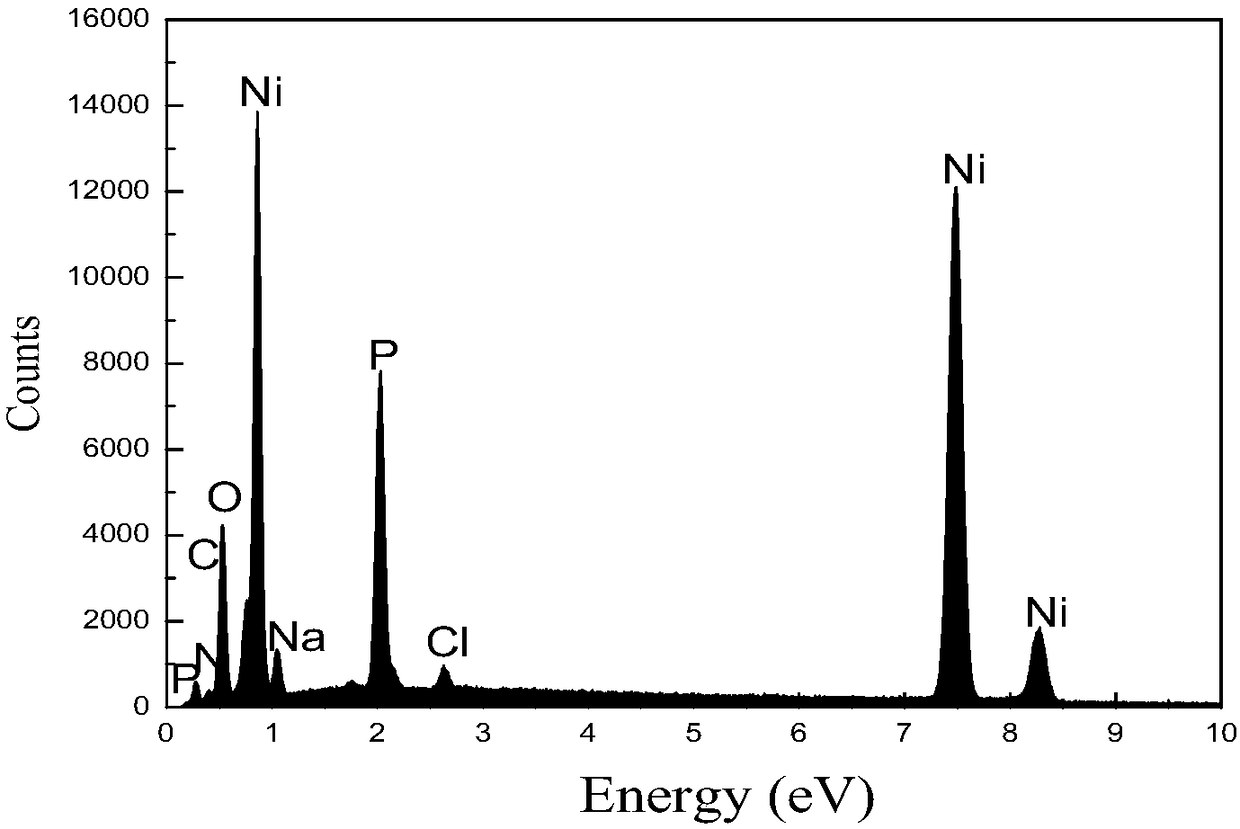
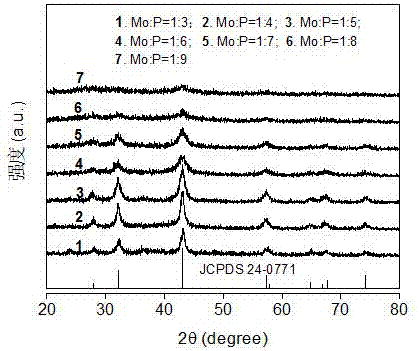
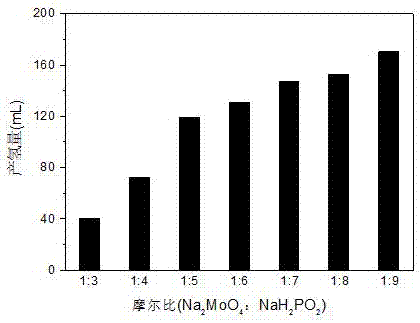
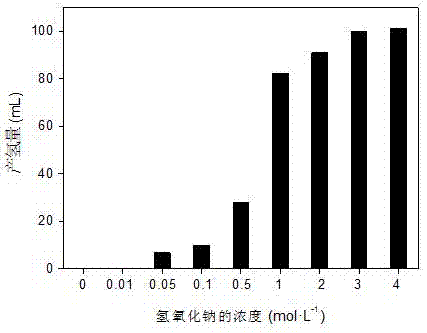
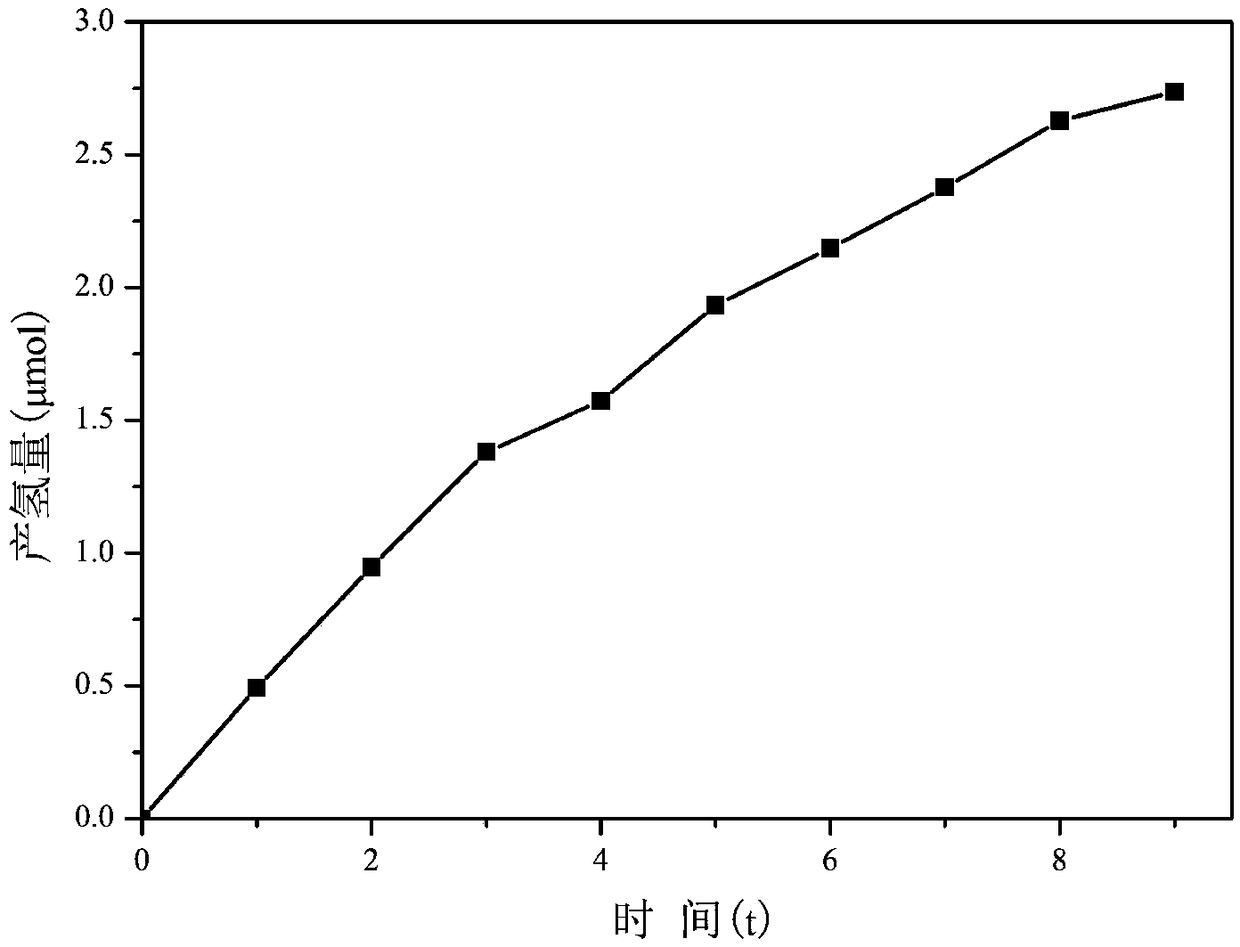
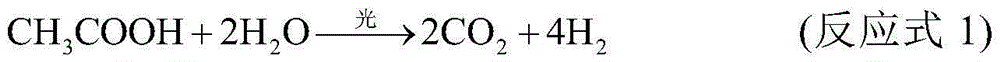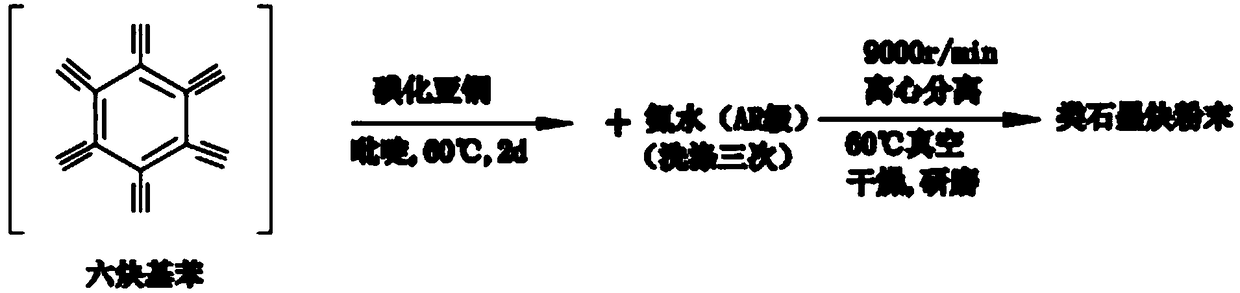Patents
Literature
140results about How to "Increase the rate of hydrogen production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
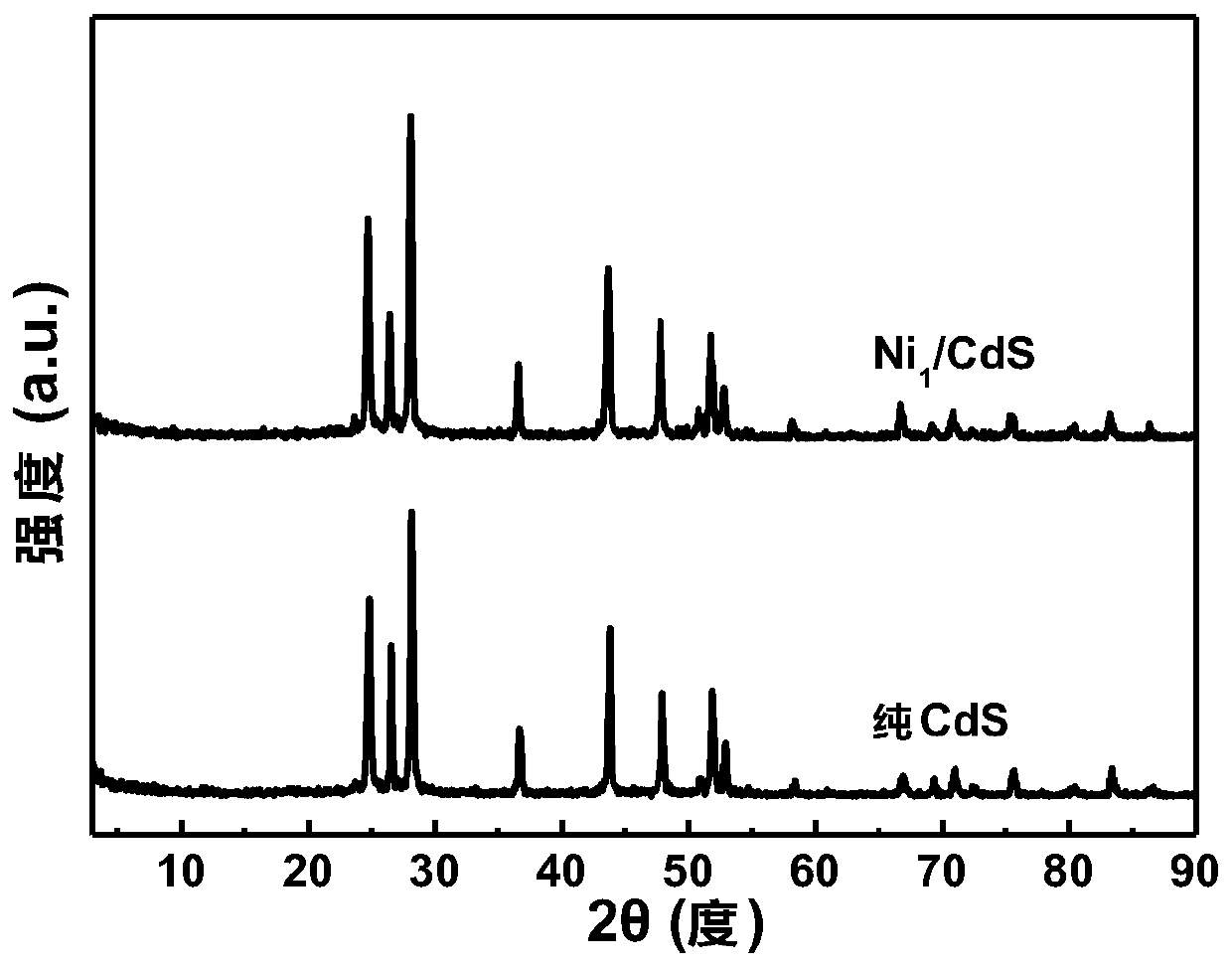
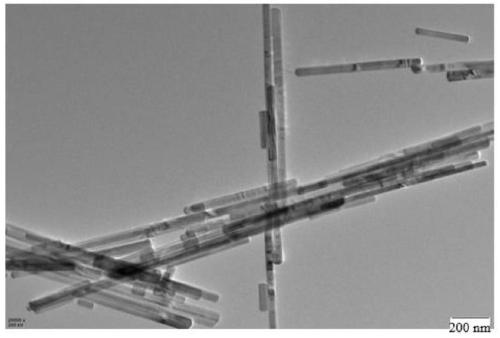
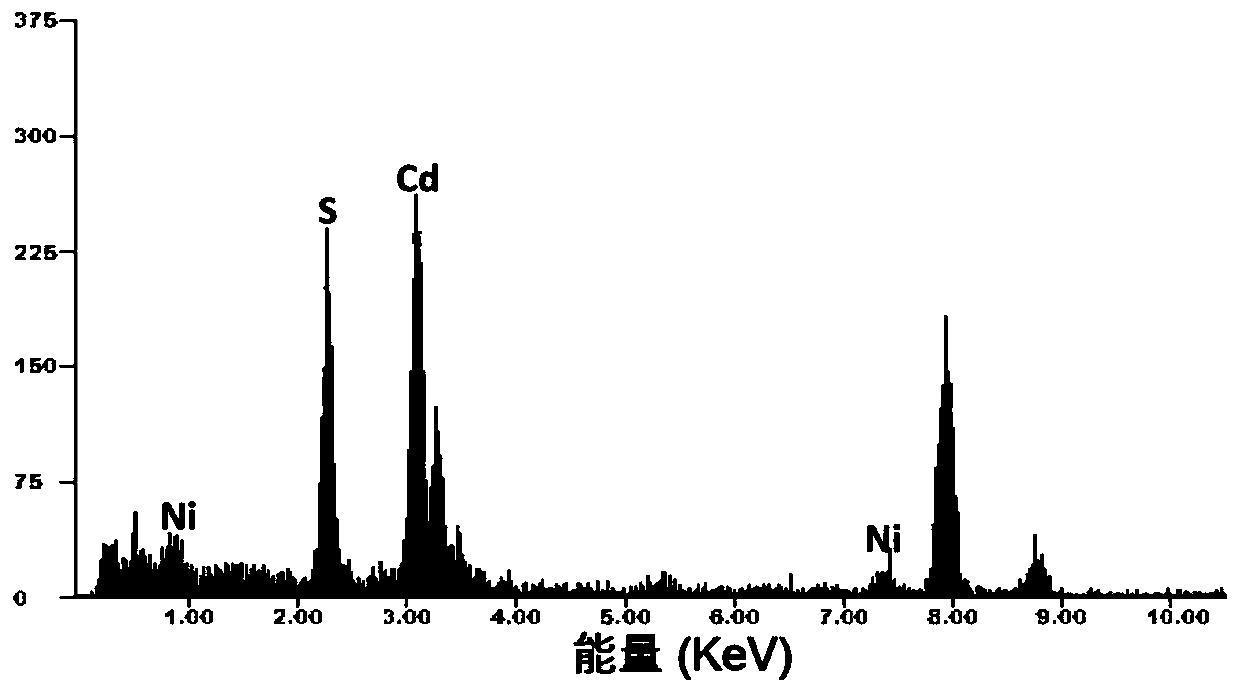
Preparation method and application of non-noble metal monoatomic catalyst
ActiveCN110449176AReduce manufacturing costLow costCellsPhysical/chemical process catalystsChemical industryNon noble metal
Belonging to the technical field of chemistry, chemical industry and material science, the invention discloses a preparation method and application of a non-noble metal monoatomic catalyst. The invention adopts cheap raw materials and simple method to prepare the monoatomic catalyst. In essence, under a lighting condition, a metal is anchored on a light absorption carrier in a monatomic state formto generate the monoatomic catalyst. The invention for the first time utilizes a photochemical synthesis route to prepare the transition metal monoatomic catalyst. The monoatomic catalyst synthesizedby method provided by the invention is dispersed on the surface of an optical active substance. Nickel single atom is adopted as the cocatalyst for photocatalytic decomposition of water to hydrogen,the price is low, and the catalytic efficiency is greatly improved. Compared with other types of non-noble metal modified composite photocatalysts, the non-noble metal monoatomic catalyst has higher photocatalytic activity.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing hydrogen by alkalescent microbe electrolysis
InactiveCN102400169AInhibitionReduce methane contentWater/sewage treatmentEnergy based wastewater treatmentGeneration rateBatch operation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe electrochemistry and aims to provide a method for producing hydrogen by alkalescent microbe electrolysis. The method comprises steps of: (1) starting an electrolytic bath under a microbiological fuel cell mode: accessing a resistor in a closed-loop of a system and replacing a solution in the electrolytic bath when a voltage is low; continuing to replace until voltages at two ends of the resistor are higher than 500mV to finish anode starting; (2) producing hydrogen under a microbe electrolytic bath mode: replacing a cathode in the started electrolytic bath with stainless steel net or foamed nickel, keeping solution in the whole electrolytic bath in a anaerobic state and applying 0.4-0.8 V voltage at two ends of the cathode and the anode by using direct-current power supply and realizing hydrogen production of the electrolytic bath at 20-35 DEG C. The invention can effectively inhibit generation of methane, realize long time continuous operation or multiple batch operation and generate gas with low methane content; the method has a low cost and can obtain high hydrogen generation rate; utilization rate of organic matter under an alkalescent environment is increased, and hydrogen generation stability of the system is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing hydrogen by water electrolysis assisted with photocatalysis
InactiveCN102534645AReduce voltageImprove hydrogen evolution efficiencyElectrodesElectrolysed waterHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for producing hydrogen by water electrolysis assisted with photocatalysis. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: based on an industrialized device for producing the hydrogen by the water electrolysis, modifying an anode of an electrolytic cell through photocatalysis material, and adopting a light source to irradiate the anode; and coupling a photocatalysis process in the process of water electrolysis so as to achieve the purpose of producing the hydrogen by the water electrolysis assisted with the photocatalysis. The method is characterized in that the photocatalysis and the water electrolysis are organically coupled together to generate a synergistic effect; the defects of low efficiency of producing the hydrogen by the water photolysis and high power consumption of producing the hydrogen by the water electrolysis are overcome, the voltage of an electrolytic cell is reduced, and the efficiency of hydrogen producing is increased. The method for producing the hydrogen by the water electrolysis assisted with the photocatalysis provided by the invention has simple process and is easy to realize industrialization.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
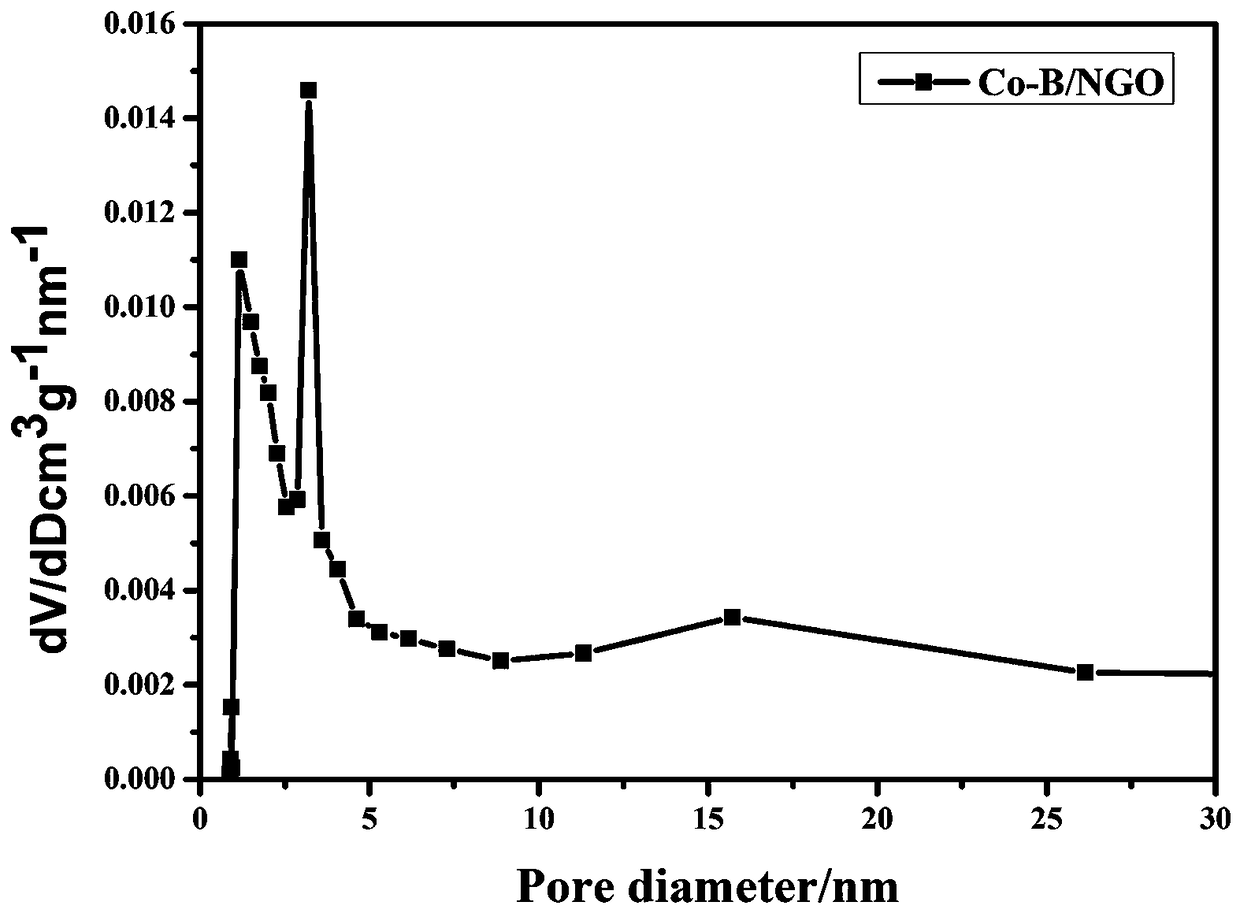
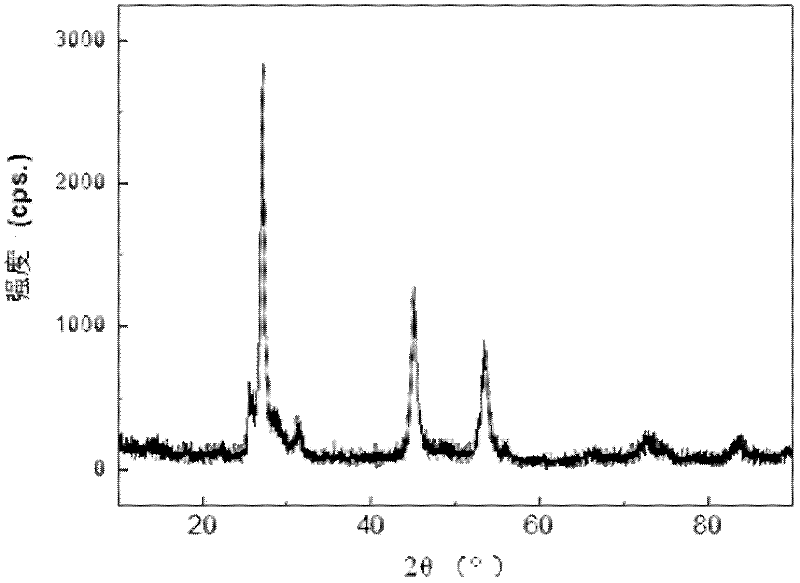
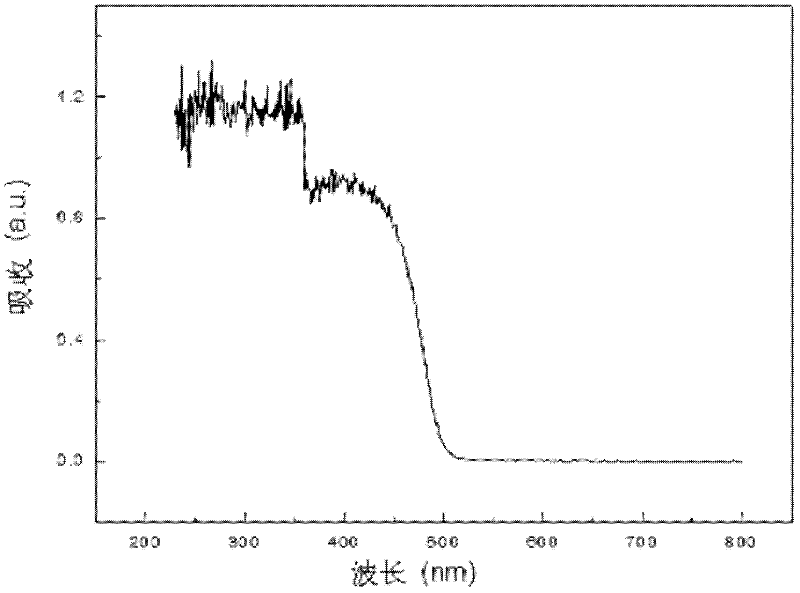
Co-B/NGO composite nanometer material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109499576AChange catalytic performanceLower activation energyMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationFreeze-dryingHydrogen desorption
The invention discloses a Co-B / NGO composite nanometer material. The Co-B / NGO composite nanometer material is prepared by firstly performing in-site reduction on nitrogen-doped graphene and inorganiccobalt salt through sodium borohydride and then performing freezing-drying, the specific area is 40-100 m<2>g<-1>; the material is magnetic, and can be attracted by a magnet. When the composite nanometer material is used as a catalyst for hydroboron hydrogen generation by hydrolysis, the hydrogen desorption rate is 500-1700mL / min<-1>g<-1>, and the hydrogen production rate is 100%; the material canbe adsorbed and recycled by the magnet, the recycling rate reaches 99.5%, and the hydrogen production rate after being circulated is maintained at 100-1530mL min<-1>g<-1>, namely, maintaining 50-85%of the initial hydrogen production rate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) precursor preparation: adding nitrogen-doped graphene and inorganic cobalt salt in an aqueous solutionfor ultrasonic dispersion mixing, reducing by using sodium borohydride, and finally centrifuging and washing to obtain a precursor; 2) preparation of the Co-B / NGO composite nanometer material: freeze-drying the precursor to obtain the Co-B / NGO composite nanometer material. The Co-B / NGO composite nanometer material disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation, has more excellent catalysis performance, and has an extensive application prospect in the application field of the hydroboron hydrogen generation by hydrolysis.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Composite photocatalyst for splitting water to produce hydrogen under visible light and its preparation method
InactiveCN102259030AUniform particle size distributionGood monodispersityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionSpectral responseDecomposition
The invention discloses a composite photocatalyst for hydrogen production by hydrolysis in a visible light and a method for preparing the composite photocatalyst, relates to the composite photocatalyst for the hydrogen production by the hydrolysis and the method for preparing the composite photocatalyst, and solves the technical problems of poor stability of the conventional photocatalyst for thehydrogen production by the hydrolysis in the visible light, low hydrogen-producing speed rate and wide spectral response range. The composite photocatalyst is prepared by Zn(Ac)2.2H2O, Cd(Ac)2.2H2O, a rare earth compound and thioacetamide. The method comprises the following steps of: adding the Zn(Ac)2.2H2O, the Cd(Ac)2.2H2O and the rare earth compound into a solvent, and stirring at the temperature of 60 to 80 DEG C; adding the thioacetamide, continuously stirring to obtain a mixture, and adding the mixture into a reaction kettle for reaction; and cooling, washing and drying to obtain the composite photocatalyst. The hydrogen-producing speed rate of the composite photocatalyst is 360 to 640 mmol.h<-1>.g<-1>. The composite photocatalyst can be applied to hydrogen production by solar hydrolysis.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG PATENT TECH DEV
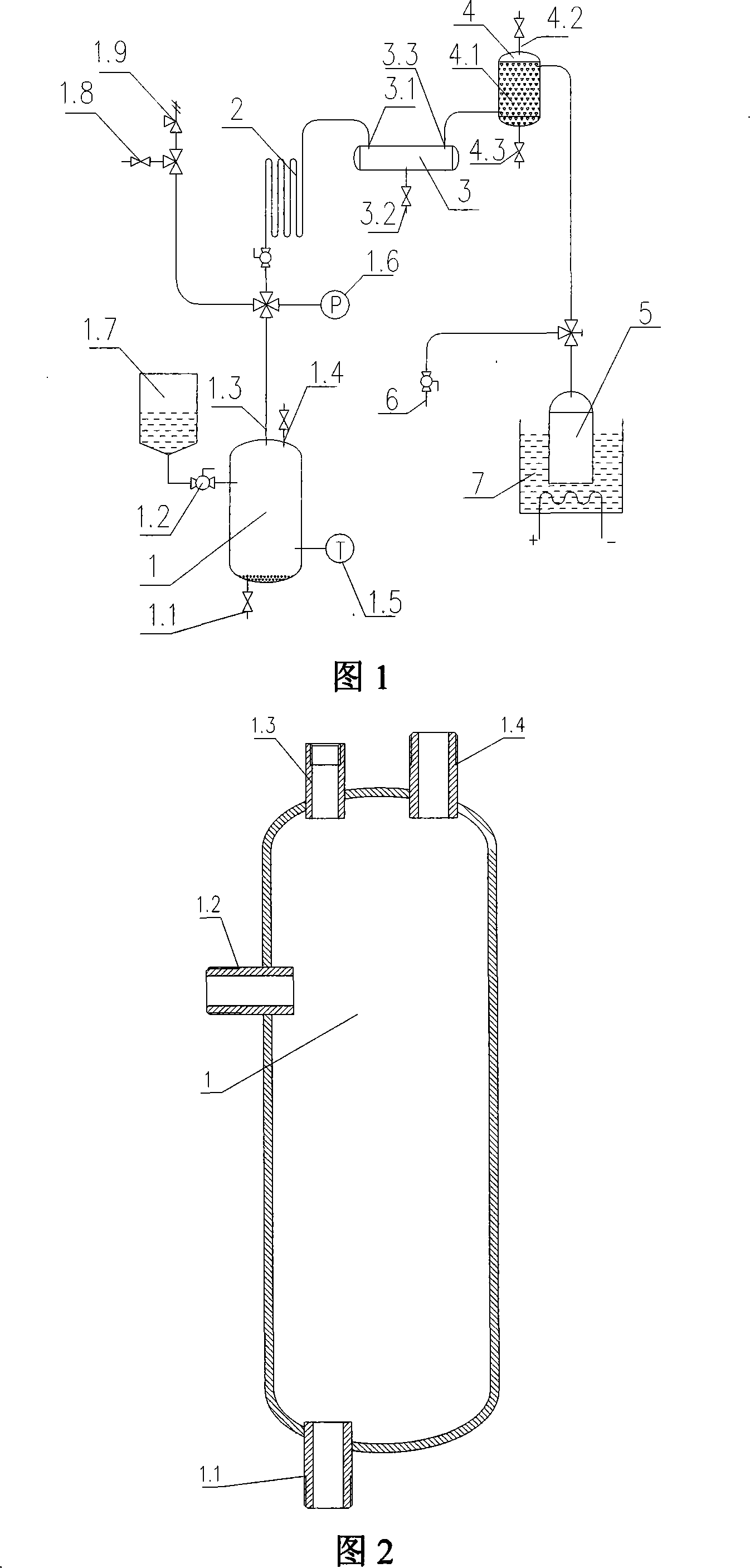
Mobile hydrogen-generating hydrogen-storing integrated device and hydrogen supplying method thereof
InactiveCN101186275AWide variety of sourcesSimple structureHydrogen productionTemperature controlChemical reaction
The invention relates to a movable integrated device for generation and storage of hydrogen and a hydrogen supply method, which belongs to the hydrogen preparation technical field. The movable integrated device for generation and storage of hydrogen comprises a hydrogen generator and a hydrogen storage tank. The device is characterized in that: the hydrogen generator is connected with a gas-water separator through a pipeline, and the gas-water separator is connected with a hydrogen purifier through a pipeline; the hydrogen purifier is connected with the hydrogen storage tank through a pipeline, and the hydrogen storage tank is provided with a temperature controlling apparatus. The hydrogen supply method is that: chemical reaction happens in the hydrogen generator to produce hydrogen, and the water and the hydrogen are separated by the gas-water separator; then purified by the hydrogen purifier, the hydrogen is stored into the storage tank after temperature regulated; while the hydrogen is needed, the hydrogen storage tank supplies the hydrogen through controlling the temperature. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, low construction cost, reliable technique, safety, high hydrogen generating speed, high purity of the hydrogen, less energy consumption and no pollution, etc., and is particularly applicable to movable situations.
Owner:天津海蓝德能源技术发展有限公司
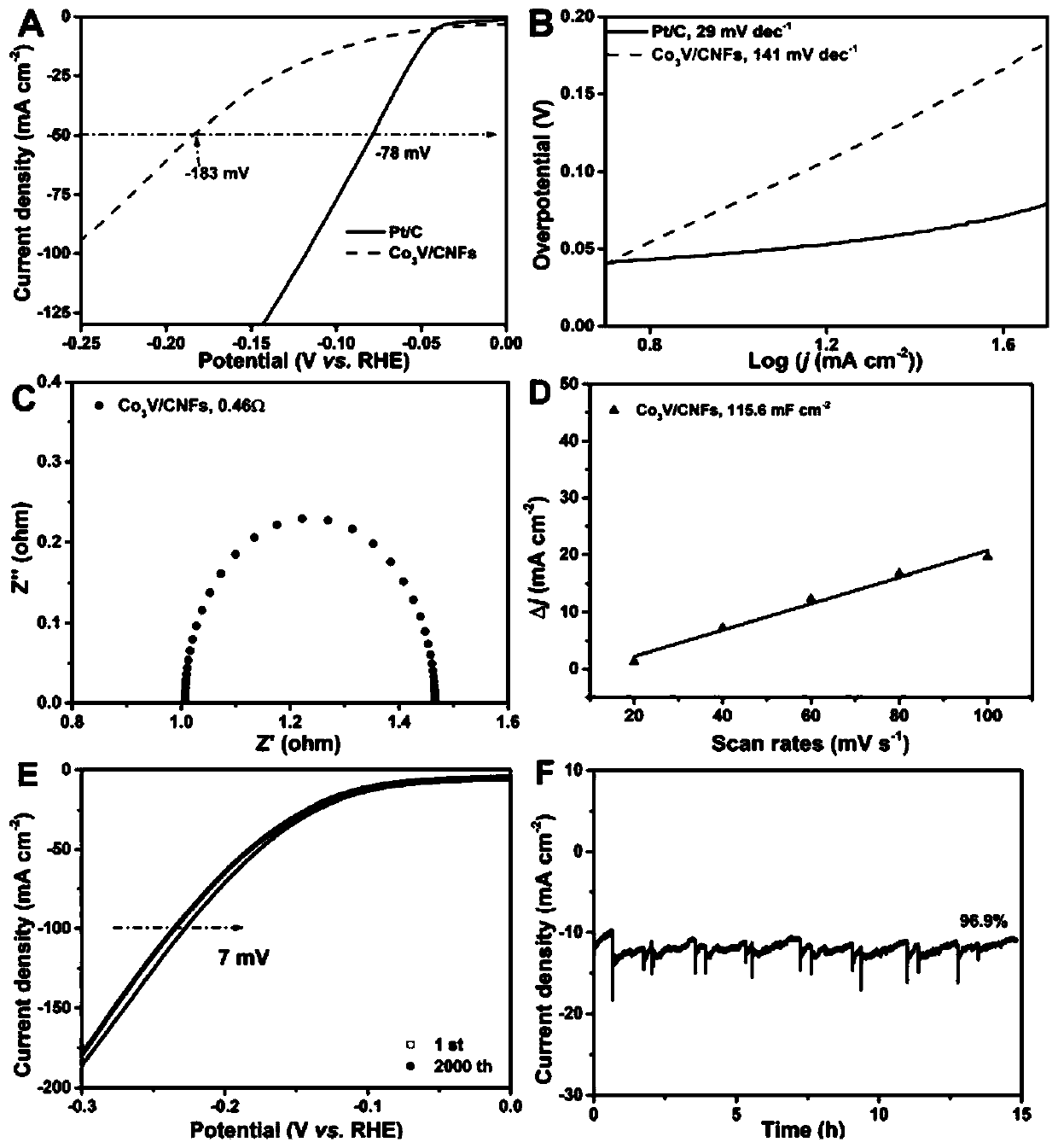
Electrocatalytic material loaded with vanadium-cobalt alloy nanoparticles and preparation method of electrocatalytic material
ActiveCN109701545AHigh catalytic activityImprove the electrochemical active areaMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationElectrospinningHydrogen production
The invention discloses an electrocatalytic material loaded with vanadium-cobalt alloy nanoparticles and a preparation method of the electrocatalytic material, and belongs to the technical field of composite material preparation. The carbon nanofiber-supported vanadium-cobalt alloy nanoparticle catalytic material for water electrolysis is prepared by loading a vanadium source and a cobalt source onto an ultrafine fiber carbon precursor by utilizing an electrospinning method, performing pre-oxidation, and performing reduction; and the catalytic material for the water electrolysis is composed ofreaction active matter and a carrier, wherein the reaction active matter is a vanadium-cobalt alloy nanoparticles, and the carrier is a carbon nanofiber material prepared by the electrospinning method. The catalytic material for the water electrolysis prepared by the method has a high specific surface area, thereby facilitating electrolyte diffusion and gas desorption; hydrogen evolution can be performed under acidic and alkaline conditions, and the hydrogen production speed under large voltage is much higher than that of a commercial Pt / C electrode; and in addition, the catalytic material for the water electrolysis prepared by the method does not need to coat an electrode, and can be directly used as an electrode for electrolyzing water.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
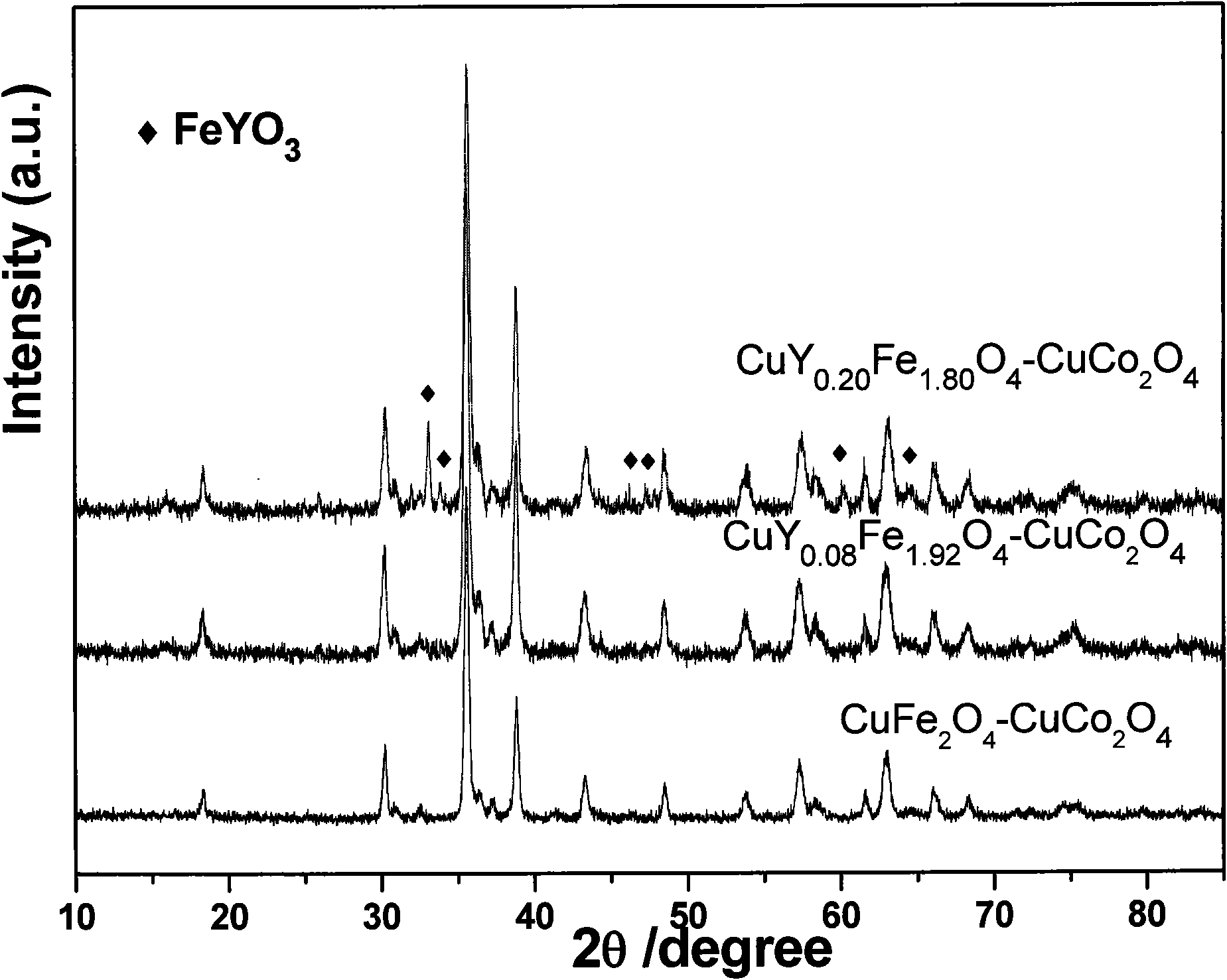
Preparation of visible light response composite cuprate photocatalysis material and application thereof
InactiveCN101623638AStable in natureExtended service lifeHydrogen productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsWater bathsCuprate
The invention relates to a method for preparing yttrium-doped copper ferrite- copper cobalt composite photocatalyst, comprising: adding ferric nitrate, cobalt nitrate and yttrium nitrate into copper nitrate solution, and obtaining a mixed cuprate solution; under the agitation in water bath, dripping citric acid solution into the newly prepared mixed cuprate solution to obtain transparent colloidal sol; continuously heating the transparent colloidal sol in the water bath to obtain gel; transferring the gel into a drying oven and drying at a certain temperature to obtain precursor, and obtaining the yttrium-doped copper ferrite- copper cobalt composite photocatalyst by calcination. The photocatalyst has the best mole ratio of 1: 1 between Fe and Co and the best yttrium-doped quantity being 4% (mole percentage) of Fe, and is good in photocatalysis hydrogen production activity under visible light. The photocatalyst has good application prospect in the aspect of hydrogen production of visible light catalytic material, simple technique, convenient operation, lower cost and long service life.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
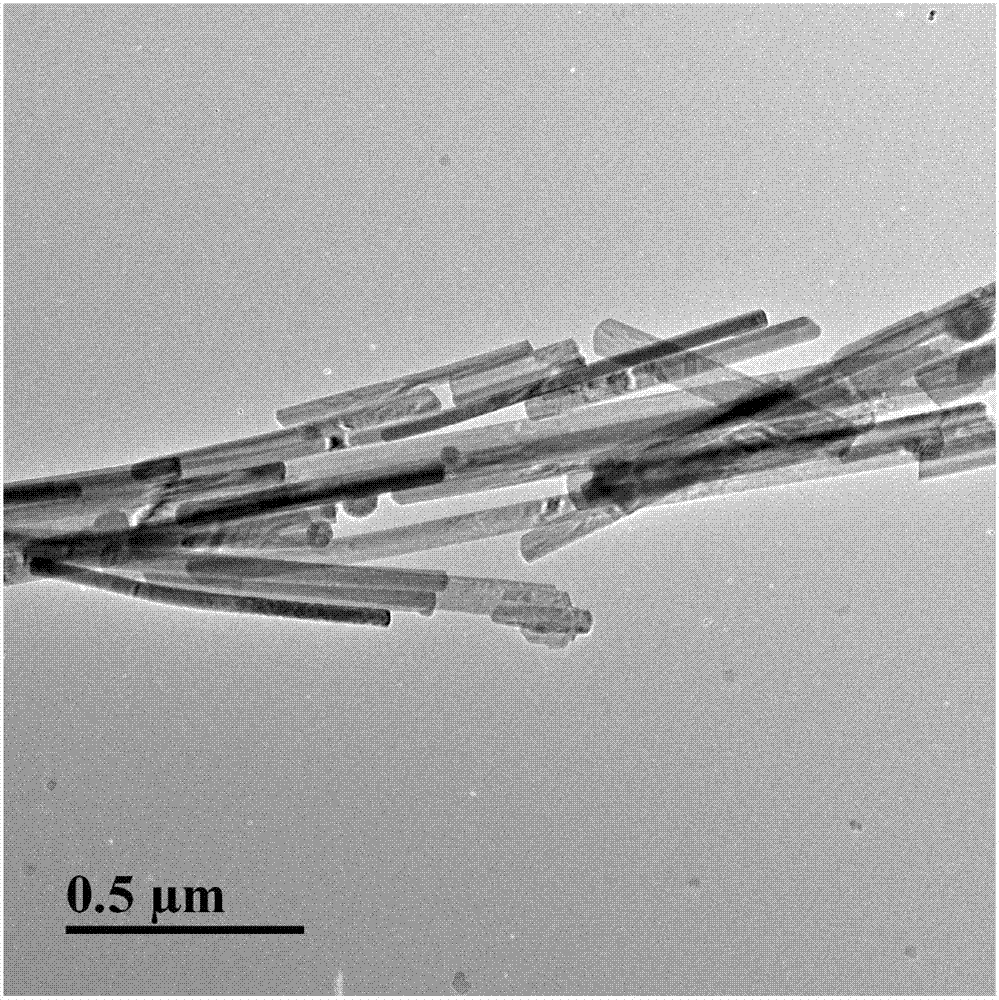
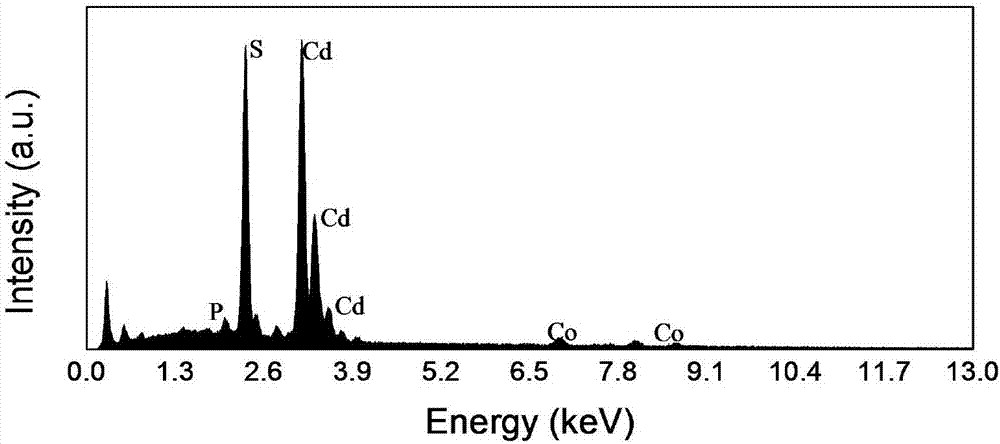
Simple and convenient preparation method of irregular cobalt phosphide/cadmium sulfide nanorod composite catalyst
InactiveCN107115876ALow costImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsDecompositionSynthesis methods
The invention aims to the problems such as environment pollution and energy crisis at present, and discloses a simple and convenient preparation method of an irregular cobalt phosphide / cadmium sulfide nanorod composite catalyst, and aims to reduce the cost of photocatalysts and increase velocity of hydrogen production by photocatalysis decomposition of water. The preparation method of the composite catalyst is green and environmental-friendly, and the prepared composite catalyst is relatively long in service life, and still has relatively high catalysis activity even after 25 hours. The irregular cobalt phosphide / cadmium sulfide nanorod composite catalyst prepared by using the method is simple and convenient in synthesis method, high in photocatalysis hydrogen production velocity, high in stability and low in price, is capable of greatly reducing the cost when being applied to industrial production, and is a novel catalysis material with relatively large industrial photocatalysis hydrogen production prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
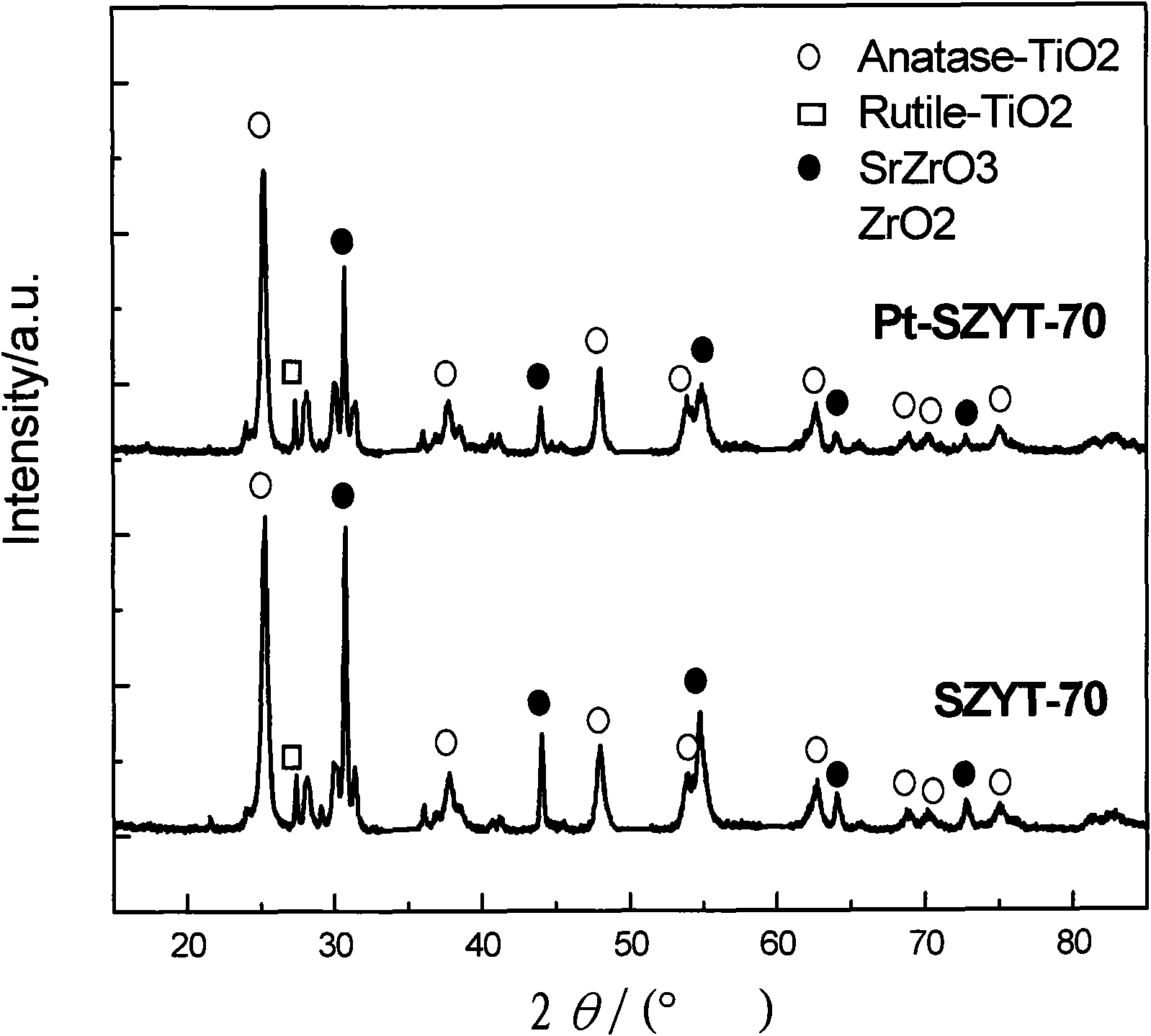
Visible light response composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
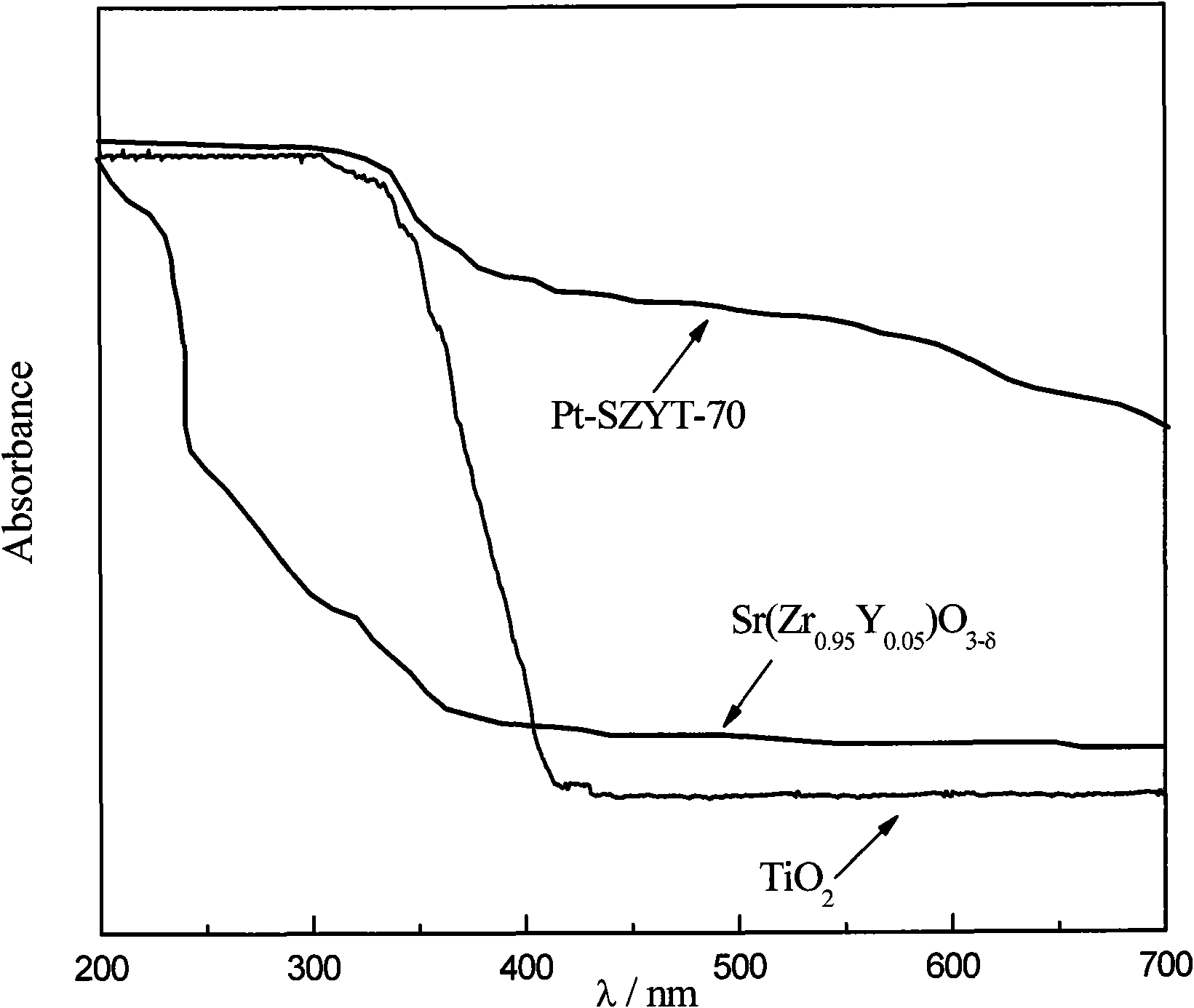
InactiveCN101623635AStable in natureExtended service lifeZirconium compoundsCatalyst activation/preparationZirconateNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a method for preparing platinum-supported and yttrium-doped strontium zirconate-titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst, comprising: (1) adding sodium oxalate solution into zirconium oxychloride, and obtaining Na2 ZrO (C2O4)2 solution; mixing Sr(NO3)2 solution and the Na2 ZrO (C2O4)2 solution, obtaining white precipitate, filtering, washing, drying and calcining the precipitate, and obtaining the strontium zirconate; (2) fully grinding yttrium oxide and the strontium zirconate, tabletting and calcining to obtain yttrium-doped strontium zirconate; (3) mixing the yttrium-doped strontium zirconate and TiO2, and sintering to obtain composite catalyst; (4) dispersing the product in methanol solution containing chloroplatinic acid to be processed by ultrasound and agitation and directly irradiated by a high-pressure mercury lamp under the nitrogen atmosphere; filtering, washing and calcining the product, and obtaining the finished product; the catalyst has good hydrogen production activity under visible light. The photocatalyst has good application prospect in the aspect of hydrogen production of visible light catalytic material, simple technique, convenient operation, lower cost and long service life.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of tantalate photocatalytic material
InactiveCN102626615AImprove stabilityLow priceCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogen productionLow activityPhotocatalytic water splitting
A tantalate photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof. The invention relates to a preparation method of a photocatalytic material. The present invention aims to solve a technical problem that an existing hydrothermal preparation method of tantalate photocatalytic material has long synthesis time, low activity and weak stability. The method comprises steps of: 1. mixing and grinding NaCl and KCl to obtain a eutectic fused salt powder; 2. mixing and grinding Na2CO3, K2CO3 and Ta2O5 to obtain a raw material powder; 3. evenly mixing the raw material powder and the eutectic fused salt powder to obtain a mixed powder; 4. calcining the mixed powder at a temperature of 700-850 DEG C for 1-4 hours, and washing and drying the products to obtain the tantalate photocatalytic material. The tantalate photocatalytic material of the present invention can reach hydrogen production rate up to 5-8 mmol / h and activity attenuation less than 3% after 20 h reaction and can be used in fields of hydrogen production by photocatalytic water splitting and water treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
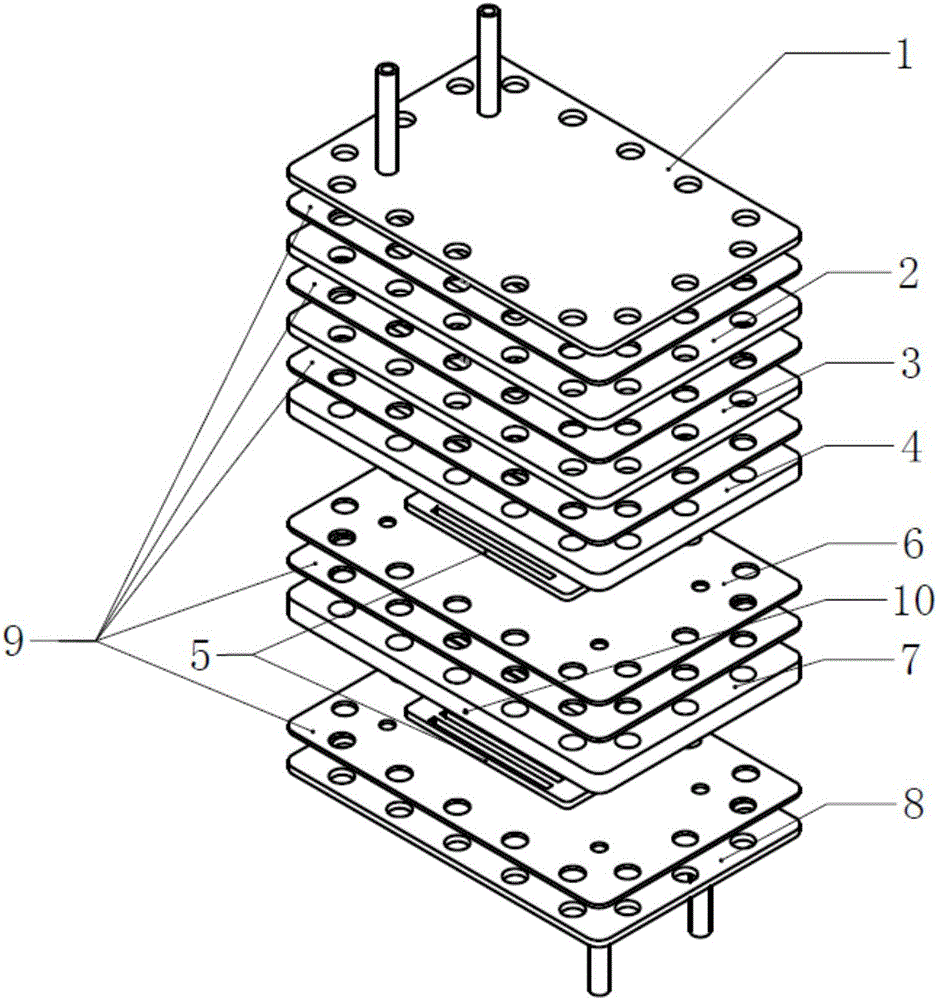
Self-heating type reactor used for hydrogen production by reforming and filled with high-temperature phase-change material
InactiveCN106629598AInhibition of excessive temperatureSuppress supercoolingHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionHeating efficiencyPhase-change material
The invention discloses a self-heating type reactor used for hydrogen production by reforming and filled with a high-temperature phase-change material. The self-heating type reactor used for hydrogen production by reforming is formed by sequentially laminating an upper cover plate provided with a methanol steam reforming reactant inlet pipe and a methanol catalytic combustion reactant inlet pipe on the upper surface, a graphite washer, an upper evaporation plate, a graphite washer, a lower evaporation plate, a graphite washer, a methanol reforming heat absorbing plate for hydrogen production filled with the high-temperature phase-change material on the lower surface, a sealing plate, a graphite washer, a methanol catalytic combustion plate filled with the high-temperature phase-change material on the lower surface, a graphite washer and a lower cover plate provided with a reformed gas outlet pipe and a combustion tail gas outlet pipe on the lower surface from top to bottom. The heat stability of a self-heating reactor is effectively improved by means of latent heat of phase change of the high-temperature phase-change material, the temperature gradient in the reactor and the temperature fluctuation of the reactor during working are reduced, catalyst activity reduction and peeling caused by overheating of the reactor are inhibited, and the heat efficiency and the methanol conversion rate of the reactor are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Efficient online measurement system of biological membrane photobioreactor
ActiveCN103528622AAdd up and down swing deviceAdd regulatory bypassMeasurement devicesWater bathsPeristaltic pump
The invention discloses an efficient online measurement system of a biological membrane photobioreactor. The efficient online measurement system comprises a biological membrane photobioreactor system, a biomass concentration and biological membrane thickness sensing system, an FBG (Fiber Bragg Grating) temperature sensing system and a hydrogen concentration and PH (Potential of Hydrogen) sensing system, wherein the biological membrane photobioreactor system comprises a photobioreactor, a reactor light source, a peristaltic pump, a constant-temperature water bath, a culture medium liquid storage bottle, a gas collection bottle, a gas-liquid separation bottle and the like; the biomass concentration and biological membrane thickness sensing system comprises an optical fiber light source, a light filter, multi-mode optical fibers, an optical branching device, an optical coupler, a biomass concentration sensing probe, a biological membrane thickness sensor and the like; the hydrogen concentration and PH sensing system comprises an H2 electrode, a pH reference electrode, a pH electrode and the like. As the sensors for the online measurement of biomass concentration, pH and hydrogen concentration are adopted in the online measurement system, the biomass concentration and the pH in the reactor can be regulated according to the real-time measurement results of the sensors, and the regulated hydrogen producing speed of the biological membrane reactor is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
cds/in2s3/cos composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102284298AIncrease the rate of hydrogen productionUniform powder particlesPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionAnhydrous ethanolLow activity
The invention discloses a CdS / In2S3 / CoS composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof, relating to a photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof. The invention aims to solve the problems of low activity of existing catalysts for hydrogen production by photolysis of H2O and low hydrogen production rate under visible light. The composite photocatalyst is made of Cd(Ac)2·2H2O, Co(Ac)2·4H2O, InCl3·4H2O and thioacetamide. Method: Add Cd(Ac)2·2H2O, Co(Ac)2·4H2O, InCl3·4H2O and thioacetamide to acetone or absolute ethanol; seal it and put it into an ultrasonic reactor for reaction; the product is cooled to room temperature , washed with absolute ethanol, and dried to obtain a composite photocatalyst. The particle diameter of the composite photocatalyst of the invention is about 500nm, the hydrogen production rate is high, the catalyst activity is good, no noble metal needs to be loaded, and the powder particles are uniform and high in purity. Applied in the field of photocatalytic materials.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Phosphorus-containing compound, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108499585AWeak crystallinityIncrease the rate of hydrogen productionPhysical/chemical process catalystsCell electrodesPhotocatalytic reactionNon noble metal
The invention discloses a phosphorus-containing compound, and a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the fields of material science and technology and chemistry. The phosphorus-containing compound is prepared from cheap raw materials through the simple method; the method is essentially characterized in that the compound is prepared from metal ions and a phosphorus source under the illumination condition of a photoactive material; and the temperature in the prior art is more than 100 DEG C, and the method in the invention is a normal temperature synthesis process, so the obtained compound has a weak crystallization degree. The phosphorus-containing compound has a high photocatalytic activity as a conventional catalyst and a photocatalytic reaction cocatalyst, and achieves a high hydrogen production rate for a photocatalytic hydrogen production reaction. The method and the phosphorus-containing compound can be used for producing an electrode and producing a battery, so the production cost of the electrode and the battery is reduced, the preparation method is simplified, and the obtained electrode is a non-noble metal catalyst, and has the advantages of low cost, low overpotential, high stability and certain industrial application values.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of molybdenum phosphide to catalytic hydrogen generation in alkaline formaldehyde solution
ActiveCN107473183AEffective hydrogen productionIncrease the rate of hydrogen productionHydrogenPhysical/chemical process catalystsAqueous solutionNoble metal
The invention provides application of molybdenum phosphide to catalytic hydrogen generation in an alkaline formaldehyde solution. Catalytic reaction conditions are as follows: reaction is carried out at room temperature under a heating condition; the concentration of sodium hydroxide in a formaldehyde water solution is 0.01mol.L<-1> to 10mol.L<-1>, and the concentration of the formaldehyde solution is 0.1mol.L<-1> to 3mol.L<-1>; the dosage of a molybdenum phosphide catalyst in 100mL of the formaldehyde solution is 5mg to 30mg. According to the application provided by the invention, hydrogen prepared under an inert gas atmosphere can be directly used for a fuel cell, and oxygen does not need to be separated. The catalytic hydrogen generation in alkaline formaldehyde solution can be effectively performed at the room temperature and under the heating condition, and a hydrogen source is provided for a fuel cell. Under the room temperature, the rate of catalytic hydrogen generation in alkaline formaldehyde solution through the molybdenum phosphide reaches 150mL.min<-1>.g<-1>, is two times that of catalytic formaldehyde hydrogen generation through noble metal Pd, and is 7 times that of catalytic formaldehyde hydrogen generation through metal Cu. Under the heating condition, the rate of catalytic formaldehyde hydrogen generation by molybdenum phosphide can be increased exponentially.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Preparation method and photocatalytic hydrogen production application of CdS-PAN/graphene composite nano fiber
InactiveCN108927222AInhibition of agglomerationLarge specific surface areaOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionFiberPotassium persulfate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a CdS-PAN / graphene composite nano fiber. The preparation method comprises following steps: at first, preparing S-n-propyl-S'-(alpha-methyl-alpha'-acetic acid)-trithiocarbonate (PTTC) and CdS-PTTC; then taking acetonitrile as monomers and potassium persulfate as an initiator to carry out reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerizationreactions to prepare CdS-PAN; and finally carrying out thermally induced phase separation to prepare the CdS-PAN / graphene composite nano fiber with a diameter of 110 to 300 nm. The preparation methodcan effectively inhibit the agglomeration of CdS nano particles. The nano fiber has a large specific surface area, and the photocatalytic activity of CdS can be effectively exerted. The CdS-PAN / graphene composite nano fiber has a high hydrogen production speed.
Owner:晋江瑞碧科技有限公司 +1
Titanium dioxide nanotube photocatalytic material with hollow laminated structure and preparation method of titanium dioxide nanotube photocatalytic material
InactiveCN109759041ALarge specific surface areaRich pore structurePhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionTio2 nanotubeGlycerol
The invention provides a titanium dioxide nanotube photocatalytic material with a hollow laminated structure and a preparation method of the titanium dioxide nanotube photocatalytic material. The diameter of a titanium dioxide nanotube is 2 to 3 [Mu]m; the titanium dioxide nanotube is formed by stacking nanosheets; the thickness of the nanosheets is 10 to 15 nm; the size of the nanosheets is 20 to30 nm; the nanosheets form a mesoporous structure. The method comprises the following steps: taking a mixed solution of ethanol, glycerol and diethyl ether as a solvent; taking titanyl sulfate as a titanium source; carrying out solvothermal reaction and sintering to form the titanium dioxide nanotube photocatalytic material with the hollow laminated structure. The preparation method disclosed bythe invention has the advantages of quickness, simplicity, easiness in large-scale production and high repeatability; in addition, the titanium dioxide nanotube prepared by the method is formed by stacking the nanosheets, and has a higher specific surface area and an abundant porous structure and excellent performance of producing hydrogen by water photolysis; the hydrogen producing rate of waterphotolysis is 2.35 times that of commercial P25; in addition, the catalyst can be recycled.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
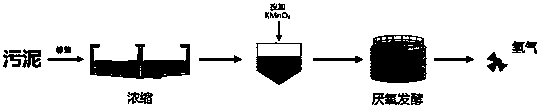
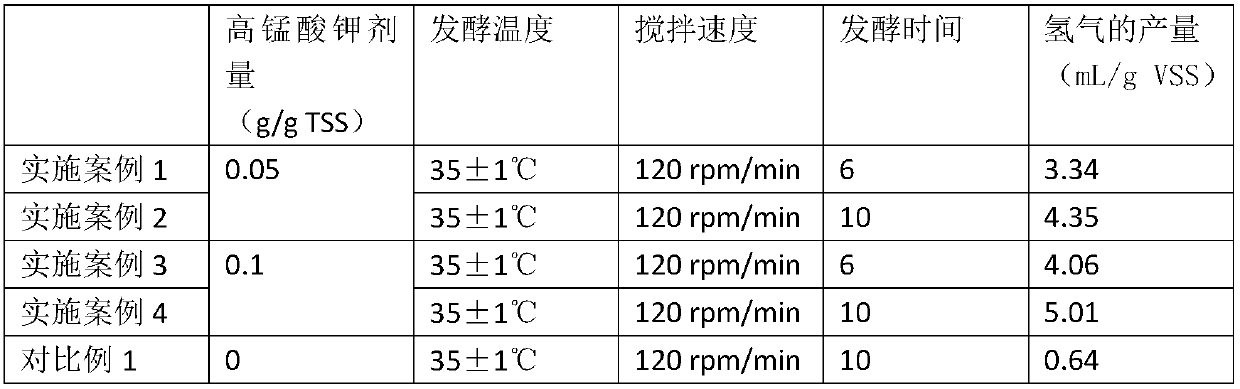
Method for producing hydrogen gas through reinforcing anaerobic fermentation of surplus sludge
InactiveCN109680012AAchieve reductionImplement resourcesSpecific water treatment objectivesFermentationHydrogenMunicipal sewage
The invention relates to a method for producing hydrogen gas through improving anaerobic fermentation of sludge by adding potassium permanganate (a typical oxidant). The specific method comprises thesteps: (1) subjecting primary sludge and surplus sludge generated from an urban sewage treatment plant to free settling treatment, removing supernatant, and carrying out concentrating, so as to obtainfermented feedstocks; (2) adding potassium permanganate into the obtained fermented feedstocks, and carrying out treatment under anaerobic conditions, thereby producing hydrogen gas. After the sludgeis treated with potassium permanganate, lysing of the sludge is promoted, organics such as proteins and saccharides can be extensively digested, and the activity of hydrogen-addicted methane producing microbes is seriously limited, so that the volume of hydrogen gas generated by the sludge can be greatly promoted. Through simple, cheap and effective operations, the decrement of the sludge is achieved, the resource-converting utilization of the sludge is further promoted, and the method has an important significance in treatment and disposal of the sludge.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
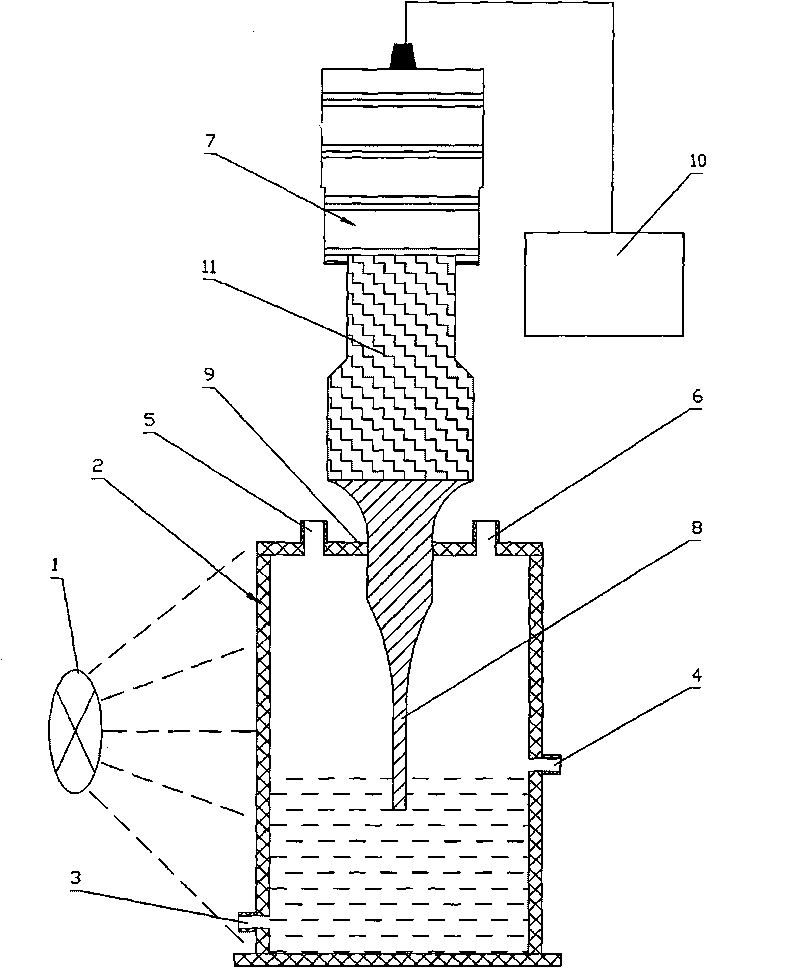
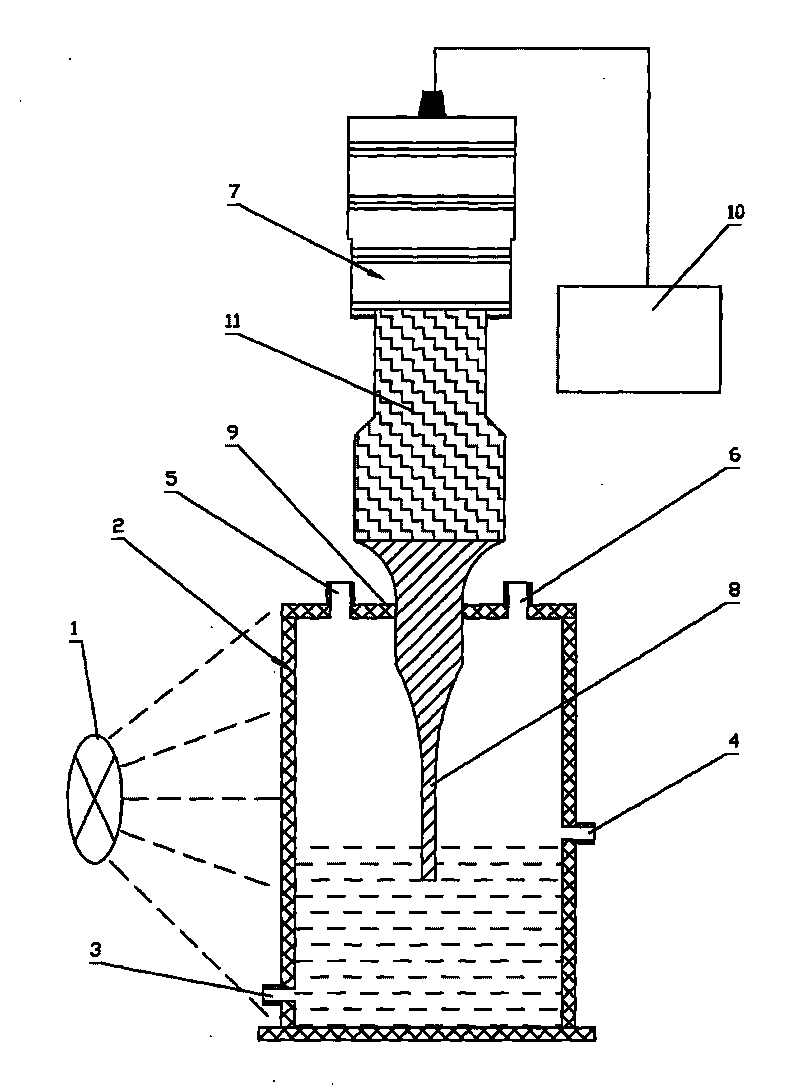
Continuous-flow and ultrasonic-wave light biological hydrogen producing reactor
InactiveCN101735941AImprove metabolic activityIncrease the rate of hydrogen productionGas production bioreactorsPhotobioreactorsCarbon sourceLight source
The invention discloses a continuous-flow and ultrasonic-wave light biological hydrogen producing reactor comprising a light source, a transparent tank irradiated by the light source and an ultrasonic cell crusher, wherein one side of the transparent tank is provided with a liquid inlet, the other side is provided with a liquid outlet, and the top of the transparent tank is provided with an air inlet and an air outlet; an amplitude transformer of the ultrasonic cell crusher vertically and downwards extends into a bacterium suspension filled in the transparent tank, and air sealing is arranged between the amplitude transformer and an upper cover of the transparent tank. The continuous-flow and ultrasonic-wave light biological hydrogen producing reactor combines a flat plate type reactor and the ultrasonic cell crusher so as to enhance organic matter as a carbon source in a degraded solution and raise the hydrogen producing speed of photosynthetic bacteria; when low-strength ultrasonic waves propagate in a medium, the continuous-flow and ultrasonic-wave light biological hydrogen producing reactor can change the permeability of a cell membrane, reinforce matter delivery, increase the metabolic activities of bacteria and promote the generation of useful matter; the continuous-flow and ultrasonic-wave light biological hydrogen producing reactor enhances the speed of a reactant entering the active position of enzyme or cells, promotes the mass transfer diffusion process that a product departs from the active center of the enzyme and enters a liquid medium, raises the enzyme activity, promotes the catalytic reaction of the enzyme and raises the speed of biological reaction.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Multifunctional clostridium bifermentans and application thereof
ActiveCN107217023AMay alter metabolic pathwaysEnhanced acetate pathwayBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteBacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and specifically relates to multifunctional clostridium bifermentans and application thereof in producing hydrogen through fermentation and increasing the yield of acetic acid. A bacterial strain is clostridium bifermentans EZ-1, and the preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO. 13913. The multifunctional clostridium bifermentans is capable of generating clean fuel hydrogen and metabolites such as acetic acid and butyric acid by utilizing glucose. Due to addition of nano magnetite and ferrihydrite in appropriate concentrations, a metabolism path of the multifunctional clostridium bifermentans can be regulated, so that the yield of the acetic acid can be increased. By microbial fuel cell detection, the situation that the bacterial strain has power generation ability is discovered, and the maximum current output density can be up to 6.3 mA / m<2>. The bacterial strain is first multifunctional novel clostridium bifermentans which is reported at present, can be applied to biological products of hydrogen, acetic acid and butyric acid generated through biomass fermentation, has power generation potential and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
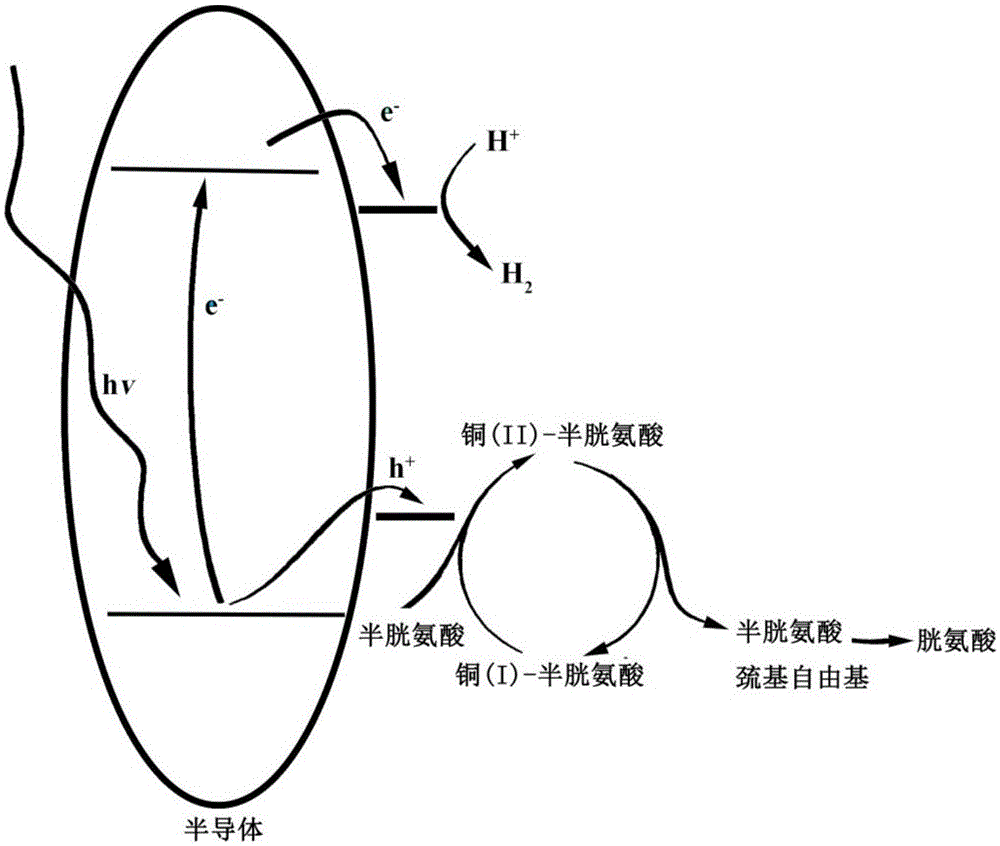
Visible light catalytic system with copper ion-thiol complex, preparation method, and hydrogen production method
ActiveCN105013536AIncrease the rate of hydrogen productionImprove photocatalytic hydrogen production rateOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionSemiconductor materialsElectron
The present invention disclose a catalytic system of using visible light to photodecompose water to produce hydrogen, and particularly a visible light catalytic system with a copper ion-thiol complex, a preparation method, and a hydrogen production method. The system comprises the following raw materials: a semiconductor photocatalyst, a copper salt or a copper ion-thiol complex and a thiol compound. The preparation method comprises: using a semiconductor material as a photocatalyst; using a thiol compound as a hole consumption agent; adding a copper salt or copper ion-thiol complex; photodecomposing water to produce hydrogen under irradiation of visible light (lambda > 400 nm). The copper ion-thiol complex of the present invention has the effect of promoting hole transport and consumption in a semiconductor, and can increase efficiency of separation between photogenerated electrons and holes in a semiconductor photocatalytic system, thereby improving activity of the system in photodecomposing water to produce hydrogen. The present invention proposes the copper ion-thiol complex as a hole consumption cocatalyst in the photocatalytic system, and the cocatalyst is high in catalytic activity, simple in synthesis, low in raw material price, and recyclable.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
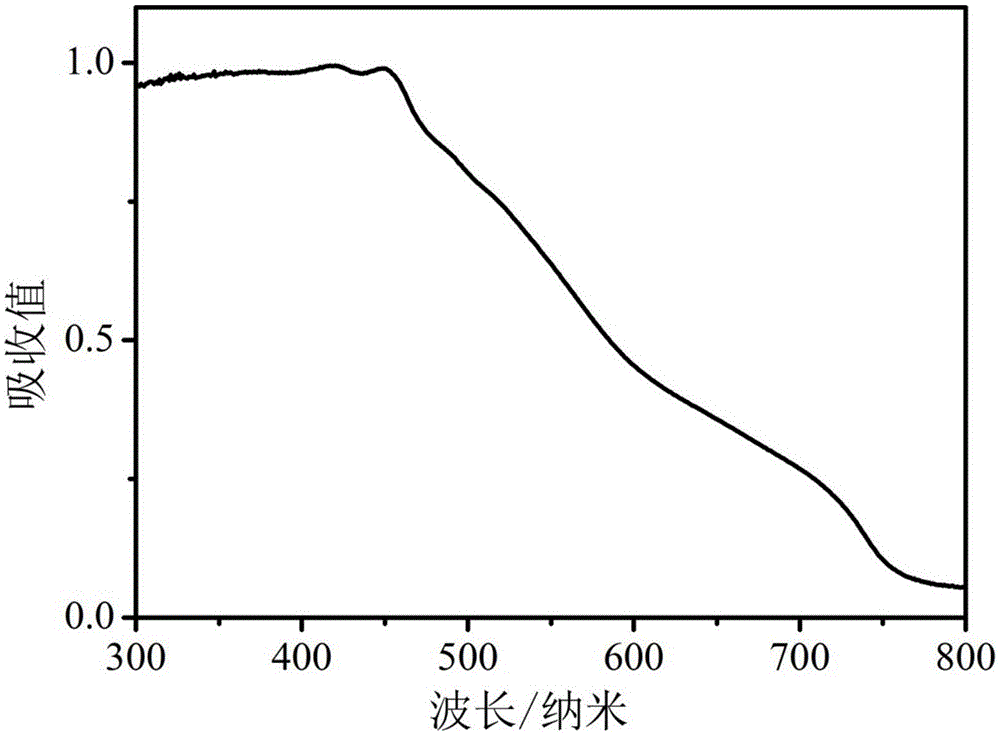
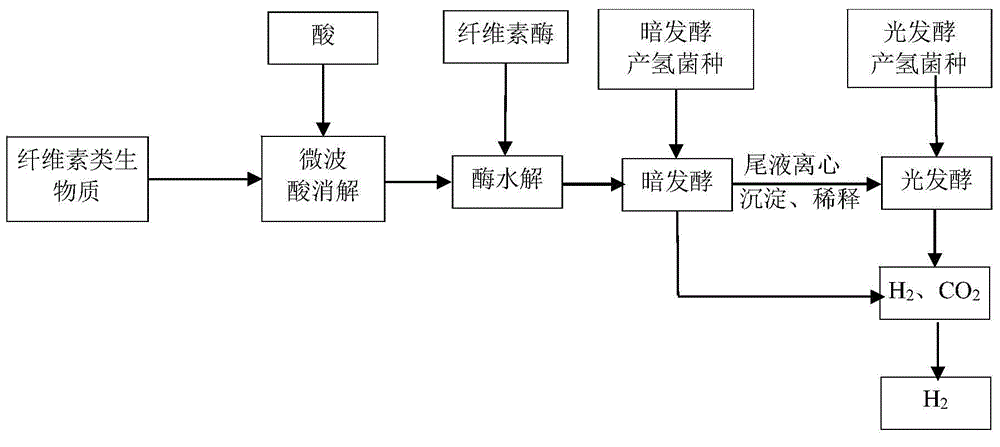
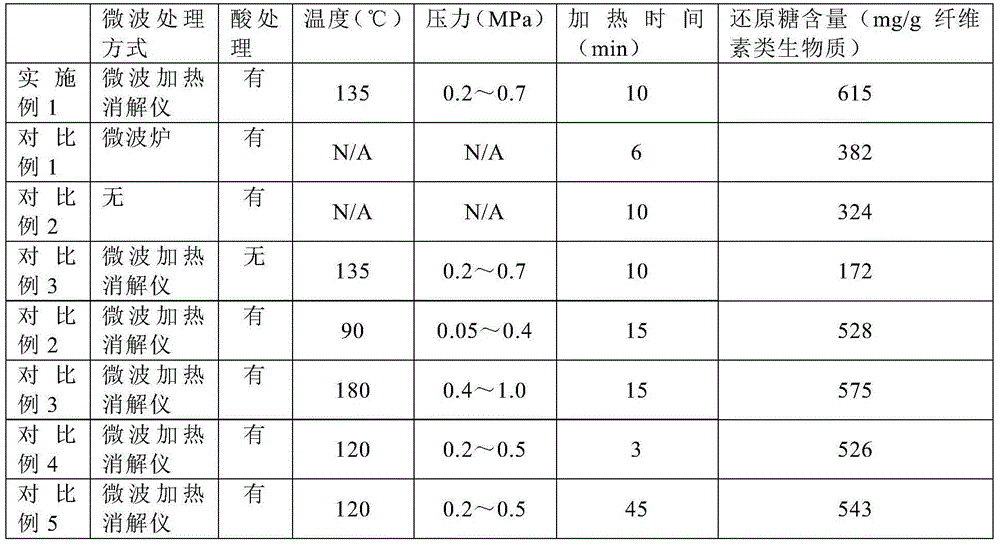
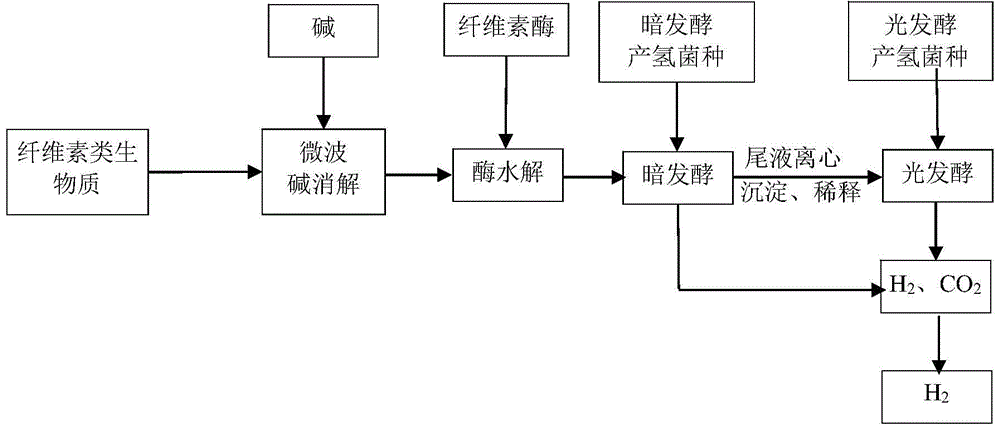
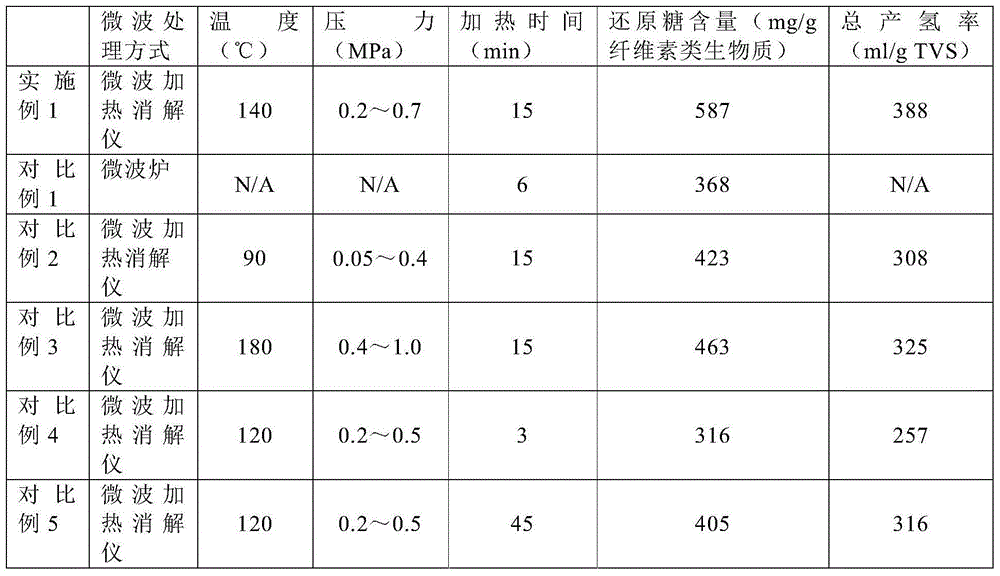
Method used for producing hydrogen by taking cellulose as raw material
InactiveCN105713926AReduce crystallinityImprove degradation efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseMicrowave
The invention provides a method used for producing hydrogen by taking cellulose as a raw material. The method comprises following steps: 1, microwave acid digestion; 2, enzyme hydrolysis; 3, dark fermentation hydrogen production; 4, photo fermentation hydrogen production; and 5, purification. The method is high in hydrogen yield, hydrogen production efficiency, substrate utilization ratio, and energy conversion efficiency.
Owner:COFCO GROUP +1
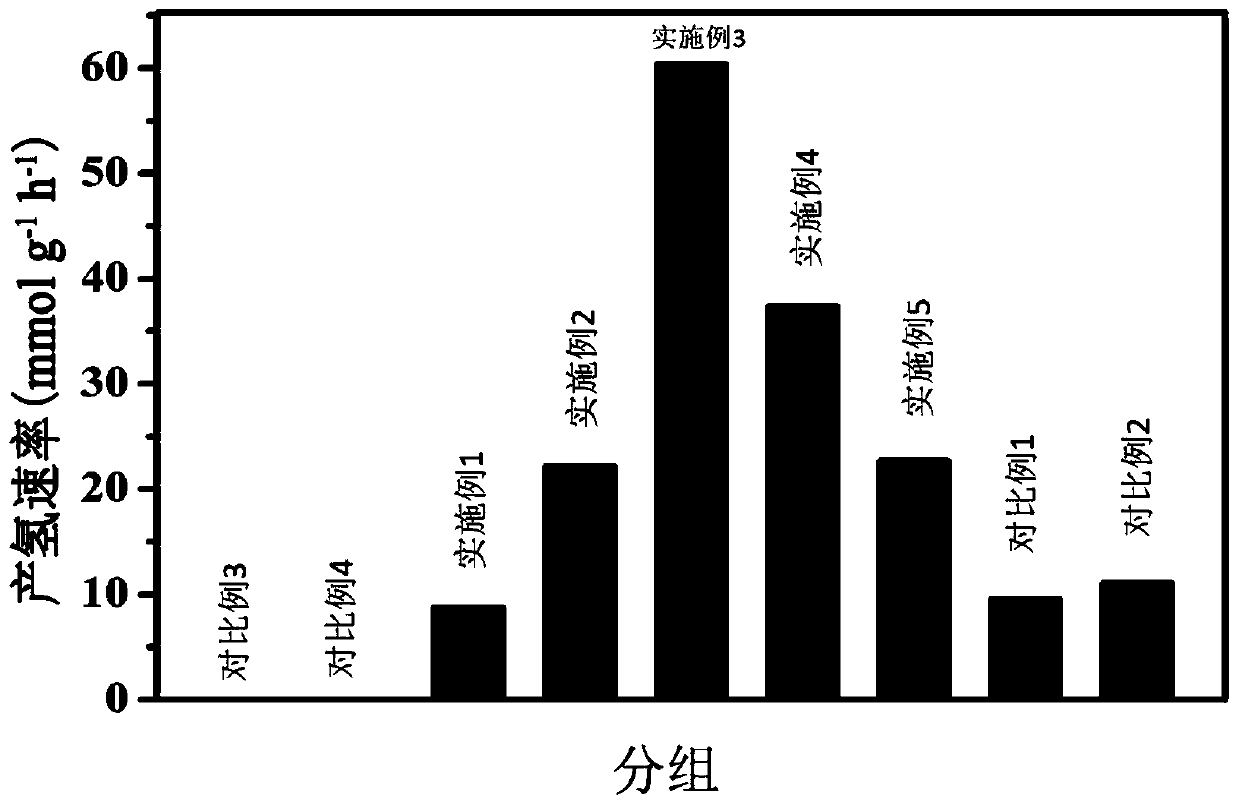
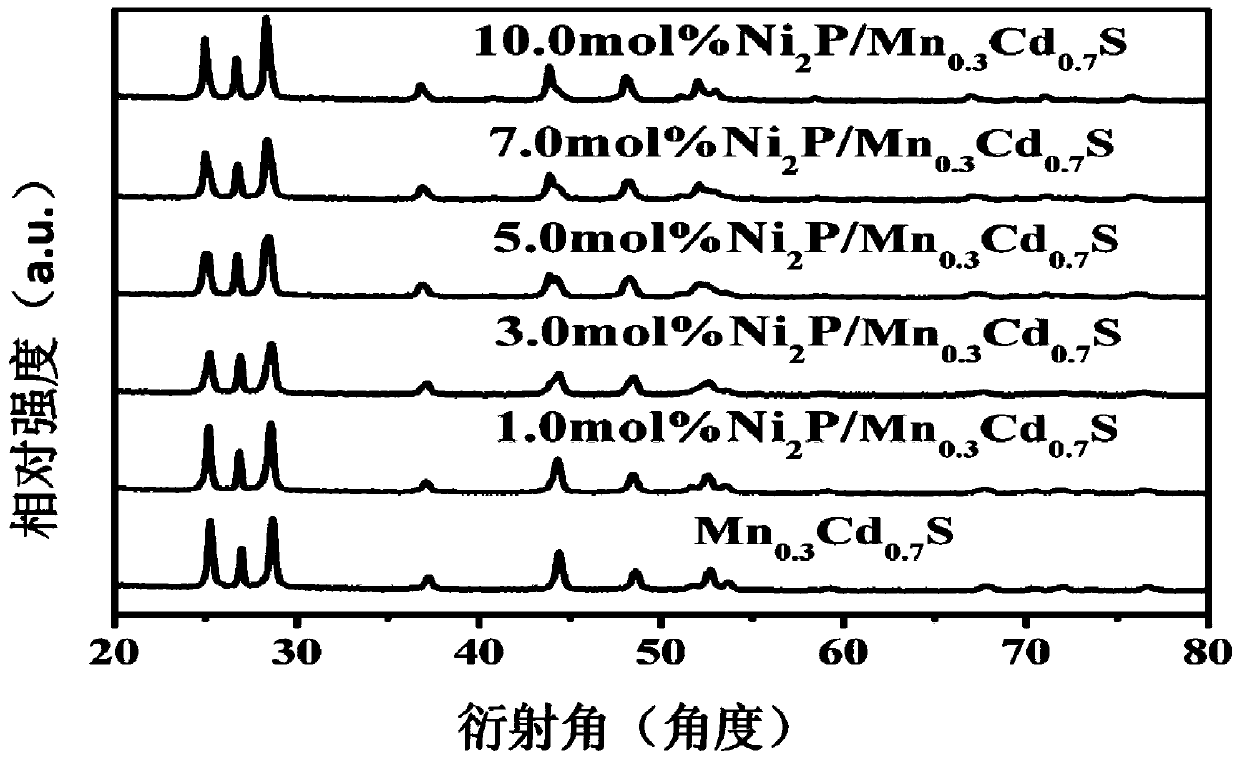
Ni2P/Mn0.3Cd0.7S photocatalytic water-decomposition composite catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110756203ALarge aspect ratioIncrease the rate of hydrogen productionPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionPhoto catalyticPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a Ni2P / Mn0.3Cd0.7S photocatalytic water-decomposition composite catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing red phosphorus with a solvent evenly, performing grinding so as to obtain pre-treated red phosphorus, adding a Mn0.3Cd0.7S catalyst to an ethanol solution so as to disperse the Mn0.3Cd0.7S catalyst uniformly and obtain a suspension, adding a NiCl2.6H2O and the pre-treated red phosphorus to the suspension, performing a solvothermal reaction, and performing filtration and drying so as to obtain the Ni2P / Mn0.3Cd0.7S photocatalytic water-decomposition composite catalyst. The composite photocatalyst has a rod-like structure and a large aspect ratio, transfer and separation of photo-generated carriersare facilitated, the problem of serious photocorrosion of sulfide catalysts can be solved significantly, and a high photocatalytic hydrogen-production rate is achieved; and in addition, the preparation method of the catalyst has simple operation and an environment-friendly and non-toxic preparation process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation and application of efficient hydrogen production photo-catalyst MoS2-SrZrO3
InactiveCN104289234ASave raw materialsMild reaction conditionsPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionHeterojunctionUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to preparation and application of a hydrogen production photo-catalyst MoS2-SrZrO3, aiming at solving the problems of low hydrogen production rate under ultraviolet light, instability and wide light response range of the catalyst. The catalyst is a heterojunction catalyst formed by MoS2 and SrZrO3. A preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps: adding SrOC12.8H2O and Sr(NO3)3 into a KOH solution, fully dissolving SrOC12.8H2O and Sr(NO3)3, putting the solution in a hydrothermal kettle for heating, washing and drying a product to obtain SrZrO3, then adding SrZrO3 a Na2MoO4.2H2O and CH3CSNH2 solution, ultrasonically stirring the solution, putting the solution in the hydrothermal kettle for heating, washing and drying the product to obtain the catalyst. The catalyst prepared by the method is environmentally friendly, and is high in hydrogen production rate which reaches 5.96mmol / L under ultraviolet light with wavelength being 365nm, and is long in service life, low in cost and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
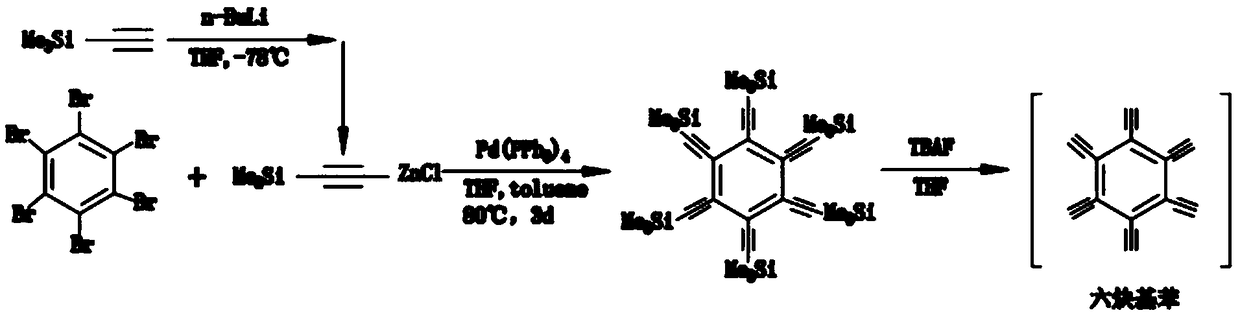
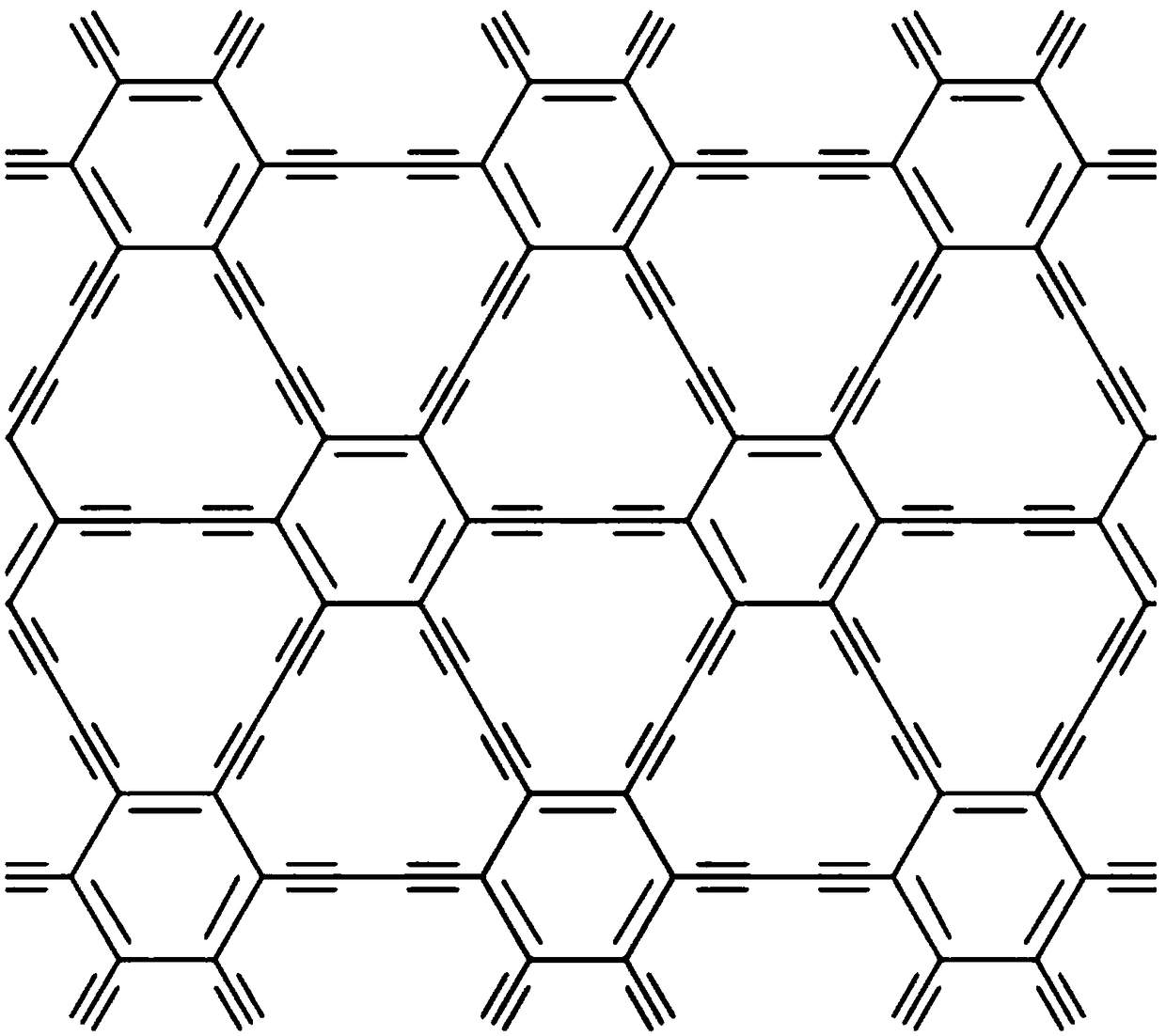
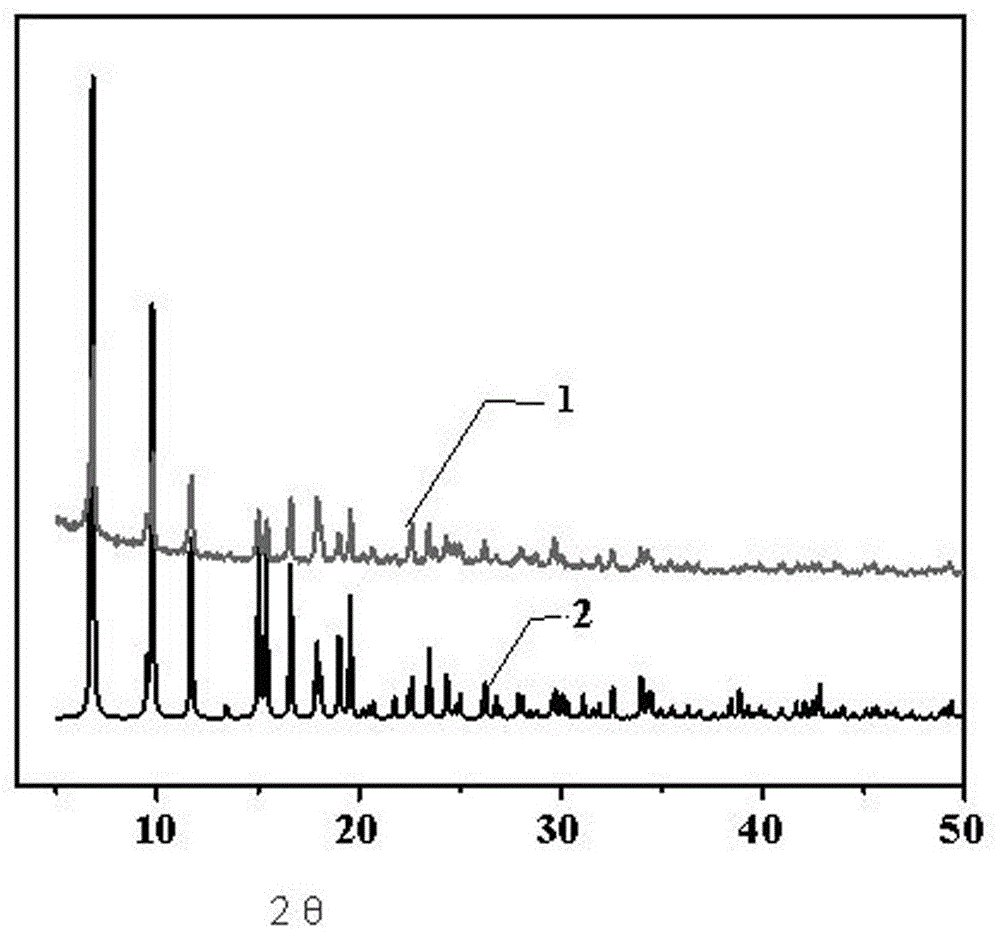
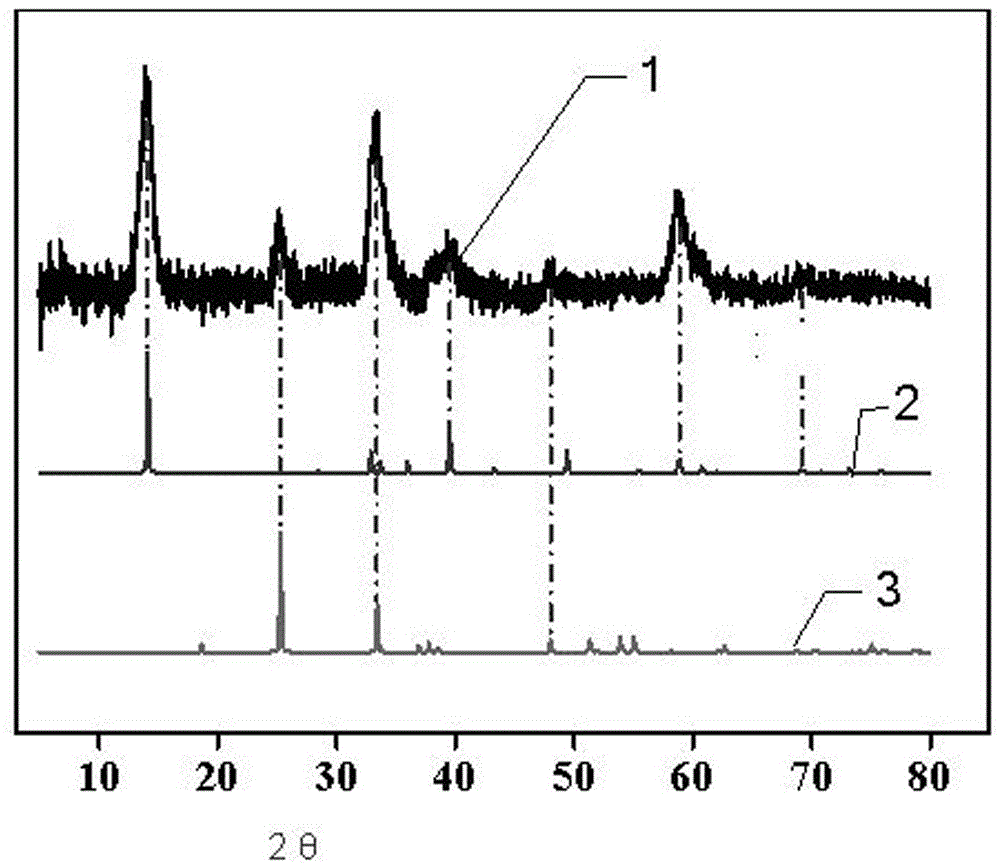
Preparation method of graphdiyne-like substance
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphdiyne-like substance. The method includes: with cuprous iodide being a substrate, performing a coupling reaction to hexaalkynyl benzene under catalysis by the cuprous iodide in a solvent; removing the cuprous iodide with ammonia water through corrosion, and performing centrifugal separation and drying, and grinding the product to obtain the graphdiyne-like powder product. The method can prepare the graphdiyne-like substance at large scale, shortens the researching period of the graphdiyne in other fields, and makes the graphdiyne possibleto be applied to other fields.
Owner:BEIFANG UNIV OF NATITIES
Semiconductor hydrogen production catalyst based on compounding of titanium dioxide and molybdenum sulfide, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105944739AIncrease the rate of hydrogen productionPotential Applicability in Resolving CrisisPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionNano catalystThiourea
The invention discloses a semiconductor hydrogen production catalyst based on compounding of titanium dioxide and molybdenum sulfide, and a preparation method and application thereof, which relate to the technical field of nano-catalysts and photocatalysis. The preparation method of the compound catalyst comprises the following steps of adopting a ti-based MOF (NH2-MIL-125) as a precursor; dissolving the precursor, thiourea and sodium molybdate dehydrate in water in the moderate hydrothermal reaction; sealing in a reaction kettle; reacting at the constant temperature of 200 to 220 DEG C; reducing the temperature to be the room temperature under the natural condition to obtain a nano composite. The hydrogen production rate of the semiconductor hydrogen production catalyst reaches up to 10,046 mu mol h<-1>g<-1>, the semiconductor hydrogen production catalyst can be recycled through centrifugal separation, and the utilization rate of the catalyst is improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Preparation method and application of porous single-layer MoS1.85 nanonet
ActiveCN107570176AImprove transmission performanceReduce the number of layersCatalyst activation/preparationElectrode shape/formsAlcoholAmmonium hydroxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous single-layer MoS1.85 nanonet. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a hydrothermal method is adopted to prepare a MoS2 nanosheet; a ball mill rotates or vibrates to enable a stainless steel ball to fiercely impact the MoS2 nanosheet, defects are introduced onto the MoS2 nanosheet, and MoS2 is stripped; the MoS2 nanosheet processed by the ball milling method is placed into a beaker containing water, ultrasonic treatment is performed for 4-8 h under the ultrasonic conditions of 15-25 DEG C and 100-200 W to obtain a black precipitate; and the black precipitate is washed with ethyl alcohol and ammonium hydroxide for several times and dried at 40-60 DEG C for 10 h to obtain the porous single-layer MoS1.85 nanonet. The ballmilling method and the ultrasonic auxiliary method are adopted to prepare a catalyst, and the preparation method is simple, feasible, green and environmentally friendly, and can quickly realize large-scale preparation of the porous single-layer MoS1.85 nanonet.
Owner:HENAN INST OF ENG
Method used for producing hydrogen by taking cellulose as raw material
InactiveCN105713925AReduce crystallinityImprove degradation efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseMicrowave
The invention provides a method used for producing hydrogen by taking cellulose as a raw material. The method comprises following steps: 1, microwave alkali digestion; 2, enzyme hydrolysis; 3, dark fermentation hydrogen production; 4, photo fermentation hydrogen production; and 5, purification. The method is high in hydrogen yield, hydrogen production efficiency, substrate utilization ratio, and energy conversion efficiency.
Owner:COFCO GROUP +1
Method for catalyzing hydrogen production from formic acid
ActiveCN108675262AEasy to makeHigh catalytic efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionPalladium catalystCatalytic efficiency
The invention discloses a method for catalyzing hydrogen production from formic acid by using a palladium-based catalyst Pd / CTF. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a covalent triazine polymeric porous material (CTF) by an ionic thermal copolymerization method; loading precious metal Pd by a precipitation deposition method to obtain the catalyst Pd / CTF; adding the Pd / CTF into aformic acid solution, and catalyzing the hydrogen production from the formic acid at 298-328K. The prepared loaded palladium catalyst Pd / CTF adopts a suitable pore structure, the atomic proportion ofN element on the surface is 8.76-9.89%, and the diameter range of the Pd is 1.58-1.87nm. According to the method, a carbon nitrogen material CTF is used as a carrier of the Pd-based catalyst, so thaton one hand, the catalytic activity of the catalyst is significantly improved, and on the other hand, the charge structure on the surface of the noble metal is changed and production of a byproduct COis eliminated. By the method, the catalyst is easy to prepare, the operation is convenient, the catalytic efficiency is high, and the catalyst can be recycled.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com