Ultrahigh pressure metal hydride hydrogen compression material
A hydride and ultra-high pressure technology, which is applied in the field of hydrogen compressor materials and ultra-high pressure metal hydride hydrogen compression materials, can solve the problems of large hydrogen absorption and desorption hysteresis, difficult activation, and failure to meet requirements, and achieve hydrogen absorption and desorption hysteresis Small, easy to activate, avoiding the effect of energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Preparation of ZrFe 2.05 Alloy (the alloy composition is the atomic percentage, at.%, the same below): the starting material is the commercial metal element zirconium sponge and rod iron, the element purity is higher than 99%, according to the nominal composition ZrFe 2.05 After being formulated into an alloy, it is repeatedly smelted three times in a high-frequency suspension melting furnace protected by a high-purity Ar (99.999%) atmosphere to produce an alloy ingot with a weight of about 30 g. The alloy ingot was sealed into an argon-protected quartz tube and annealed at 800°C for 72h. Then quench the quartz tube into cold water, and take out the alloy ingot after cooling.
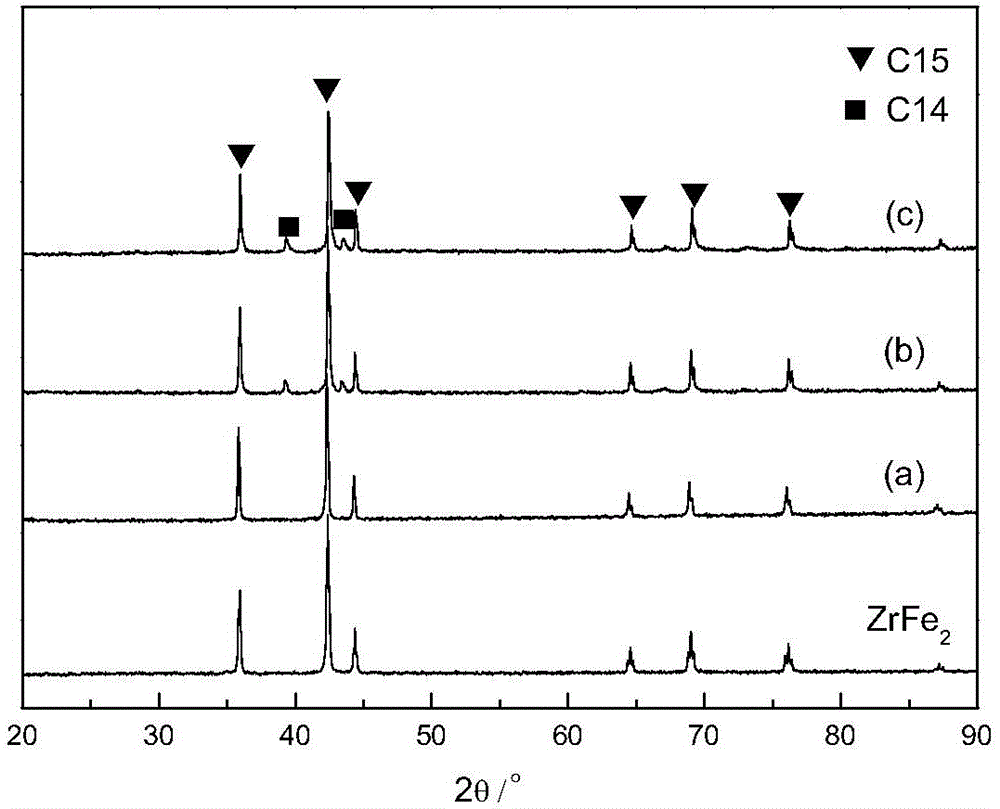
[0028] The alloy ingot is mechanically crushed, and about 1 g of sample is taken, which is mechanically ground into powder below 300 mesh and analyzed by X-ray diffraction. The X-ray diffraction spectrum is as follows: figure 1 (a) shows that the alloy is a single C15 type Laves phase structure...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Preparation of Zr 0.9 Ti 0.1 Fe 1.95 V 0.1 Mmm 0.015Alloy: starting materials are commercial metal elements sponge titanium, sponge zirconium, rod iron, granular vanadium and massive cerium-rich rare earth Mm, the element purity is higher than 99%, and the composition of cerium-rich rare earth Mm is: Ce52.5%, La30 .4%, Nd11.4%, Pr4.5%, other elements 1.2%. Formulated to a nominal composition of Zr 0.9 Ti 0.1 Fe 1.95 V 0.1 Mmm 0.015 The alloy is smelted into a flake alloy with a weight of about 10kg in an intermediate frequency induction melting furnace protected by a high-purity Ar (99.999%) atmosphere, and the alloy material is placed in a vacuum heat treatment furnace, annealed at 900 ° C for 24 hours, and cooled Then remove the alloy material.
[0031] Carry out X-ray imaging diffraction analysis to alloy sample, analysis method is the same as embodiment 1. Its X-ray diffraction spectrum is as figure 1 As shown in (b), the main phase in the alloy is a C15...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Preparation of Zr 0.85 Ti 0.15 Fe 1.95 V 0.1 Mmm 0.015 Alloy: starting materials are commercial metal elements sponge titanium, sponge zirconium, rod iron, granular vanadium and massive cerium-rich rare earth Mm, the element purity is higher than 99%, and the composition of cerium-rich rare earth Mm is: Ce52.5%, La30 .4%, Nd11.4%, Pr4.5%, other elements 1.2%, formulated to have a nominal composition of Zr 0.85 Ti 0.15 Fe 1.95 V 0.1 Mmm 0.015 alloy, and then smelted into an alloy ingot with a weight of about 30g. The alloy ingot smelting method, heat treatment method, X-ray diffraction analysis method, activation method and hydrogen absorption and desorption PCT curve test method are the same as in Example 2. Its X-ray diffraction spectrum is as figure 1 As shown in (c), the main phase in the alloy is a C15-type Laves phase structure, and contains a small amount of C14-type Laves phase structure.
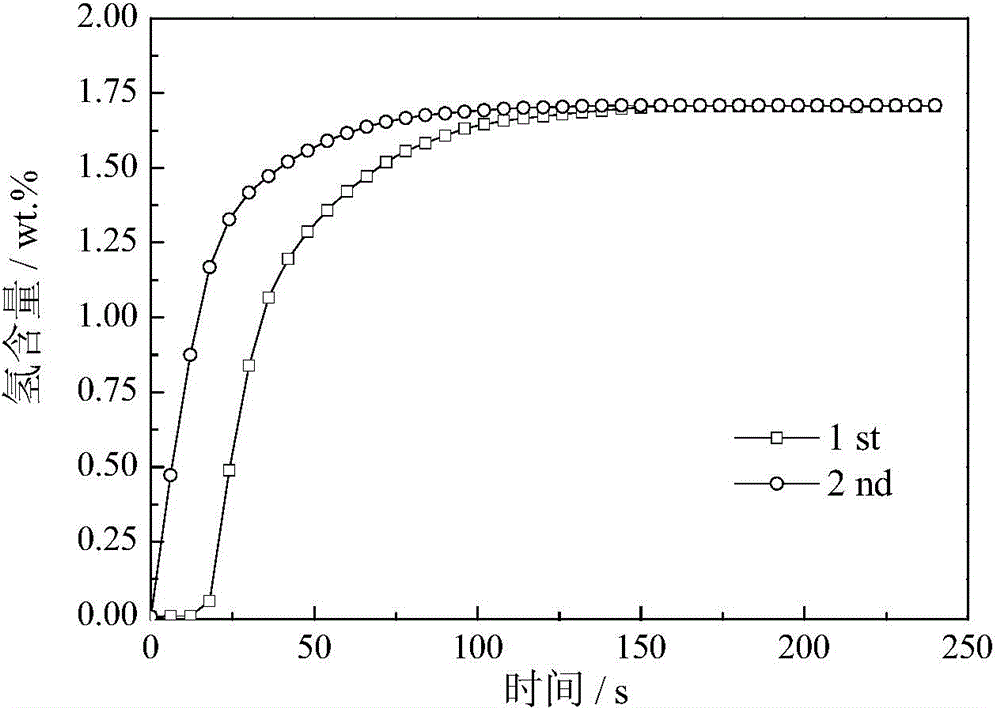
[0035] The test results show that the alloy can be fully activ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com