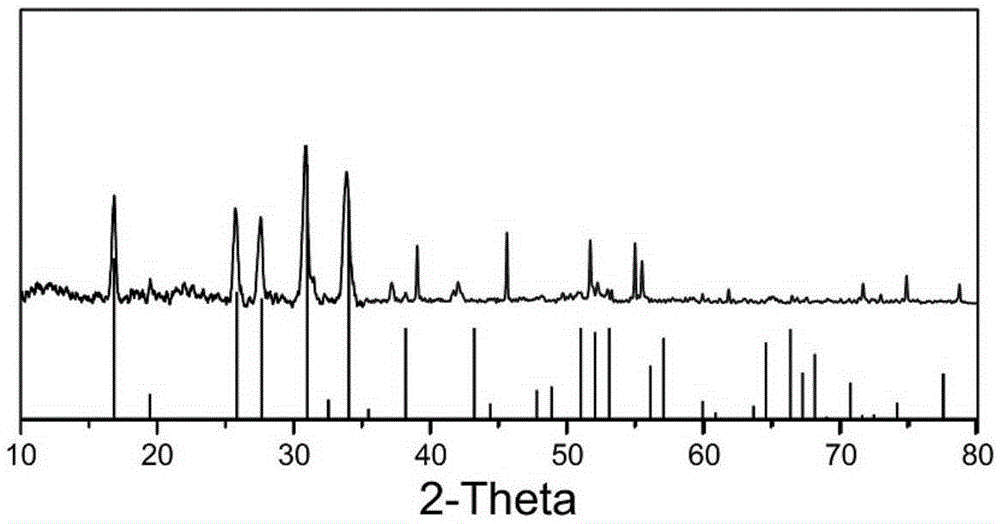
Sintering method for reducing lithium ion loss of solid-state lithium ion electrolyte material Li7La3Zr2O12
A technology of electrolyte material and sintering method, which is applied to circuits, electrical components, secondary batteries, etc., can solve the problems of reducing battery manufacturing cost, high temperature sintering and high energy consumption, and mixing molten salt into powder, etc., so as to reduce production costs and reduce Calcination temperature, the effect of shortening the reaction period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Weigh lithium carbonate Li 2 CO 3 3.70g, lithium nitrate LiNO 3 10.33g, lithium hydroxide LiOH6.27g, dilanthanum trioxide La 2 o 3 35.75g, zirconium dioxide ZrO 2 17.87g, and then pour the weighed raw materials into an agate mortar and grind them fully for 15 minutes to mix the raw materials evenly, and then transfer the ground powder to a magnesia crucible. The crucible was placed in a tube furnace, and high-purity argon gas was introduced slowly for 10 minutes to remove the air in the tube. Then ignited and calcined, the furnace temperature was raised to 750°C at a speed of 30°C / min, and calcined at this temperature for 3 hours. After the calcination, the temperature was naturally cooled to room temperature in an argon atmosphere.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Weigh lithium carbonate Li 2 CO 3 2.10g, lithium nitrate LiNO 3 5.76g, lithium hydroxide LiOH4.0g, dilanthanum trioxide La 2 o 3 21.23g, zirconium dioxide ZrO 2 10.61g, then pour the weighed raw materials into an agate mortar and grind them fully for 15 minutes to mix the raw materials evenly, then transfer the ground powder to a magnesia crucible. The crucible was placed in a tube furnace, and high-purity argon gas was introduced slowly for 10 minutes to remove the air in the tube. Then ignited and calcined, the furnace temperature was raised to 850°C at a rate of 30°C / min, and calcined at this temperature for 2 hours. After the calcination, the temperature was naturally cooled to room temperature in an argon atmosphere.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Weigh lithium carbonate Li 2 CO 3 3.70g, lithium nitrate LiNO 3 10.33g, lithium hydroxide LiOH6.27g, dilanthanum trioxide La2 o 3 35.75g, zirconium dioxide ZrO 2 17.87g, and then pour the weighed raw materials into an agate mortar and grind them fully for 15 minutes to mix the raw materials evenly, and then transfer the ground powder to a magnesia crucible. The crucible was placed in a tube furnace, and high-purity argon gas was introduced slowly for 10 minutes to remove the air in the tube. Then ignited and calcined, the furnace temperature was raised to 900°C at a rate of 20°C / min, and calcined at this temperature for 4 hours. After the calcination, the temperature was naturally cooled to room temperature in an argon atmosphere.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com