Method for fermenting starchy raw material with mixed strain to produce hydrogen
A technology of starchy raw materials and mixed strains, applied in microorganism-based methods, fermentation, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve difficult hydrogen production process amplification, industrial application, nutrient conditions, growth environment and process parameter regulation requirements Very high, affecting the effect of hydrogen production, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
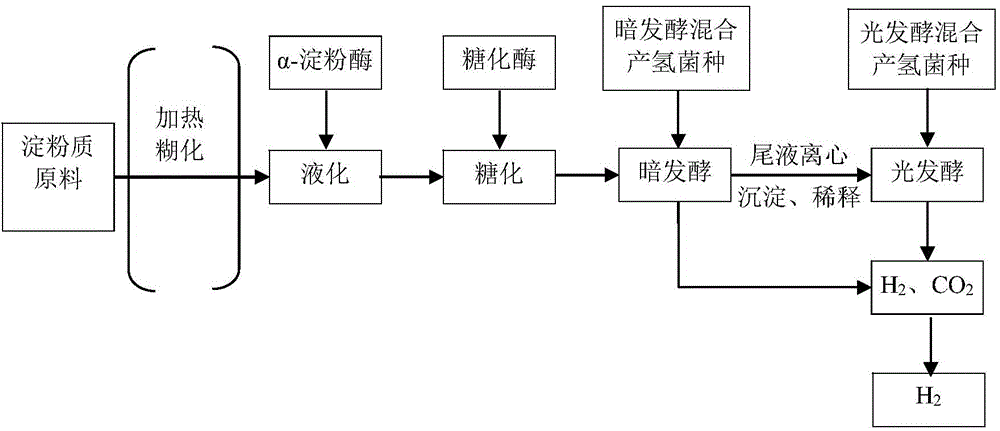
[0127] Among them, Δt is the increment (h) at time t, and when Δt approaches 0, it is the hydrogen production rate at time t. When calculating the maximum hydrogen production rate, the hydrogen production curve is made according to the total hydrogen production at different times, and then the curve is derived to obtain the hydrogen production rate at different times, and the maximum hydrogen production rate can be obtained accordingly. Embodiment 1: Utilize mixed strain, carry out two-step method fermentation to produce hydrogen to cassava starchy raw material
[0128] The cassava starch solution with a concentration of 10 g / L was placed in a high-pressure steam cooker at 115° C., and heated and gelatinized for 15 minutes. Then proceed as follows:
[0129] (1) Liquefaction: Add α-amylase to the cassava starch solution after heating and gelatinizing in step (1) for liquefaction; the mass ratio of the added α-amylase to tapioca starch is 0.05, and the control liquefaction temp...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Example 2: Using mixed strains to carry out two-step fermentation of corn starch raw materials to produce hydrogen
[0136] The cornstarch solution with a concentration of 20g / L was placed in a high-temperature oven at 120°C, and heated for gelatinization for 10 minutes. Then proceed as follows:
[0137] (1) Liquefaction: Add α-amylase to the corn starch solution after heating and gelatinizing in step (1) for liquefaction; the mass ratio of the added α-amylase to corn starch is 0.03, and the liquefaction temperature is controlled to be 58°C , the liquefaction pH is 6.2, and the time is 4 hours.
[0138] (2) Saccharification: Add glucoamylase to the solution liquefied in step (1) for saccharification, after saccharification, inactivate the glucoamylase by heating at 100°C for 10 minutes; the mass ratio of the added glucoamylase to starch is 0.03, the saccharification temperature is controlled at 40°C, the saccharification pH is 4.3, and the time is 16 hours.
[0139] ...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Example 3: Using mixed strains to carry out two-step fermentation of wheat starchy raw materials to produce hydrogen
[0144] Place the wheat starch solution with a concentration of 30 g / L in a high-pressure steam cooker at 105° C., and heat and gelatinize for 25 minutes. Then proceed as follows:
[0145] (1) Liquefaction: Add α-amylase to the wheat starch solution after heating and gelatinizing in step (1) for liquefaction; the mass ratio of the added α-amylase to wheat starch is 0.03, and the controlled liquefaction temperature is 62°C , the liquefaction pH is 5.8, and the time is 1.5 hours.
[0146] (2) Saccharification: Add glucoamylase to the solution liquefied in step (1) for saccharification, after saccharification, inactivate the glucoamylase by heating at 100°C for 10 minutes; the mass ratio of the added glucoamylase to starch is 0.03, the saccharification temperature is controlled at 58°C, the saccharification pH is 4.5, and the time is 20 hours.
[0147] (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com