Preparation method of 2,4-dihydroxyphenyl acetic acid
A technology of dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and hydroxyphenylacetic acid, applied in the field of preparation of 2,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, can solve the problems of low reaction yield, polluted environment, difficult separation and recycling of by-products, etc., and achieves the preparation route Brief, mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
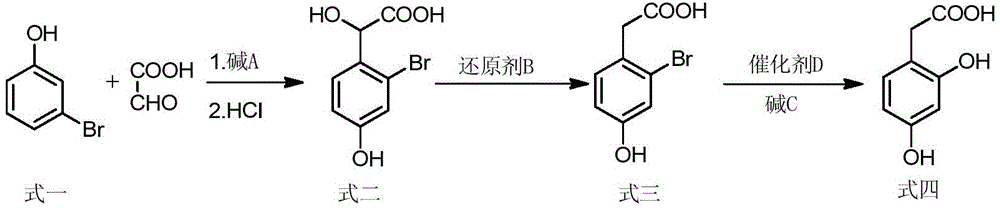
[0024] Example 1: Synthesis of 2-bromo-4-hydroxymandelic acid
[0025] Add sodium hydroxide solution (43.2g, 1.08mol) and glyoxylic acid monohydrate aqueous solution (79.5g, 0.86mol) to m-bromophenol (124.6g, 0.72mol) at the same time in a water bath at 40°C, stir and react for 8h . After the reaction is complete, add about 90 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 1. Wash with toluene (100ml×3, that is, use 100ml each time, wash three times in total), extract with ethyl acetate (100ml×3), combine the organic layers and spin dry to obtain a light yellow viscous product, 2-bromo-4 -138.73g of hydroxymandelic acid, with a yield of 78.0%.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: Synthesis of 2-bromo-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid
[0027] Add stannous chloride dihydrate (112.8g, 0.50mol) and 230ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid to 2-bromo-4-hydroxymandelic acid (111.17g, 0.45mol), stir, and react in an oil bath at 80°C for 3h. After the reaction is complete, pour it into a beaker and heat it until the solid is completely dissolved. After standing and cooling at room temperature, a solid was precipitated, filtered with suction, washed with water (100ml×3), and recrystallized with water to obtain 90.10 g of 2-bromo-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid as a white solid with a yield of 86.7%.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3: Preparation of 2,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
[0029] Add 8-hydroxyquinoline copper (10.56g, 0.03mol) and a 10% aqueous solution containing 120g and 3mol sodium hydroxide to 2-bromo-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (69.31g, 0.30mol), stir and heat to 110°C , Reaction 6h. After the reaction is complete, cool to room temperature, filter, acidify the filtrate with dilute hydrochloric acid to pH=3, extract with ethyl acetate (100ml×3), combine the organic layers, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, spin dry the organic solvent, and recrystallize with ethanol 40.87 g of 2,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid was obtained as a light yellow solid, with a yield of 81%.
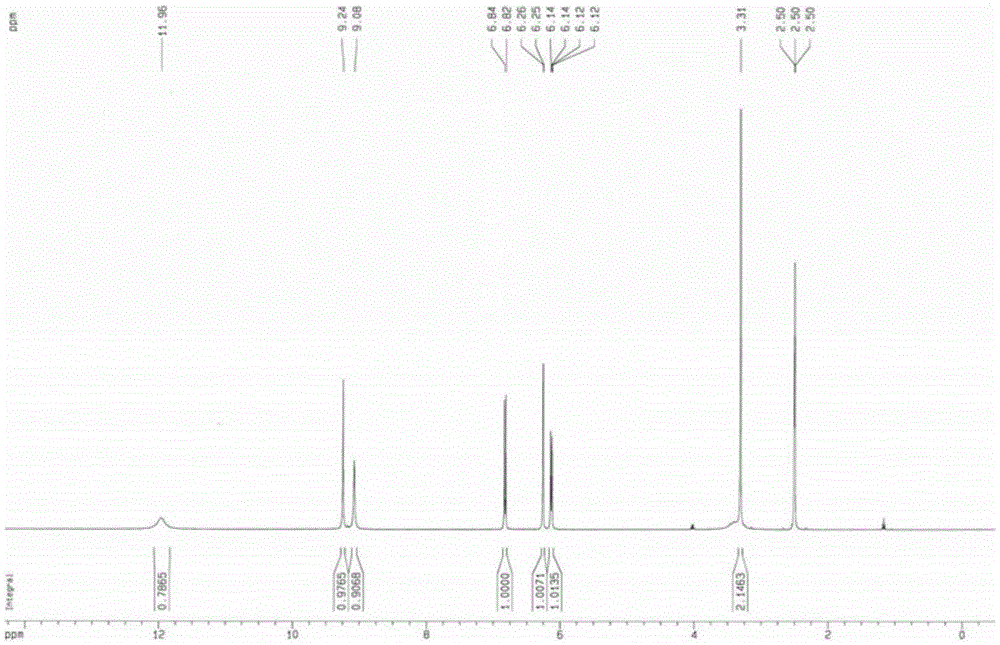
[0030] 1 HNMR(400MHz,DMSO-d 6 ,ppm)δ11.96(s,1H),9.24(s,1H),9.08(s,1H),6.83(d,J=8.0Hz,1H), 6.25(d,J=2.0Hz,1H), 6.13(dd,J 1 =8.0Hz,J 2 =2.0Hz, 1H), 3.31(s, 2H) (such as figure 1 Shown).
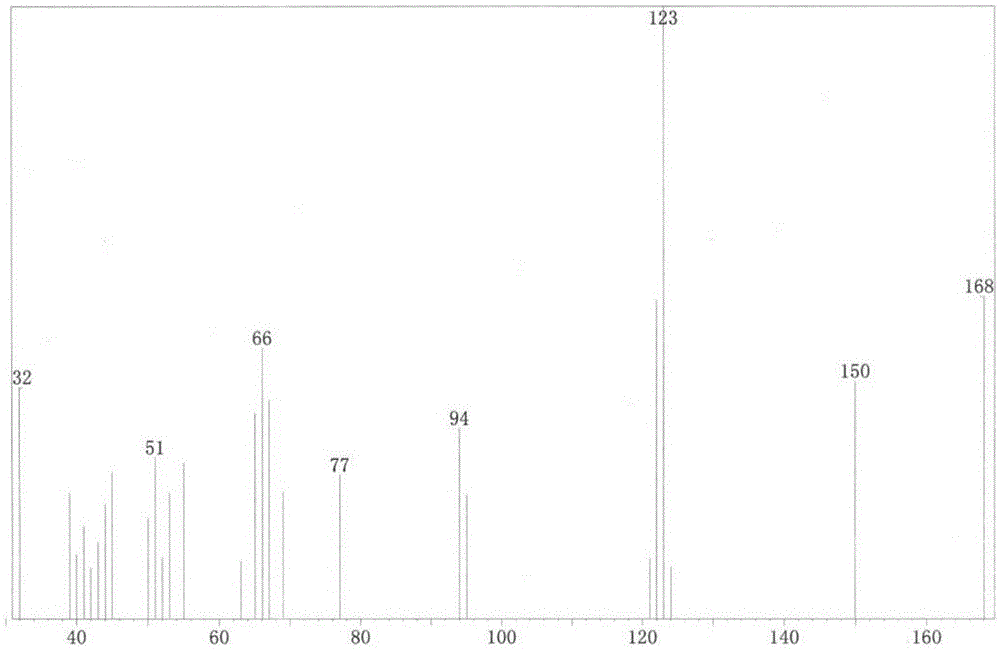
[0031] MS-EI: 32, 51, 66, 77, 94, 123, 150, 168 (such as figure 2 Shown).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com