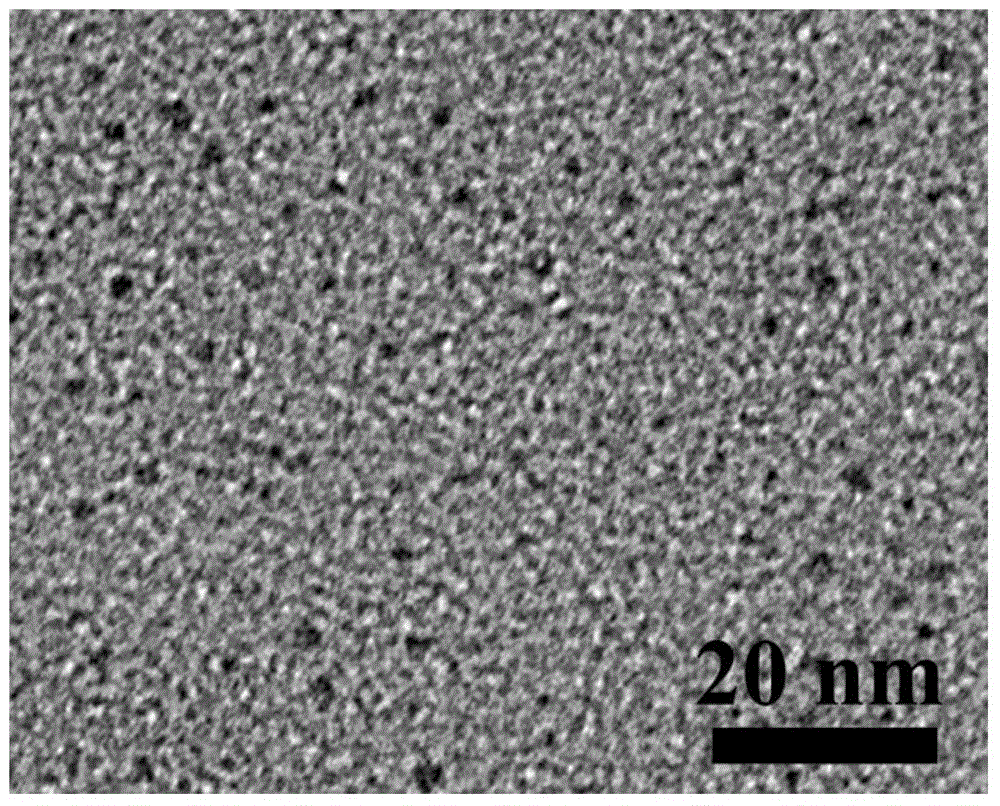
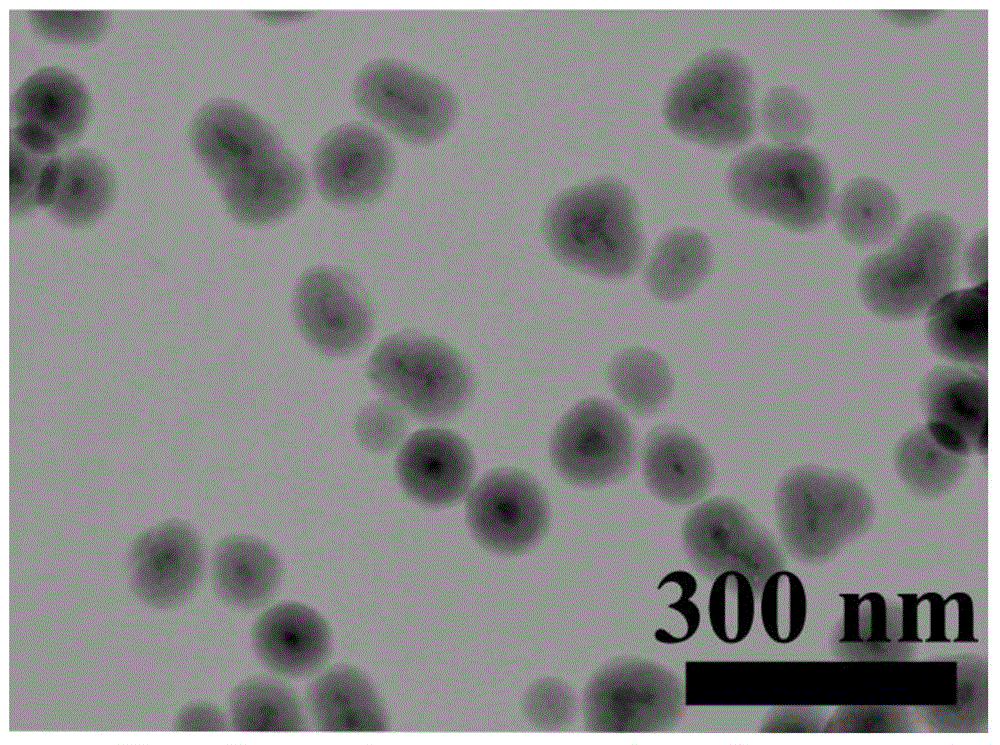
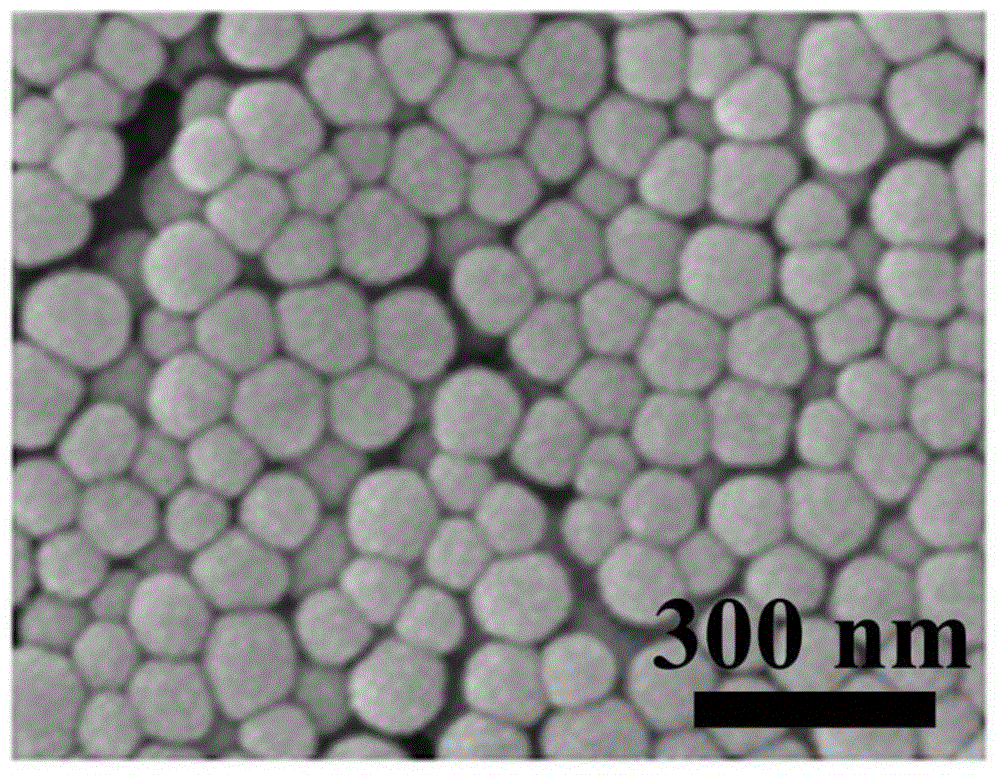
Simple and green preparation method for monodisperse core-shell-structured C-dots@SiO2 fluorescence imaging nanoprobe
A technology of fluorescence imaging and core-shell structure, which is applied in the field of nanocomposite materials and its applications, can solve the problems of complex synthesis methods, cytotoxicity, and toxic drugs, and achieve simple synthesis methods, easy centrifugation and washing, and good biocompatibility sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] First, 3 g of citric acid and 3 g of urea were uniformly mixed in 10 mL of deionized water. The above solution was then placed in a 700 W microwave for 5 min, followed by heating at 60 °C in vacuo for 1 h. Centrifuge at 3000rpm for 20min to remove large particle impurities, and take out the upper layer liquid for later use.
[0027] Take 350 μL of the above C-dots solution, add to 10mL PAAS aqueous solution (2gL -1 ), followed by adding 50 mL of ethanol and stirring for 30 min. Take the solution obtained in the above steps, add 180mL ethanol and 70mLNH 3 ·H 2 O (2M), after stirring evenly, add 20% TEOS solution (prepared with ethanol) several times, and react at 40°C for 2h. (First, add 100 μLTEOS, then add 100 μL after 40 minutes, and add 200 μL to the remaining 800 μLTEOS every 20 minutes) Finally, the obtained mixed solution is centrifuged, and the obtained solid is alternately washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol to obtain C-dotsSiO 2...
Embodiment 2
[0029] First, 6 g of citric acid and 8 g of urea were uniformly mixed in 15 mL of deionized water. The above solution was then placed in a microwave at 850W for 20min, followed by heating at 80°C in vacuum for 1.5h. Centrifuge at 3000rpm for 20min to remove large particle impurities, and take out the upper layer liquid for later use.
[0030] Take 500 μL of the above C-dots solution, add to 20mL PAAS aqueous solution (2gL -1 ), followed by adding 100mL of ethanol and stirring for 45min. Take the solution obtained in the above steps, add 100mL ethanol and 50mLNH 3 ·H 2 O (2M), after stirring evenly, add 20% TEOS solution (prepared with ethanol) several times, and react at 45°C for 2.5h. (First, add 250 μLTEOS, then add 250 μL after 40 minutes, and add 300 μL to the remaining 2000 μLTEOS every 20 minutes) Finally, the obtained mixed solution is centrifuged, and the obtained solid is alternately washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol to obtain C-dotsS...
Embodiment 3
[0032] First, 8 g of citric acid and 10 g of urea were uniformly mixed in 20 mL of deionized water. The above solution was then placed in a 1000 W microwave for 10 min, followed by heating at 100 °C in vacuum for 2 h. Centrifuge at 6000rpm for 20min to remove large particle impurities, and take out the upper layer liquid for later use.
[0033] Take 500 μL of the above C-dots solution, add to 20mL PAAS aqueous solution (2gL -1 ), followed by adding 100mL of ethanol and stirring for 60min. Take the solution obtained in the above steps, add 150mL ethanol and 100mL NH 3 ·H 2O (2M), after stirring evenly, add 25% TEOS solution (prepared with ethanol) several times, and react at 50°C for 3h. (First, add 400 μLTEOS, then add 400 μL after 40 minutes, and add 700 μL to the remaining 2800 μLTEOS every 20 minutes) Finally, the obtained mixed solution is centrifuged, and the obtained solid is alternately washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol to obtain C-dots...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com