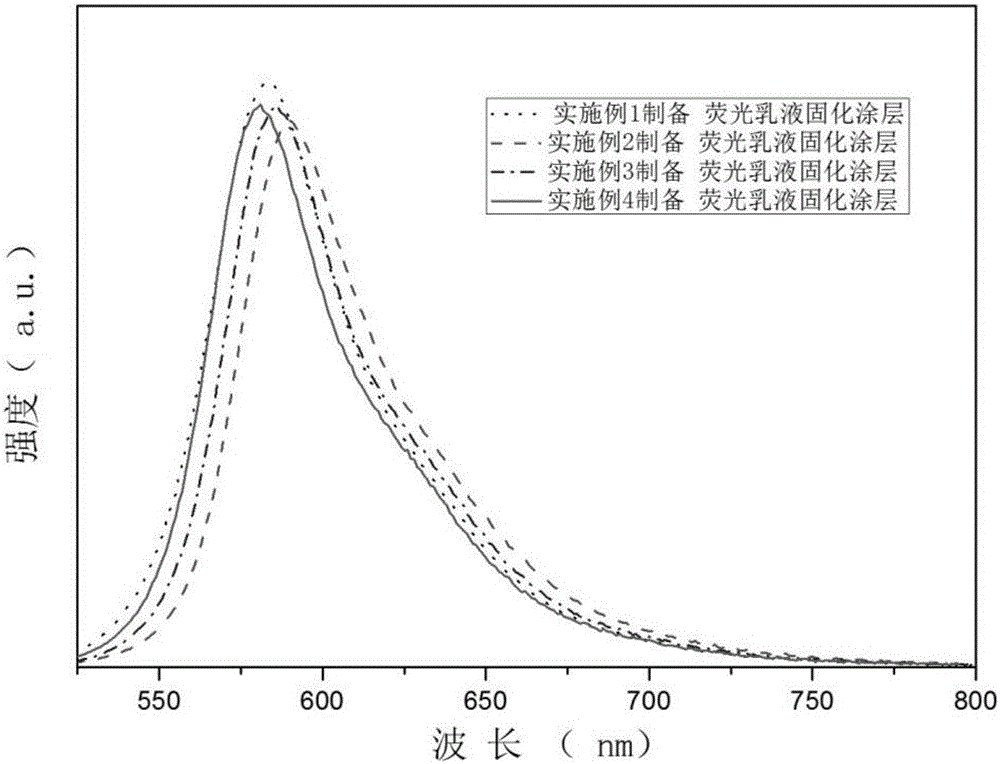
Fluorescent latex containing rhodamine B and preparing method thereof
A latex and fluorescent technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, luminescent materials, luminescent coatings, etc., can solve problems such as lifespan reduction of light-emitting devices, aggregation and crystallization quenching, excitation energy dissipation, etc., and achieve simple, effective and controllable effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The monomers that make up the fluorescent latex and their relative mass percentages are:
[0021]
[0022] The added cationic emulsifier is cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, and its mass content relative to the monomer mixture is 2wt%. The thermal initiator used is azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride, and its mass content relative to the monomer mixture is 1 wt%. The relative amount of water added is controlled so that the polymer solid content of the prepared water-based fluorescent latex is in the range of 40 wt%.
[0023] Prepare the fluorescent latex of experimental design, it is characterized in that:
[0024] The first step: mix methyl methacrylate, styrene, and butyl acrylate, then add cationic emulsifier, rhodamine B, and cationic polymerization initiator, and add the mixture to the same quality water as the monomer mixture, At 400 rpm, mechanically stirred for 15 minutes to fully pre-emulsify to obtain a pre-emulsified mixture.
[0025] The second step: the...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The monomers that make up the fluorescent latex and their relative mass percentages are:
[0031]
[0032] In order to obtain the designed fluorescent latex, the added cationic emulsifier is dodecyl ammonium chloride, and its mass content relative to the monomer mixture is 1.2 wt%. The thermal initiator used is azobisisobutylimidazoline hydrochloride, and its mass content relative to the monomer mixture is 0.8 wt%. The relative amount of water added is controlled so that the polymer solid content of the prepared water-based fluorescent latex is in the range of 30 wt%.
[0033] Prepare the fluorescent latex of experimental design, it is characterized in that:
[0034] The first step: mix methyl methacrylate, styrene, and butyl acrylate, then add cationic emulsifier, rhodamine B, and cationic polymerization initiator, and add the mixture to the same quality water as the monomer mixture, Stir mechanically for 20 minutes at a speed of 300 rpm to fully pre-emulsify to o...
Embodiment 3
[0038] The monomers that make up the fluorescent latex and their relative mass percentages are:
[0039]
[0040]
[0041] In order to obtain the designed fluorescent latex, the added cationic emulsifier is dodecylpyridinium chloride, and its mass content relative to the monomer mixture is 0.8wt%. The thermal initiator used is azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride, and its mass content relative to the monomer mixture is 0.4 wt%. The relative amount of water added is controlled so that the polymer solid content of the prepared water-based fluorescent latex is in the range of 20 wt%.
[0042] Prepare the fluorescent latex of experimental design, it is characterized in that:
[0043] The first step: mix methyl methacrylate, styrene, and butyl acrylate, then add cationic emulsifier, rhodamine B, and cationic polymerization initiator, and add the mixture to the same quality water as the monomer mixture, At a speed of 200 rpm, mechanically stir for 25 minutes to fully pre-emul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com