Microorganism having detoxifizyme activity and with fermentation residues applicable to feed
A technology for detoxifying enzymes and recombining microorganisms, applied in the field of microorganisms, which can solve problems such as waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Construction of a yeast strain derived from aflatoxin detoxification enzyme from Peniophorasp.
[0069] According to the reported detoxification enzyme sequence from Peniophora sp. aflatoxin (International Journal of Food Microbiology 135 (2009) 47-52), the complete ORF sequence (Genbank Y18012) encoding aflatoxin detoxification enzyme was synthesized by the method of whole gene synthesis.
[0070] Using the Gibsonassembly method, the aflatoxin degradation gene was ligated into the pCpA1 / G-XI vector (Diao et al. BMC Biotechnology 2013, 13:110) and replaced with the XI gene in the pCpA1 / G-XI vector, and the obtained plasmid was named pCpA1-HQ1. The sequence was confirmed to be correct by sequencing. The aflatoxin detoxification enzyme gene is located between the TPI1 promoter and the CYC1 terminator.
[0071] Transform pCpA1-HQ1 into Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCTCCM94055 (CCTCC is China Center for Type Culture Collection), so as to obtain dozens of yeast strain transform...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Yeast with aflatoxin detoxifying enzyme activity of Peniophorasp. can ferment (enzyme change) grain into ethanol
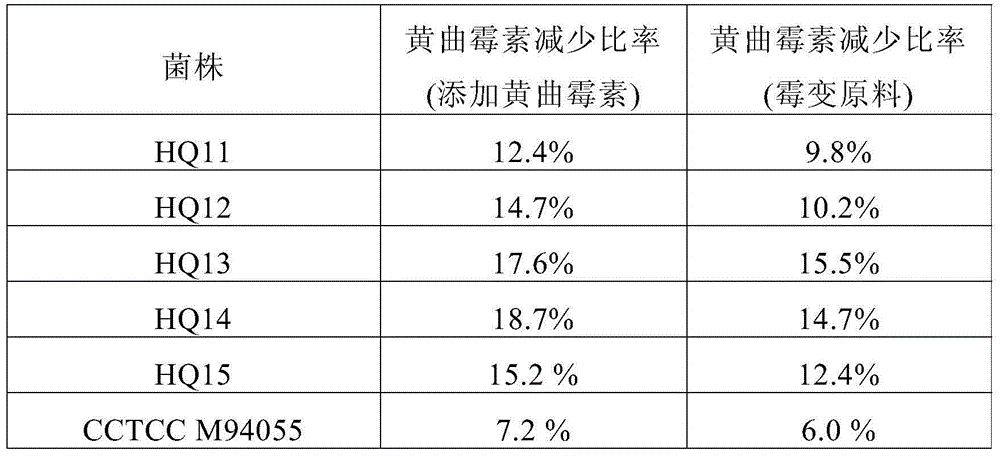
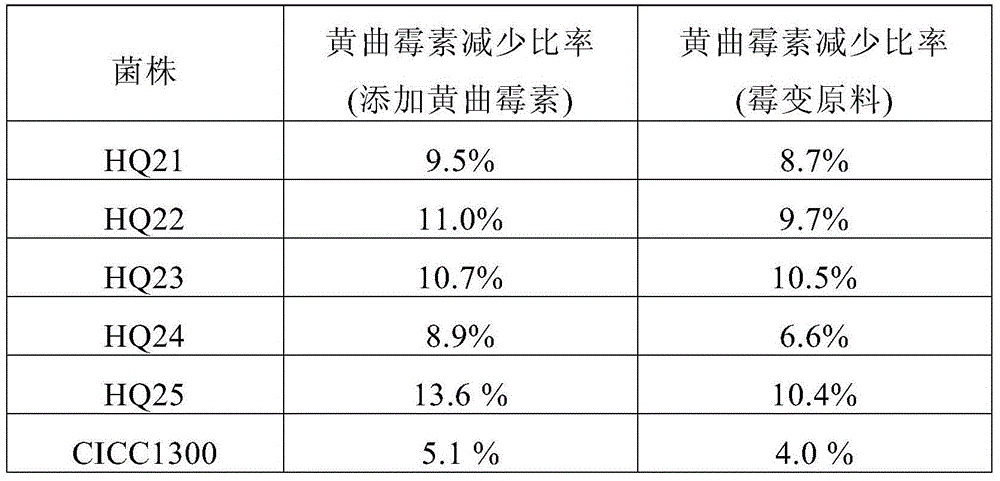
[0075] The five transformants HQ11, HQ12, HQ13, HQ14, HQ15 constructed in Example 1 and the control strain CCTCCM94055 were used for ethanol fermentation respectively.
[0076] The raw materials with no aflatoxin detected were prepared according to the literature (Research on the Production of Ethanol by Fermentation of Corn Raw Meal, Food and Fermentation Industry, Issue 02, 2008), and the shake flask test of fermentation to produce ethanol was carried out. Before the start of fermentation, 10 mg / L aflatoxin was added to the medium. After 96 hours of fermentation, the ethanol output of each strain was basically the same, and the utilization rate of starch was between 85% and 90%.
[0077] The content of aflatoxin B1 was detected before and after fermentation. As shown in Table 1, the aflatoxin in the control strain group only decreased by 7.2%, which may...
Embodiment 3
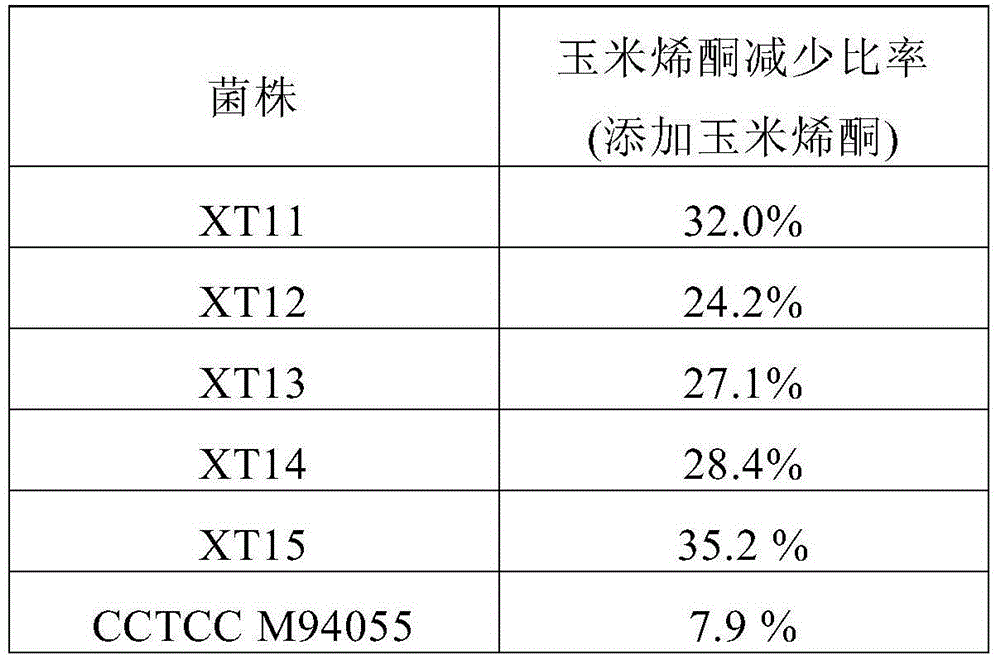
[0083] Aflatoxin detoxification enzyme activity of residual bacteria after fermentation
[0084] Take 10 mg of wet yeast cells obtained by fermenting with moldy raw materials in Example 2, and resuspend in 800 μL of PBS buffer. Take 200μL aflatoxin B1 (500ppm) for reaction.
[0085] The blank control group was 800 μL PBS buffer. Take 200μL aflatoxin B1 PBS solution (500ppm) for reaction.
[0086] After each treatment was reacted at 35 degrees for 5 hours, the concentration of aflatoxin was determined.
[0087] As can be seen from Table 2, after the treatment of each bacterial strain, aflatoxins were all reduced. But the control strain had the smallest reduction, probably only by physical adsorption. When the yeast cell with aflatoxin detoxification enzyme gene was treated with aflatoxin, the reduction of aflatoxin was higher than that of the control strain. It shows that the aflatoxin detoxification enzyme in the bacteria has played a role.
[0088] The effect of table 2 t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com