Energy regeneration method for solid organic waste alkaline thermal hydrolysis supernate
An organic waste, energy-based technology, applied in the removal of solid waste, waste fuel, etc., can solve the problems of increased equipment investment and operating costs, no thermal hydrolysis pretreatment process, and no process practicability. , to improve the fluidity, shorten the digestion time, and achieve the effect of stabilization treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
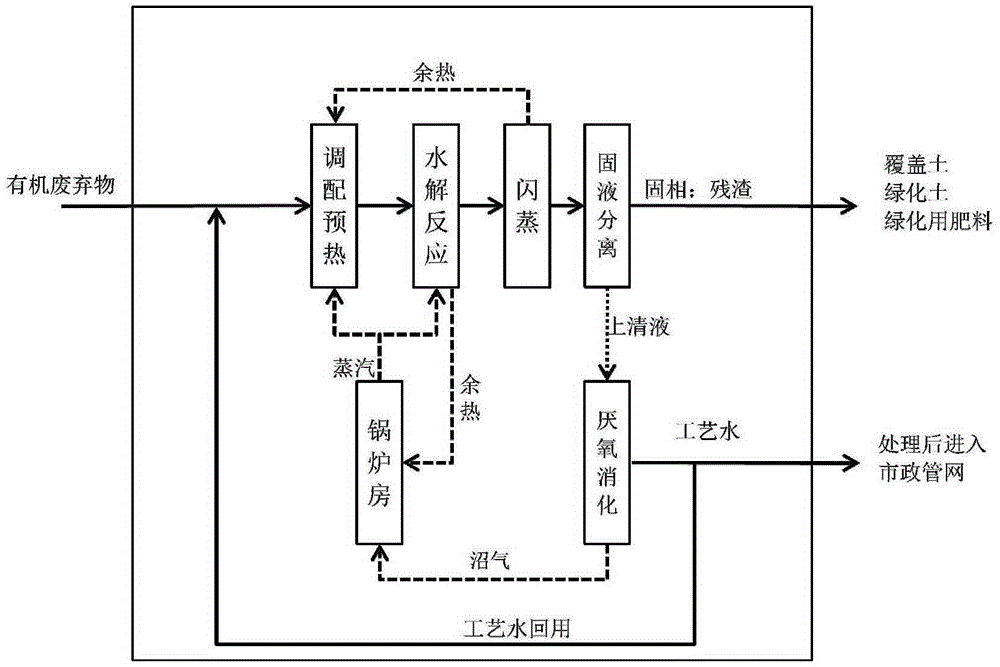
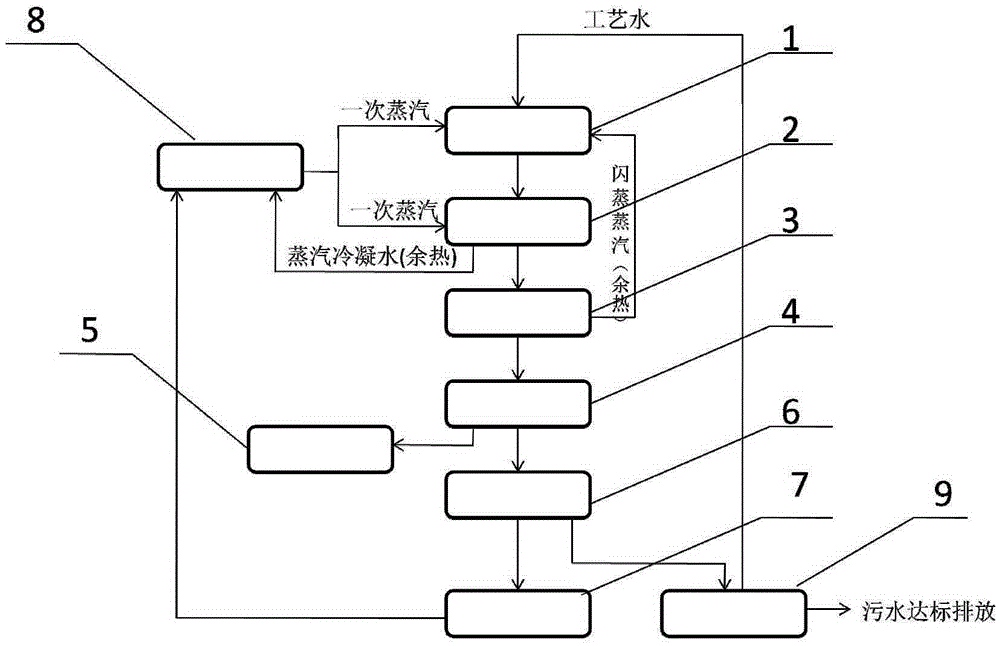
[0077] A method for energy conversion of supernatant liquid from thermal alkali hydrolysis of solid organic waste, comprising the following steps:
[0078] 1 ton of sludge with a moisture content of 80% + 0.32 tons of process water + 0.03 tons of calcium oxide + 0.02 tons of magnesium oxide are preheated to 70°C by direct steam heating in the deployment preheating tank, and then transported to the hydrolysis reaction by a screw pump Inside the kettle, heat up to 120°C through indirect steam heating in the hydrolysis reactor, and stay at this temperature for 100 minutes; The temperature of the hydrolyzate is lowered to 65°C, and the flash process produces 0.11 tons of flash secondary steam, all of which are reused in the deployment preheating tank for recycling. The material after flash evaporation is decalcified by sodium carbonate + hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value to 7-9. After flash evaporation, the material is transported into a plate and frame filter press by a sc...
Embodiment 2
[0080] A method for energy conversion of solid organic waste thermal alkali hydrolysis supernatant, comprising the following steps:
[0081]0.5 tons of sludge with a moisture content of 82% + 0.5 tons of kitchen waste + 0.3 tons of process water + 0.035 tons of calcium oxide + 0.01 tons of sodium hydroxide are preheated to 90°C by steam direct heating in the deployment preheating tank , transported to the hydrolysis reactor through a screw pump, and heated to 110°C by indirect steam heating in the hydrolysis reactor, and stayed at this temperature for 120 minutes; after the reaction, the hydrolyzate was transported into the flash evaporation through the pressure of the reactor itself In the tank, the temperature of the hydrolyzate is reduced to 65°C through two-stage flash evaporation. The flash evaporation process produces 0.11 tons of flash secondary steam, all of which are reused in the deployment preheating tank for recycling. During the flashing process, carbon dioxide ga...
Embodiment 3
[0083] A method for energy conversion of supernatant liquid from thermal alkali hydrolysis of solid organic waste, comprising the following steps:
[0084] 0.8 tons of sludge with a moisture content of 80% + 0.2 tons of kitchen waste + 0.32 tons of process water + 0.02 tons of calcium oxide + 0.02 tons of magnesium oxide are preheated to 50°C by direct steam heating in the deployment preheating tank. The screw pump is transported to the hydrolysis reactor, and the temperature in the hydrolysis reactor is raised to 110°C through indirect steam heating, and stays at this temperature for 110 minutes; after the reaction is completed, the hydrolyzate is transported into the flash tank through the pressure of the reactor itself , the temperature of the hydrolyzed solution is reduced to 100°C through primary flash evaporation, and 0.05 tons of flash steam is generated during the flash evaporation process, all of which are reused in the deployment preheating tank for recycling. In the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com