Synthetic library of specific binding molecules
A technology for binding molecules and antigen-binding molecules, applied in specific peptides, drug combinations, analytical materials, etc., can solve the problem of lack of shark species or isotype recognition reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0415] Example 1: Construction of a sequence database from the VNAR of Squalusacanthias (spiny dogfish)
[0416] RNA was isolated from spiny dogfish tissue using a variety of molecular biology techniques, as detailed below.
[0417] Isolation of RNA from Tissue: Total RNA was isolated from shark tissue using Invitrogen's TRIzol reagent (SigmaAldrich, Cat. No. 15596). Approximately 50-100 mg of tissue was homogenized in 1 ml of TRIzol reagent using a standard power homogenizer. Homogenized samples were incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes to allow complete dissociation of nucleoprotein complexes, after which 0.2 ml chloroform was added per ml TRIzol used. Shake the tube vigorously by hand for 15 seconds, then centrifuge at 12,000 x g for 15 minutes at 4°C. After centrifugation, transfer the aqueous phase containing RNA to a new tube and add 1 ml of 75% ethanol or optionally 0.5 ml of isopropanol per ml of TRIzol in the initial step and incubate the sample at room tem...
Embodiment 2
[0437] Embodiment 2: Sequence (Sequence), expression of 2V and 5V spiny dogfish VNAR domain and crystallization
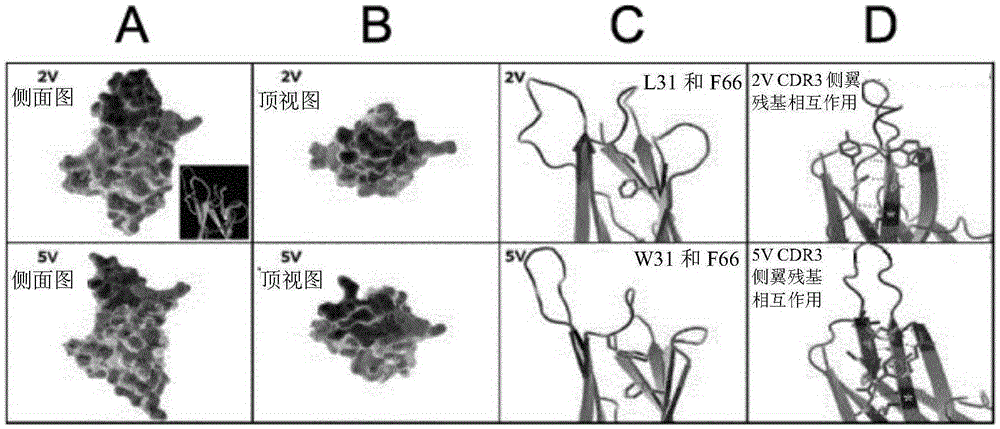
[0438] will clone 2V and 5V ( Figure 9 The sequence shown) was cloned into the phagemid display vector pWRIL-1 (Finlay, W.J., et al., J Mol Biol, 2009. 388(3): p.541-58) and showed a high level of bacterial expression. For crystallization experiments, both proteins were transiently expressed in HEK293 cells and purified by Nickel capture followed by Superdex200. Briefly, conditioned medium was adjusted to 50 mM Tris pH 8.5 before being loaded onto a 15 ml bed of Nickel resin, followed by serial washes with Tris 20 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole 0-20 mM. Gradient elution of protein in Tris20mMNaCl20-150mM imidazole. The pooled protein was diluted with 25mMMES, 25MmHEPES pH6.8 and passed through a Superdex20016 / 20300ml bed column. Tris20mM, NaCl20mMpH8.0 dialyzed, 2V and 5V protein solutions were concentrated to 10mg / ml and 19mg / ml respectively. Hanging drop exper...
Embodiment 3
[0439] Example 3: ELSS1 Synthetic Library Design
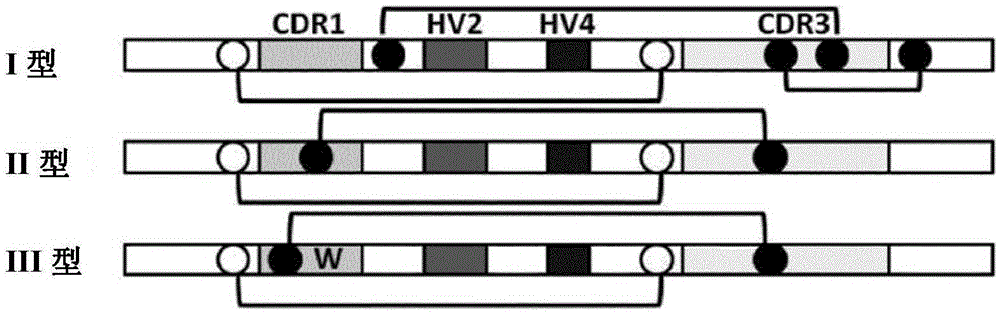
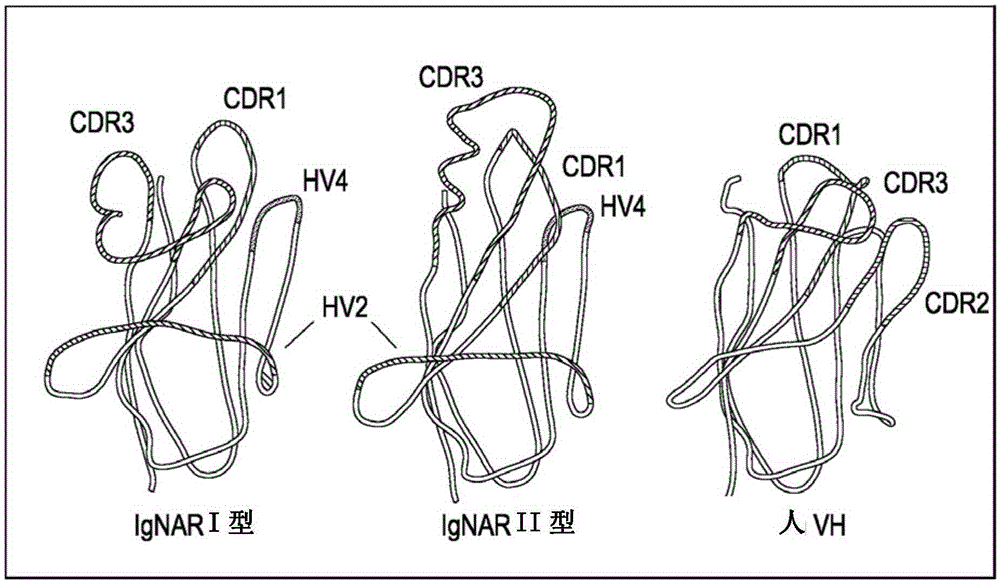
[0440] A comprehensive "native" spiny dogfish VNAR (AA) sequence database was prepared using PCR amplified cDNA as described above, consisting of full length specific cDNA VNAR clones from a range of different spiny dogfish species and tissue types. The (AA) content of compiled and translated VNAR domains, relative site conservation and frequency across analyzed populations other than the CDR3 length distribution were examined. This analysis was used to guide synthetic library design. Starting with the CDR1 and CDR3 loops, we examined the content, adjacent framework residues, and loop length range and distribution across these loops. The sequences in the database were binned into specific clones according to the length (n≥100) pool. Overall CDR3 loop lengths in the range of 11 to 16 amino acids were focused on because they corresponded to our defined average spiny dogfish CDR3 length of 13 ± 2 amino acids. Specific conten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com