Method of comprehensively recycling valuable metal from lead sulfate slag
A valuable metal, lead sulfate technology, applied in the improvement of process efficiency, photographic technology, instruments and other directions, can solve the problems of low crystal quality, low lead crystallization rate, narrow use of lead chloride, etc. Low investment, equipment and simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
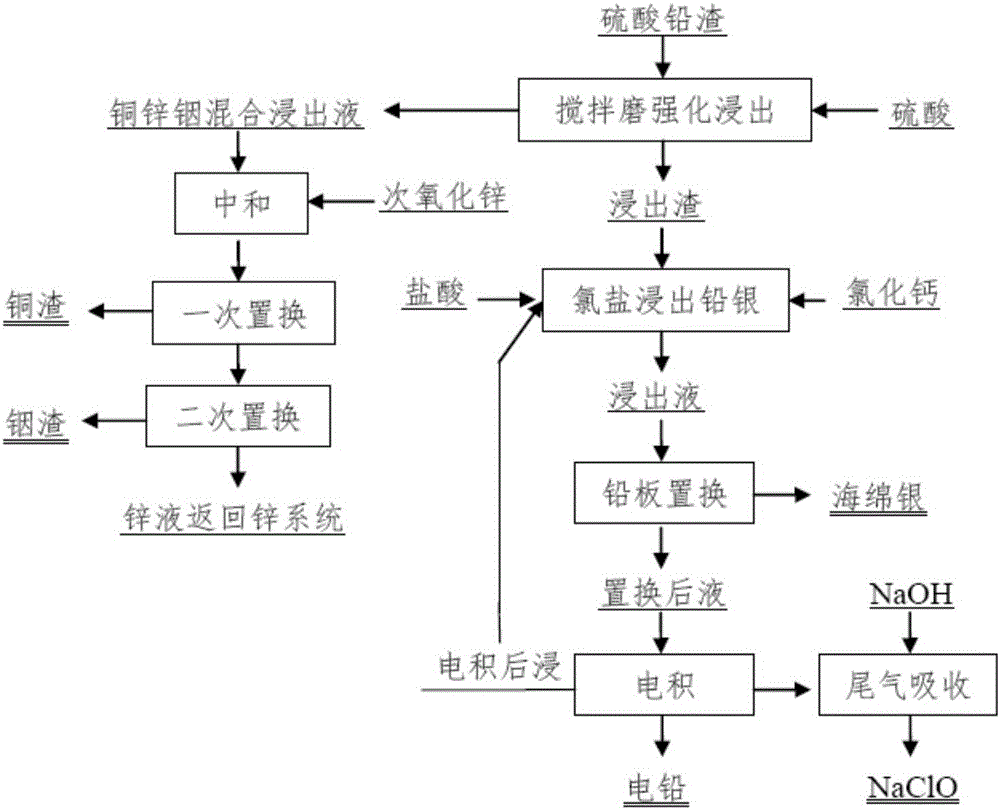
[0029] Stirring mill enhanced leaching: 1kg lead sulfate slag (Pb 28.1%, Cu 4.1%, Zn 3.6%, In 350g / t, Ag 760g / t), leaching agent is 200g / L sulfuric acid, leaching temperature 90℃, leaching time 2h, The liquid-solid ratio is 2:1. The copper leaching rate reaches 95%, the zinc leaching rate reaches 98%, and the indium leaching rate reaches 85%.
[0030] Neutralization: Neutralize the pH of the copper-zinc-indium solution to 1.0 with zinc oxide at room temperature (25°C).
[0031] One replacement: Zinc powder was used as the replacement agent, the replacement temperature was 25°C, the amount of zinc powder was 1.1 times the theoretical amount, and the replacement was performed for 1 hour to obtain 46.3 g of copper slag with a copper content of 83.7%.
[0032] Secondary replacement: Zinc powder was used as the replacement agent, the replacement temperature was 25°C, the amount of zinc powder was 2.5 times the theoretical amount, and the replacement was performed for 2 hours to ob...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Stirring mill enhanced leaching: 1kg lead sulfate slag (Pb 24.3%, Cu 5.3%, Zn 4.6%, In 310g / t, Ag 650g / t), leaching agent is 100g / L sulfuric acid, leaching temperature 70℃, leaching time 2h, The liquid-solid ratio is 2:1. The copper leaching rate reaches 95%, the zinc leaching rate reaches 97%, and the indium leaching rate reaches 84%.
[0038] Neutralization: Neutralize the pH of the copper-zinc-indium solution to 1.0 with zinc oxide at room temperature (25°C).
[0039] One replacement: Zinc powder was used as the replacement agent, the replacement temperature was 25°C, the amount of zinc powder was 1.15 times the theoretical amount, and the replacement was performed for 1 hour to obtain 59.0 g of copper slag with a copper content of 85.3%.
[0040] Secondary replacement: Zinc powder was used as the replacement agent, the replacement temperature was 25°C, the amount of zinc powder was 2.5 times the theoretical amount, and the replacement was performed for 2 hours to o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power consumption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com