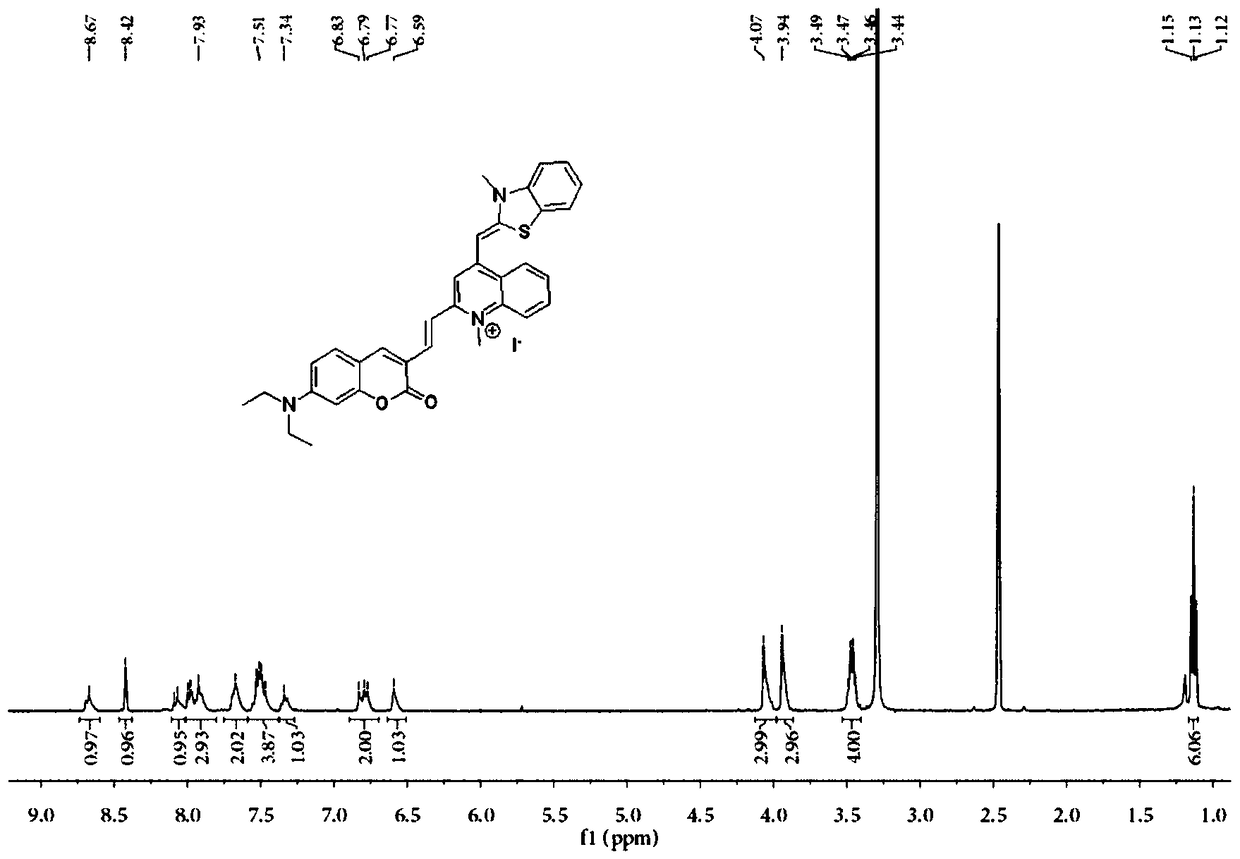
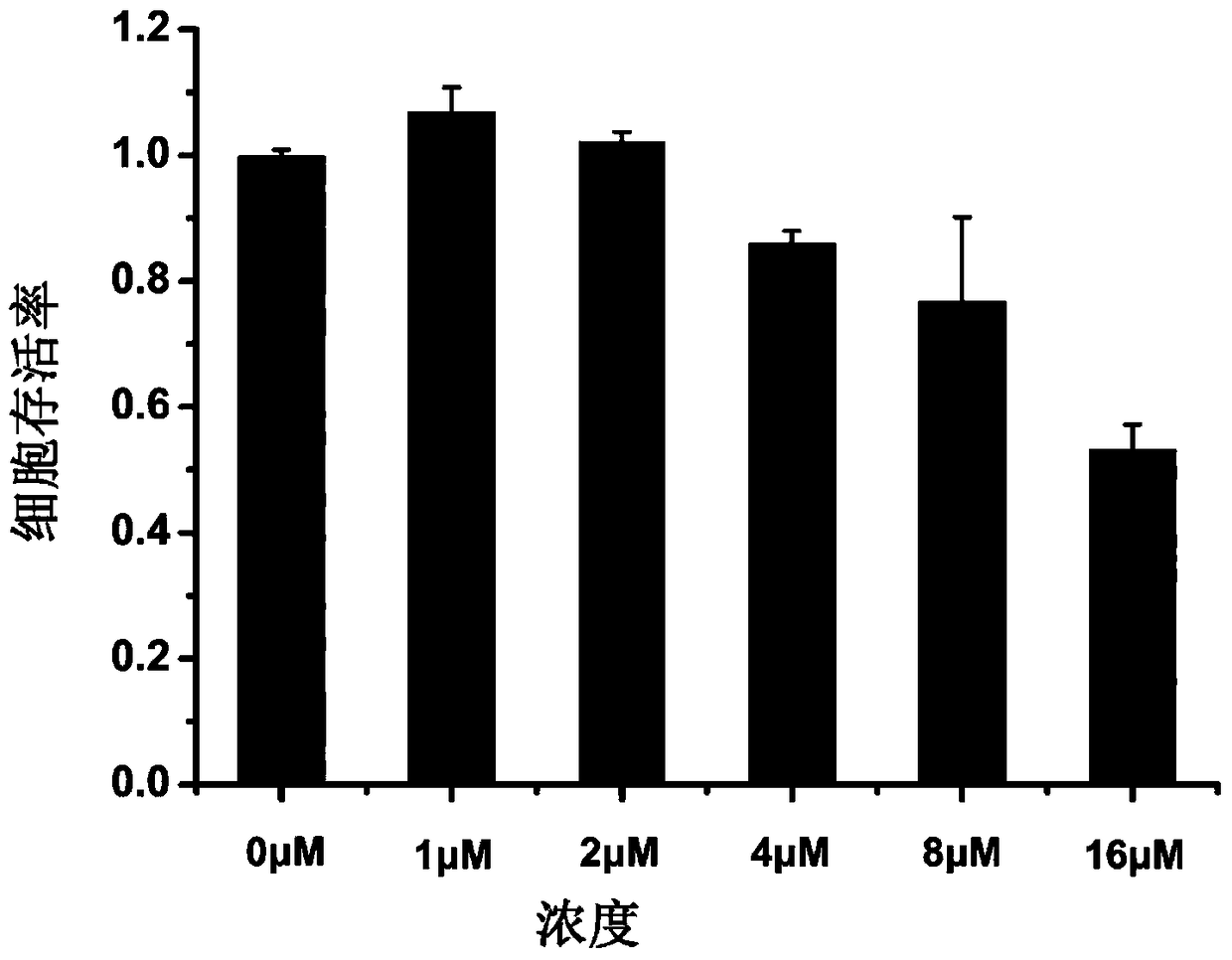
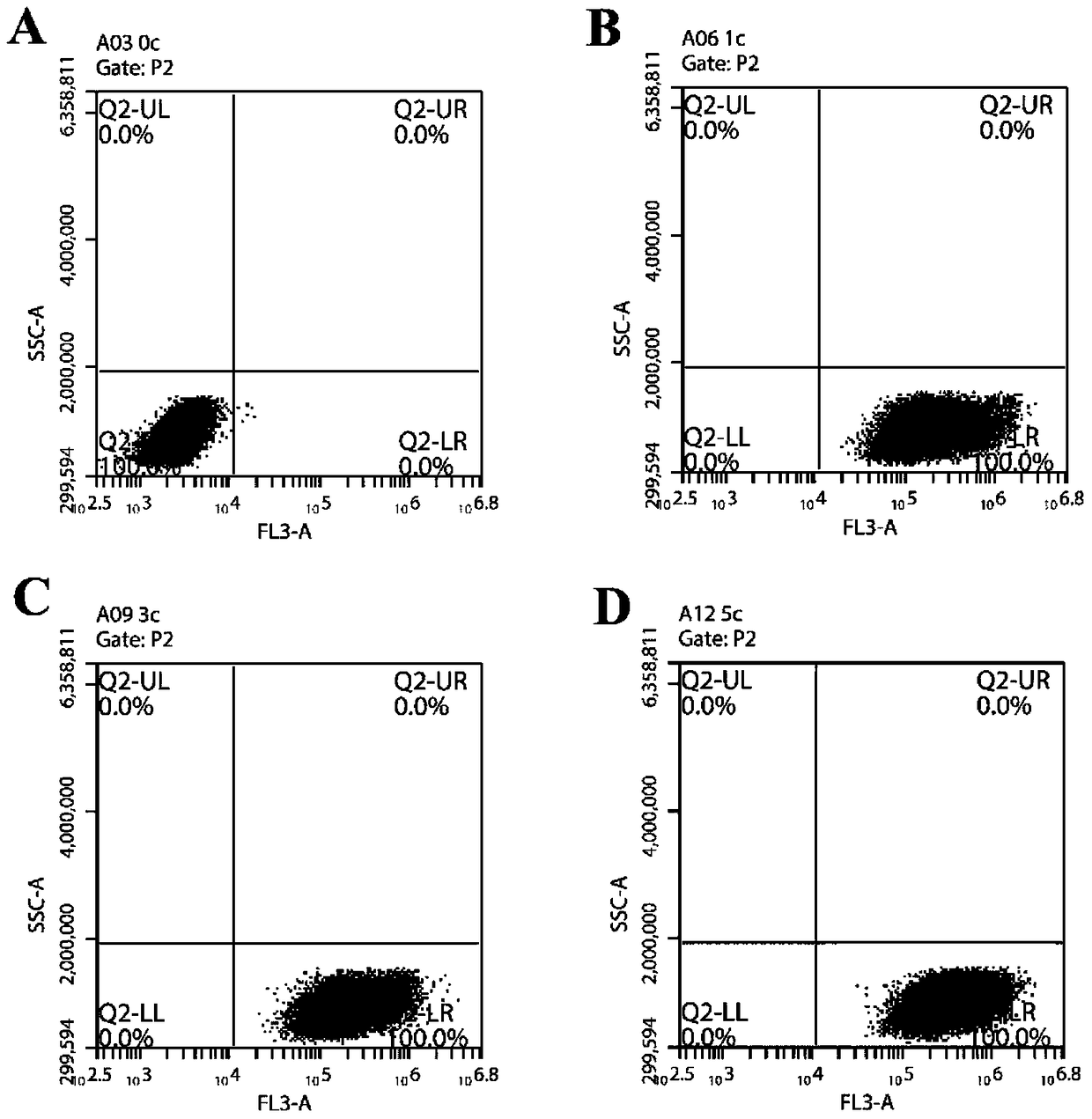
Substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivatives and their preparation and use
A technology of orange derivatives and coumarin, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of unfavorable fluorescence imaging, short fluorescence emission wavelength, etc., and achieve the effects of strong operability, low overall cost and excellent selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The preparation method of the substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative comprises the following steps:
[0031] a. Dissolve substituted salicylaldehyde and diethyl malonate in an anhydrous organic solvent, then add piperidine, and reflux for 6 to 8 hours to prepare intermediate 1; the diethyl malonate The dosage is 2.0~2.5 times of substituted salicylaldehyde, and the consumption of said piperidine is 1.2~1.6 times of substituted salicylaldehyde;
[0032] b. Dissolving intermediate 1 in a strong acid and reacting under reflux for 4 to 6 hours to prepare intermediate 2;
[0033] c. Reflux reaction of intermediate 2 and phosphorus oxychloride in anhydrous DMF (N,N-dimethylformamide) for 2.5 to 3.5 hours to prepare intermediate 3; the amount of phosphorus oxychloride 1.6 to 1.8 times that of intermediate 2;
[0034] d, the intermediate 3,2-methylthiazole orange and piperidine were refluxed in absolute ethanol for 12 hours to prepare substituted coumarin-thiazole or...
Embodiment 1
[0042] The synthesis of embodiment 1 intermediate 1:
[0043]
[0044] Dissolve 4-diethylamino salicylaldehyde (10.0g, 56.4mmol), diethyl malonate (18.0g, 112.4mmol), piperidine (2mL, 79.0mmol) in 60mL of absolute ethanol, at 80°C reflow. When the reaction was no longer monitored by TLC (about 6 hours), the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and used directly for the next reaction. 15.6 g of black oily liquid was obtained, and the crude yield was 95.7%.
[0045] 1 HNMR (400MHZ, CDCl 3 )δ8.40(s, 1H), 7.35(d, J=8.8Hz, 1H), 6.66(dd, J=8.9, 2.3Hz, 1H), 6.50(s, 1H), 4.36(q, J=7.15 Hz, 4H), 3.42 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 1.36 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.21 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 6H).
Embodiment 2
[0046] The synthesis of embodiment 2 intermediate 2:
[0047]
[0048] Intermediate 1 (5.0 g, 17.3 mmol) was dissolved in 150 mL of 18% concentrated hydrochloric acid and refluxed at 100 °C. When the reaction was no longer monitored by TLC (about 5 hours), the reaction was cooled to room temperature, saturated sodium carbonate solution was added, and the pH was adjusted to 4-5 with 45% concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, and a large amount of orange solid was observed to precipitate. After filtration under reduced pressure, a large amount of khaki solid was collected, dried in vacuo to remove water, and used directly for the next reaction. 2.7 g of yellow-green powder was obtained with a yield of 72.0%.
[0049] 1 HNMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ7.54(d, J=9.5Hz, 1H), 7.28(d, J=8.8Hz, 1H), 6.74(bs, 1H), 6.61(s, 1H), 6.08(d, J=9.2Hz, 1H), 3.4 (q, J=7.1 Hz, 4H), 1.19 (t, J=7.1 Hz, 6H).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com