Mass Spectrometry-Based Analysis of Oxygen-Linked Nitrogen-acetylglucosamine-Modified Glycoproteins
A nitrogen acetyl glucosamine and analysis method technology, which is applied in the field of analysis of oxygen-linked nitrogen acetyl glucosamine modified glycoproteins based on mass spectrometry, can solve problems such as inability to obtain better peptide fragmentation information, and achieves a large number of benefits. Large-scale sample analysis, enhanced sample mass spectral signal, and the effect of facilitating retrieval and analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Girard reagent labeling of standard glycopeptides modified with oxygen-linked nitrogen acetylglucosamine:
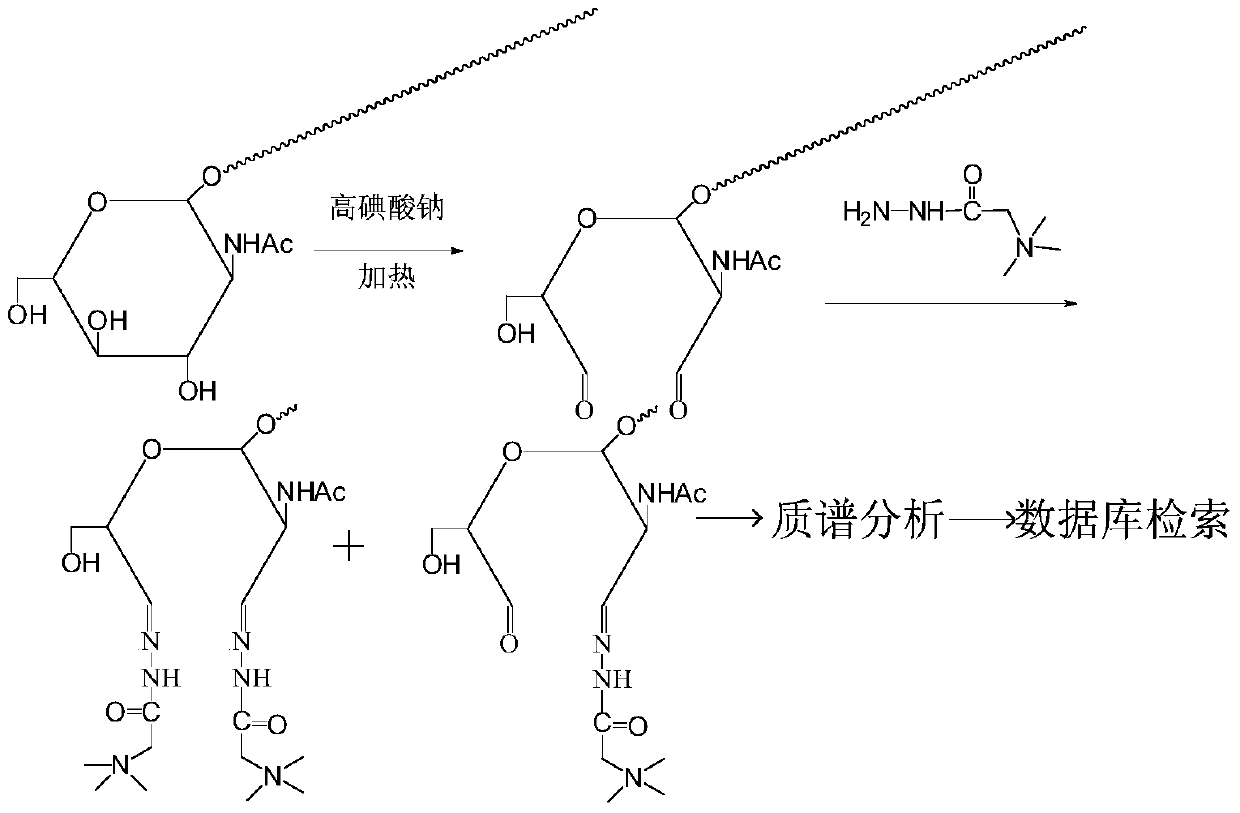
[0029] 1. If figure 1 As shown, operate as follows:
[0030] 1) Standard glycopeptide N-terminal dimethylation blocking: take 10 μg of peptide TAPTSgTIAPG, add 1 μl of 4% formaldehyde solution, 1 μl of 0.6 mM sodium cyanoborohydride, react for 0.5 hours, remove formaldehyde and sodium cyanoborohydride by reverse phase desalting .
[0031] 2) Nitroacetylglucosamine group oxidation: In 50 mM sodium acetate buffer solution with pH=5.5, the glycopeptide sample was reacted with 20 mM sodium periodate solution; the reaction temperature was 37° C., and the reaction time was 6 hours. After the oxidation reaction was finished, sodium sulfite was added in a molar amount 5 times that of sodium periodate, and reacted for 20 minutes to terminate the oxidation reaction.
[0032]3) Girard reagent derivatization reaction: the glycopeptide sample oxidized by sodium periodate wa...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Digestion and labeling of protein samples:
[0037] (1) Enzymolysis was performed on the protein samples extracted from rat brain samples after denaturation and reductive alkylation: 4 μl of 1M dithiothreitol (DTT) was added to every 100 μg of extracted proteins, and reacted at 56° C. for 1.5 hours. Afterwards, 8 μl of 1M iodoacetic acid (IAA) was added and reacted in the dark for 30 minutes. The treated protein samples were diluted with ammonium bicarbonate buffer, pH=8. Add 4 μg trypsin to every 100 μg protein for enzymatic hydrolysis, and react at 37°C for 24 hours. The enzymatic peptide was removed by reversed-phase liquid chromatography to remove small molecular salts such as ammonium bicarbonate, and the peptide sample obtained after freeze-drying was subjected to formaldehyde dimethylation to seal the N-terminal amino group. For every 100 μg of peptide, 15 μl of 4% formaldehyde solution and 15 μl of 0.6 mM sodium cyanoborohydride were added, reacted for 0.5 hou...
Embodiment 3
[0042] In order to investigate the influence of the quaternary ammonium salt modification group on the mass spectrometry signal, the above-mentioned Girard reagent T-labeled peptide was used to investigate the signal response of the mass spectrometry of the two ion sources, MALDI and ESI:
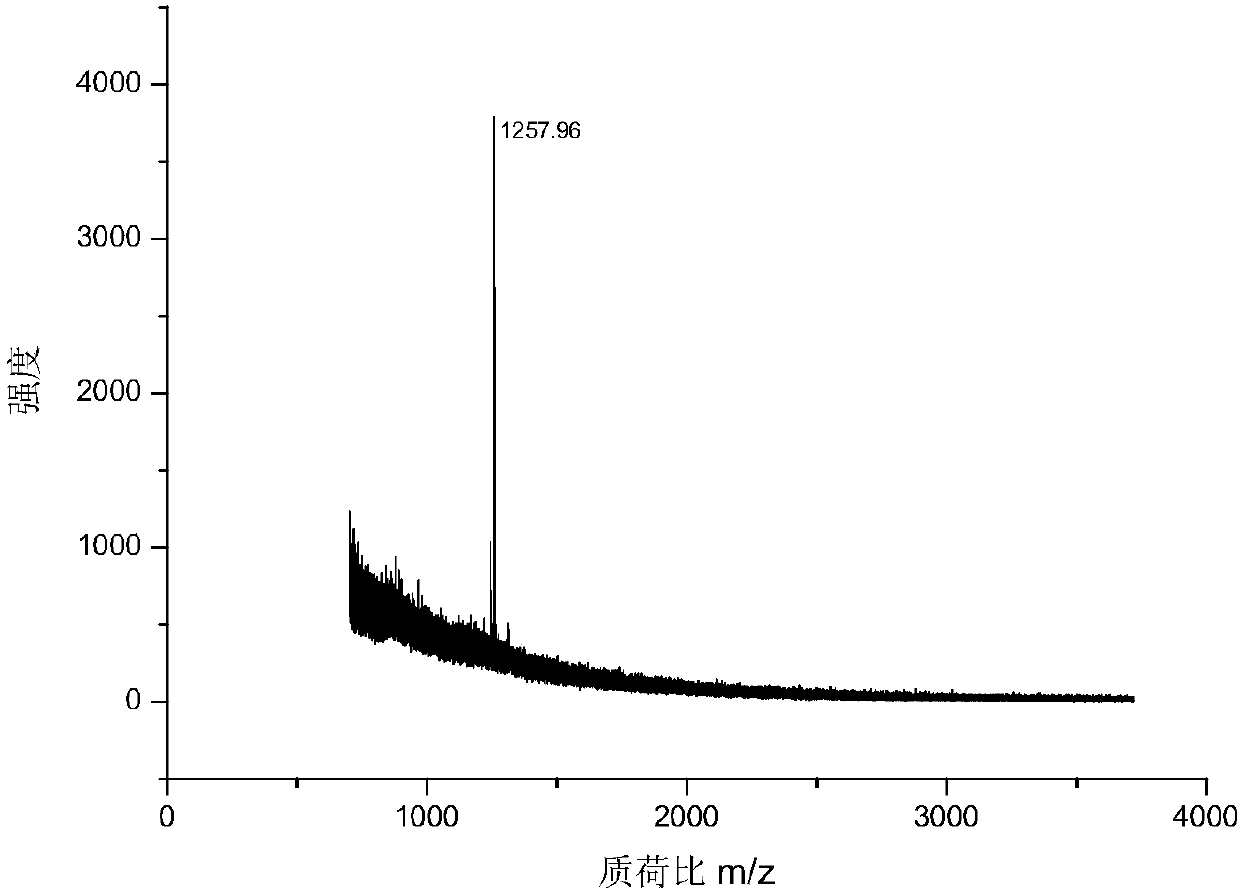
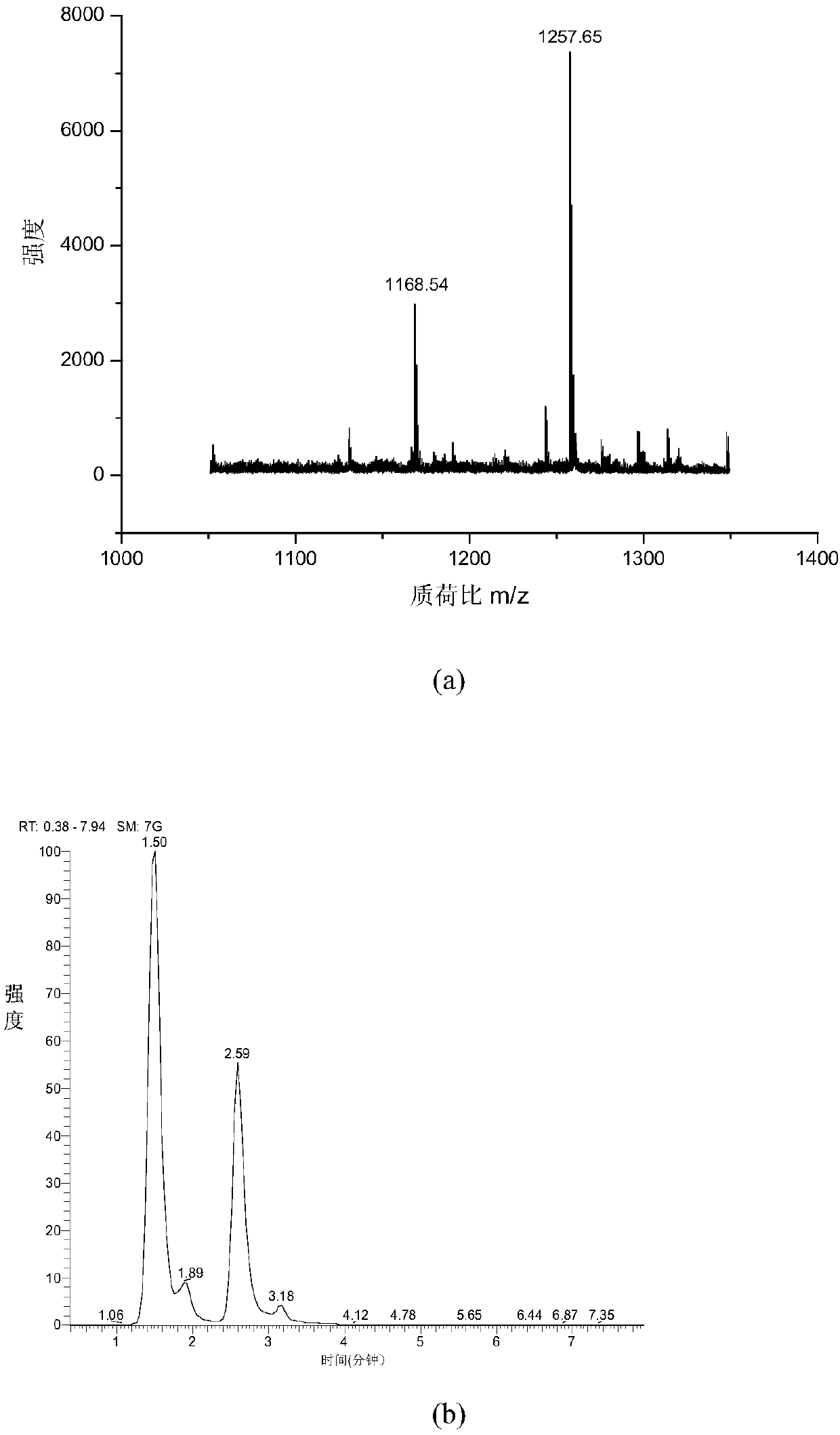
[0043] 1. MALDI mass spectrometry response: Mix the chemically derivatized standard peptide and the dimethylated blocked standard peptide at a ratio of 1:5, and use MALDI mass spectrometry to analyze the spectrum. image 3 (a), combined with the molar ratio, the MS signal is enhanced by about 10 times after derivatization,
[0044] 2. ESI mass spectrometry response: The chemically derivatized standard peptide and the dimethylated blocked standard peptide were mixed 1:1, and analyzed by RP-ESI-LTQ. The spectrum is as follows image 3 (b), the MS signal is enhanced about 2.2 times after derivatization.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com