Method for producing industrial monoammonium phosphate through fluoride salt purification method
A technology of monoammonium phosphate and fluoride, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphate, phosphorus oxyacids, etc., can solve problems such as high cost of modifiers, affecting product quality, and ineffective use of waste residues, etc., to achieve product Low cost, improved purity and water solubility, less impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A method for producing monoammonium phosphate by a fluoride salt purification process, comprising the steps of:
[0039] (1) Take 1000 kg of wet-process phosphoric acid, first add 40 kg of phosphate rock powder, stir at 60°C for 1 hour, and separate liquid and solid to obtain 34 kg of desulfurized phosphoric acid and phosphogypsum.
[0040](2) Add 14.84 kg of sodium carbonate to the desulfurized phosphoric acid and react for 2 hours to separate the liquid from the solid to obtain 968.5 kg of desulfurized defluorophosphoric acid and 15.84 kg of sodium fluorosilicate. The obtained phosphoric acid analysis results are as follows, all in mass percent.
[0041] P 2 o 5 %24.53; MgO%1.4811; Al 2 o 3 %0.5119; CaO%0.2295; Fe 2 o 3 %0.1268; SO 4 2- %0.79, SiO 2 %0.0257;F - %0.52;
[0042] (3) Add 58 kg of 20% aqueous ammonia to the sodium fluorosilicate prepared in step (2), and react at 40° C. for 1 hour to obtain 40 kg of fluoride salt scavenger and 5 kg of silicon d...
Embodiment 2
[0046] As described in Example 1, the difference is:
[0047] In step (4): Into the desulfurized and defluorinated phosphoric acid prepared in step (2), pass through ammonia gas to neutralize until the pH is stabilized at 2.5-3.0, then add the fluoride salt prepared in step (3) to neutralize to pH = 3.8, 785 kg of liquid was obtained by liquid-solid separation, and the analyzed components are as follows, all in mass percent.
[0048] P 2 o 5 %22.72; MgO%0.4105; Al 2 o 3 %0.0052; CaO%0.0611; Fe 2 o 3 %0.028; SO 4 2- %0.80; SiO 2 %0.1021;
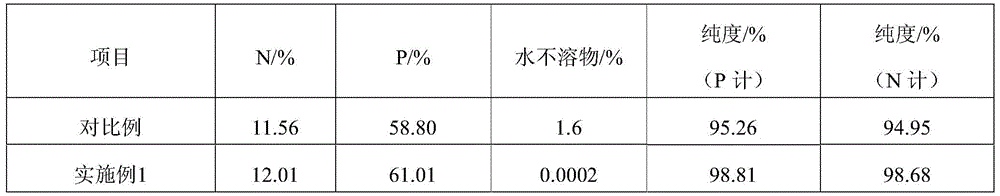
[0049] In step (5): get 100 kilograms of monoammonium solution of step (4) and add 0.5% complexing agent to concentrate to a concentration of about 40%, crystallize at 30 DEG C after 4 hours of liquid-solid separation, and obtain 21.80 kilograms of industrial monoammonium phosphate The liquid is evaporated and dried to obtain 18.21 kilograms of water-soluble fertilizers. The nutrients of industrial monoammonium phosphate are: N% 11...
Embodiment 3
[0051] As described in Example 1, the difference is:
[0052] In step (4): Into the desulfurized and defluorinated phosphoric acid prepared in step (2), pass through ammonia gas to neutralize until the pH is stabilized at 2.5-3.0, then add the fluoride salt prepared in step (3) to neutralize to pH=3.4, 796 kg of liquid was obtained by liquid-solid separation, and the analyzed components are as follows, all in mass percentage.
[0053] P 2 o 5 %22.83; MgO%0.5061; Al 2 o 3 %0.0112; CaO%0.0865; Fe 2 o 3 %0.032; SO 4 2- %0.82; SiO 2 %0.1002;
[0054] In step (5): get 100 kilograms of step (4) monoammonium solution and add 0.5% complexing agent to concentrate to a concentration of about 40%, crystallize at 40 DEG C for 3 hours after liquid-solid separation, and obtain 22.16 kilograms of industrial monoammonium phosphate ; The liquid is evaporated and dried to obtain 18.08 kilograms of water-soluble fertilizers. The nutrients of industrial monoammonium phosphate are: N% 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com