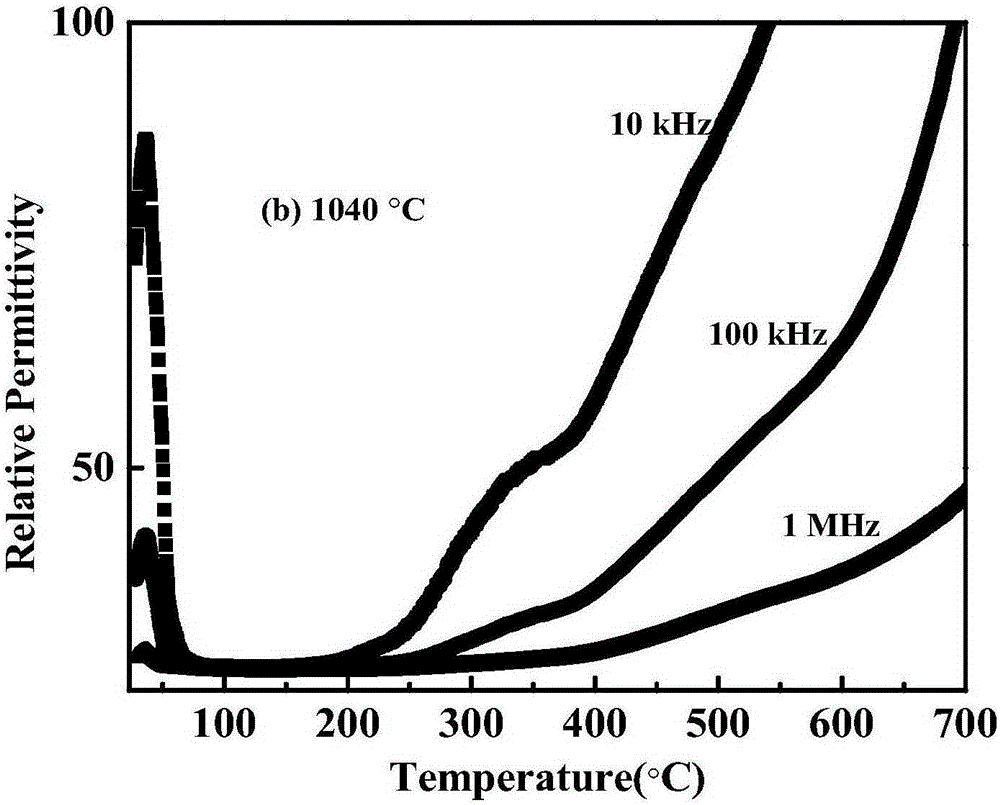
[0043] image 3 Indicates that NaBi(Ti 0.98 Mg 0.02 ) 6 o 14 Pre-fired twice at 900°C and 950°C, and calcined at 1040°C, the measured relative dielec...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com