Low-friction high-wear resistance bionic artificial joint and preparation method thereof
An artificial joint, low friction technology, used in tissue regeneration, prosthesis, coating and other directions, can solve the problems affecting the quality and service life of artificial joints, osteolysis and aseptic loosening, and the wear resistance needs to be improved. Reduced refurbishment and replacement frequency, stable hydrophilic wear layer, and improved wear resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] A method for preparing a low-friction and highly wear-resistant artificial joint of the present invention comprises the following steps:
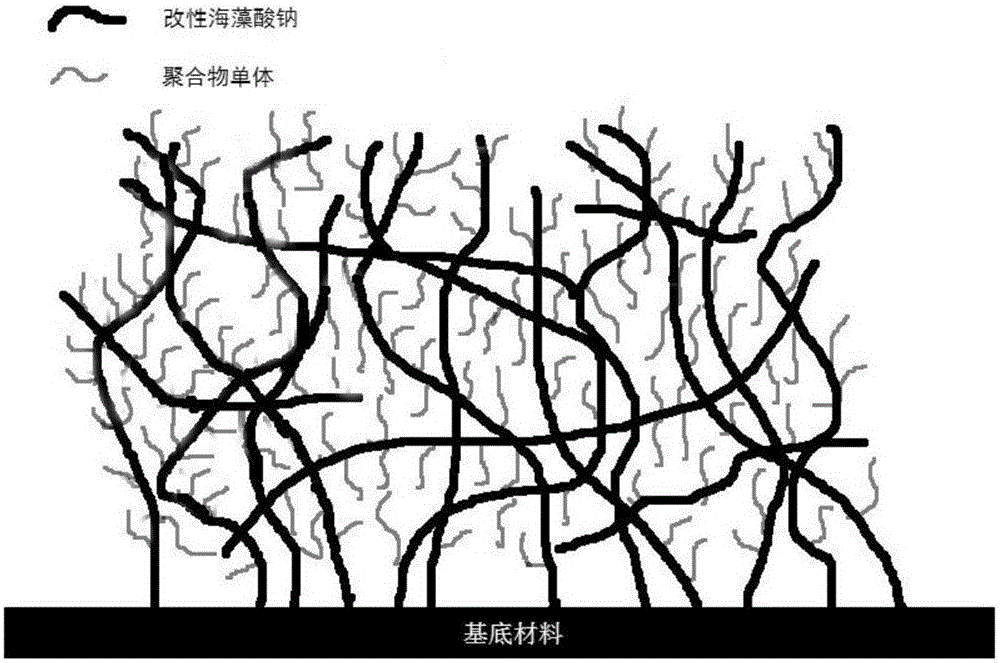
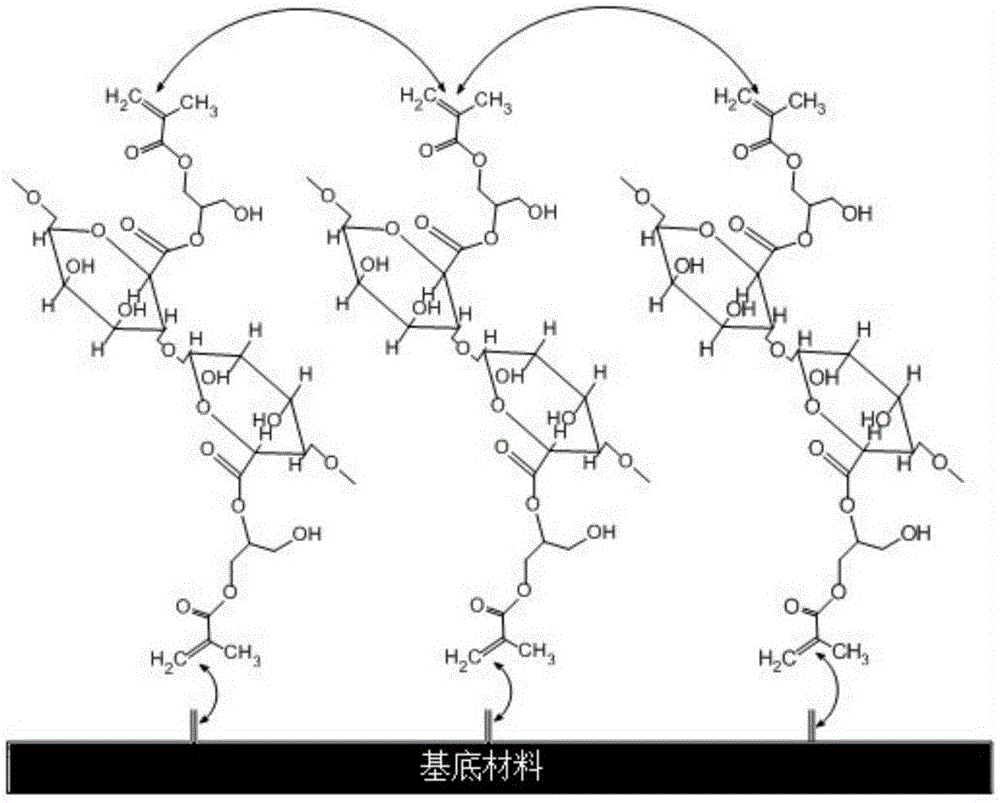
[0031] In step 1, the sodium alginate is modified by a glycidyl methacrylate reaction method, and a carbon-carbon double bond is introduced into the sodium alginate.
[0032] The specific method is: add 0.54ml triethylamine to 250ml sodium alginate aqueous solution (0.2-0.5% (wt / v)), add 1.26g tetrabutylammonium bromide after magnetic stirring for one hour, and continue magnetic stirring for one hour Then add glycidyl methacrylate (3.32ml-16.62ml) so that the molar ratio of sodium alginate to glycidyl methacrylate is 1:10-50. React for 24 hours under magnetic stirring conditions, dialyze the product in deionized water with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500D for 6 days, and finally freeze-dry to obtain a modified sodium alginate sample;
[0033] In step 2, the modified sodium alginate is grafted on the surface of...
Embodiment 1
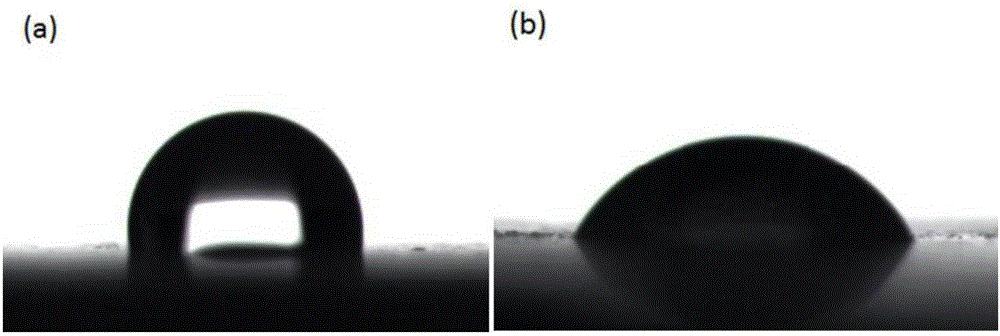
[0040] Add 0.54ml triethylamine to 0.2% (wt / v) sodium alginate aqueous solution, add 1.26g tetrabutylammonium bromide after magnetic stirring for one hour, continue magnetic stirring for one hour, then add glycidyl methacrylate 3.32 ml, so that the molar ratio of sodium alginate to glycidyl methacrylate is 1:10. The product was reacted for 24 hours under the condition of magnetic stirring, and the product was dialyzed in deionized water with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cutoff of 3500D for 6 days, and finally freeze-dried to obtain a modified sodium alginate sample. Prepare an aqueous solution of 1g / L modified sodium alginate, put the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene block material (UHMWPE) in the acetone solution (5mg / ml) of photosensitizer benzophenone, and keep it in the dark for 1min to make it The surface is coated with a photosensitizer, and dried in a dark room for 1 hour in vacuum; the sample coated with the photosensitizer is immersed in the above-me...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Add 0.54ml triethylamine to 0.3% (wt / v) sodium alginate aqueous solution, add 1.26g tetrabutylammonium bromide after magnetic stirring for one hour, continue magnetic stirring for one hour, then add glycidyl methacrylate 9.97 ml, so that the molar ratio of sodium alginate to glycidyl methacrylate is 1:20. The product was reacted for 24 hours under the condition of magnetic stirring, and the product was dialyzed in deionized water with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cutoff of 3500D for 6 days, and finally freeze-dried to obtain a modified sodium alginate sample. Prepare an aqueous solution of 3g / L modified sodium alginate, put the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene block material in the acetone solution (10mg / ml) of photosensitizer benzophenone, and keep it in the dark for 3min, so that the surface is coated The photosensitizer was vacuum-dried in a dark room for 1 h; the sample coated with the photosensitizer was immersed in the above-mentioned aqueous sol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com