Method for treating pollutants in water by taking organic fluorine conjugated microporous polymer as adsorbent
A technology of conjugated micropores and adsorbents, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve problems such as limiting the breadth, and achieve the effects of simple process flow, large adsorption capacity, and good kinetic adsorption performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
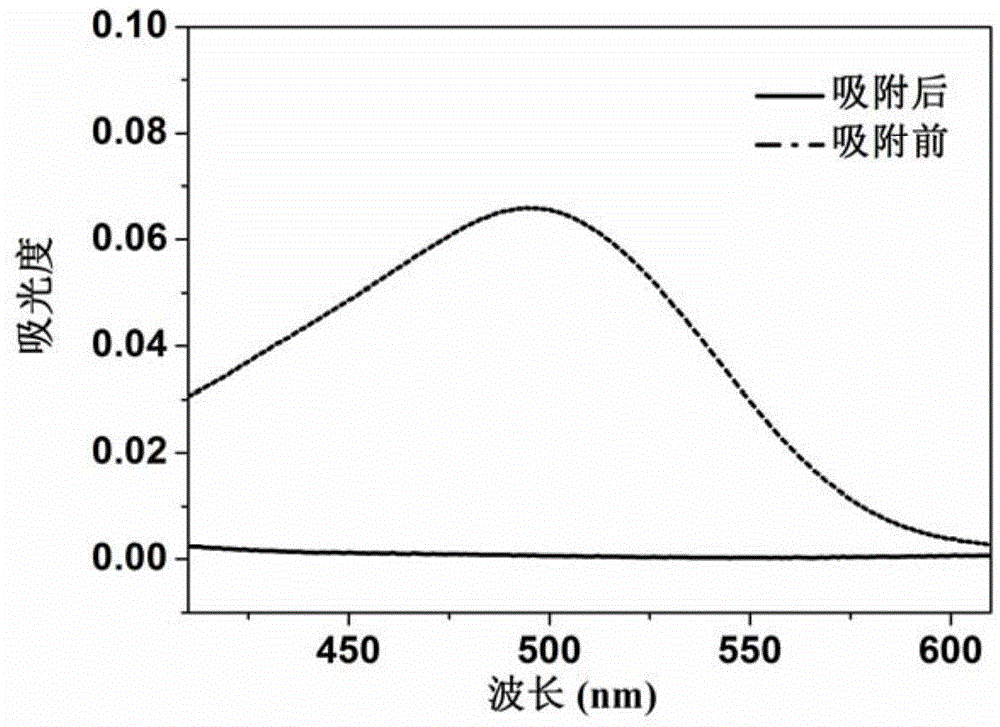
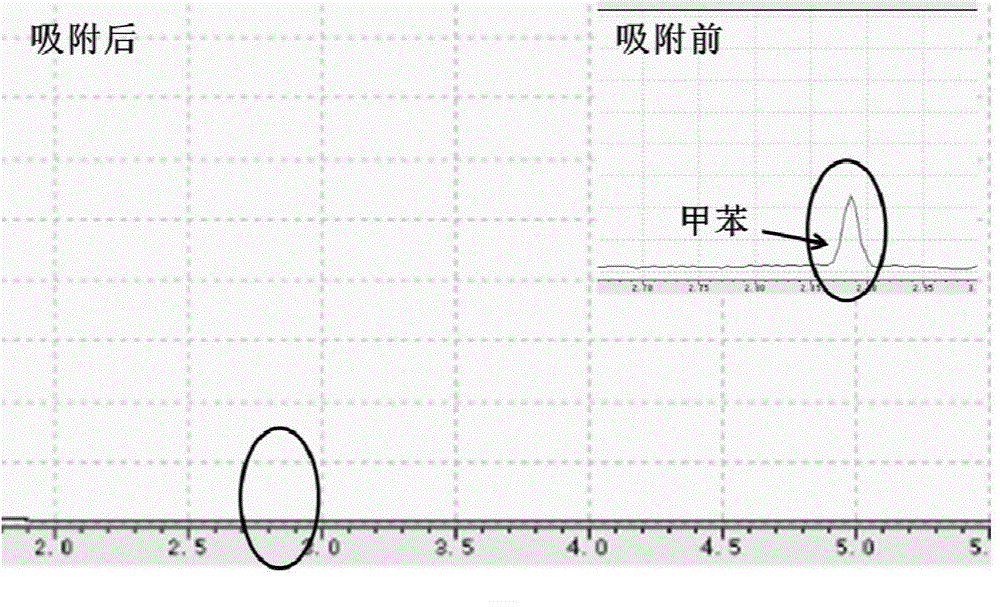
[0025] Congo red (CR), toluene (Toluene) and lead (Pb 2+ ) ion mixed solvent as an example to illustrate that the adsorbent FCMP can simultaneously adsorb various pollutants in water. Among them, the concentration of Congo red (CR) is 10mg / L, lead (Pb 2+ ) The concentration of ions is 5mg / L, and the concentration of toluene is 01%. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0026] Measure 20 mL of the above mixed solution, add 10 mg FCMP, and stir at room temperature for 3 hours. After the stirring was completed, FCMP was recovered by filtration, and the filtrate was collected for testing. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was used to detect the content change of toluene in the solution. Inductively coupled plasma spectrometer (ICP) was used to detect the content change of lead (Pb(II)) ions in the solution. Ultraviolet absorption-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) was used to detect the content change of Congo red in water. The analysis results showed tha...
Embodiment 2
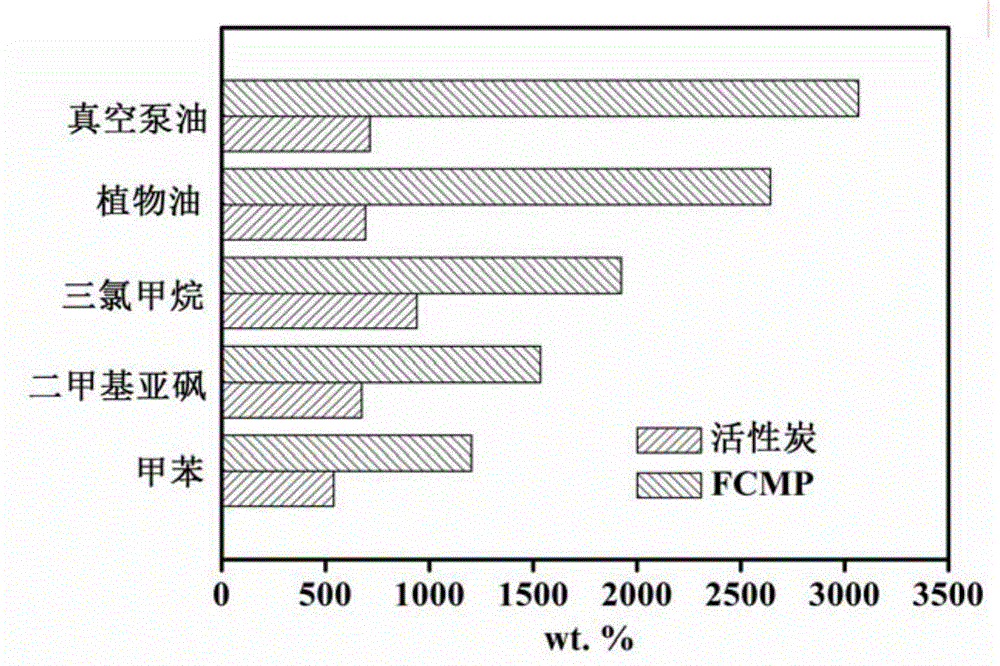
[0028] Taking vacuum pump oil, vegetable oil, chloroform, dimethyl sulfoxide and toluene as an example to illustrate that FCMP as an adsorbent can effectively absorb and remove organic solvents in water, waste oil and antibiotics in oil products. Explosive capacity. In order to provide a reference for the adsorption performance of the material, we use activated carbon as a comparison.
[0029] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0030] Take toluene as an example. Weigh a certain amount of FCMP, and record its mass, denoted as (M b ). It was then placed in 3 mL of toluene, and after 15 minutes, FCMP was recovered. Quickly weigh the mass of FCMP after absorbing the solvent (M a ), minus the mass of FCMP before adsorption (M b ) is the amount of solvent adsorbed by FCMP (M s ), use M s divide by M b That is, the mass ratio of adsorbed solvent to adsorbent is obtained. The calculation of the adsorption capacity of activated carbon to toluene is the same a...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Taking Congo red and methylene blue as examples to illustrate that FCMP as an adsorbent can effectively adsorb and remove organic dyes in sewage. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0034] Congo red (CR) aqueous solutions with initial concentrations of 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, and 600 mg / L were prepared respectively. Measure 30 mL of the above-mentioned Congo red (CR) aqueous solutions with different initial concentrations; weigh 6 parts of FCMP 5 mg, place them in the above-mentioned Congo red solutions with different initial concentrations, and stir at room temperature for 24 hours.
[0035] Prepare methylene blue (MB) aqueous solutions with initial concentrations of 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 mg / L, respectively. Measure 30 mL of the above-mentioned prepared methylene blue (MB) aqueous solutions with different initial concentrations; weigh 6 parts of FCMP5 mg, place them in the above-mentioned methylene blue (MB) solutions with different initial co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Maximum adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com