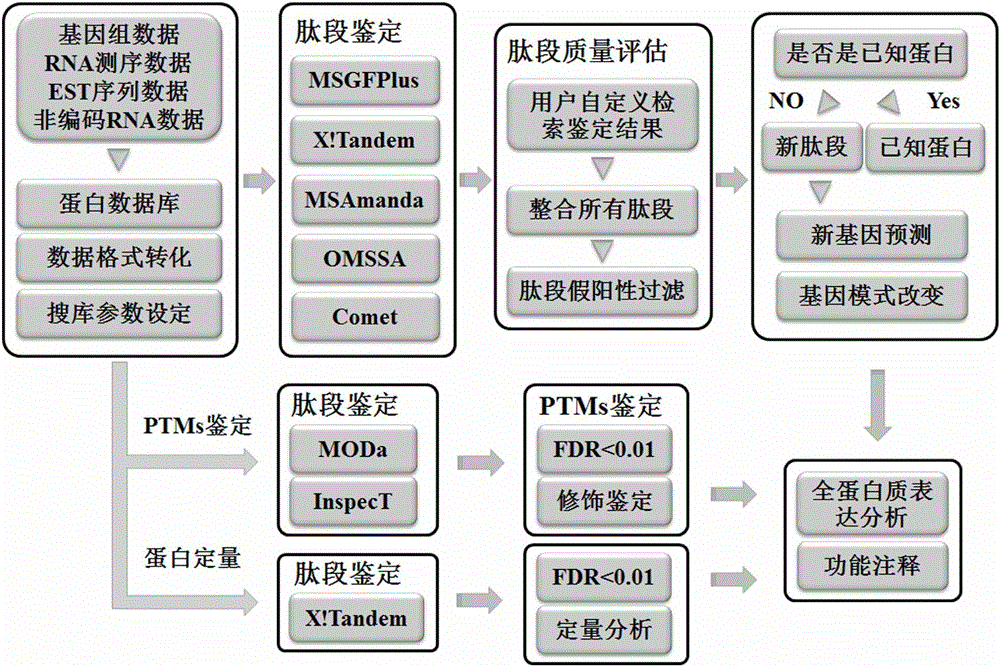
Method for analyzing data of prokaryotic proteogenomics rapidly and automatically
A protein genome and automatic analysis technology, applied in the field of protein genome data analysis, can solve problems such as hindering the development of protein genomics, complicated use settings, and limited application scope, and achieve the effect of improving identification coverage and good compatibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] The mass spectrum data in Example 1 and Example 2 are from published articles respectively [Muller, S.A., Findeiss, S., Pernitzsch, S.R., Wissenbach, D.K., Stadler, P.F., Hofacker, I.L., von Bergen, M., and Kalkhof , S, "Identification of new protein coding sequences and signalpeptidase cleavage sites of Helicobacter pylori strain 26695 by proteogenomics", Journal of proteomics, 2013, 86, 27-42] and [Albrethsen, J., Agner, J., Piersma, S.R., Hojrup, P ., Pham, T.V., Weldingh, K., Jimenez, C.R., Andersen, P., and Rosenkrands, I., "Proteomic Profiling of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Identifies Nutrient-starvation-responsive Toxin-antitoxin Systems", Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2013, 12, 1180- 1191].
[0049] Example 1 Large-scale identification of new coding genes and post-translational modifications of Helicobacter pylori, the steps are as follows:
[0050] 1) download Helicobacter pylori complete genome sequence, transcriptome sequence, GFF format file, GBK format f...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Non-marker quantitative analysis of newly encoded genes and proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the steps are as follows:
[0066] 1) adopt the method same as embodiment 1, provide whole genome sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, transcriptome sequence, GFF format file, GBK format file, the protein storehouse sequence of proteome, the present invention uses perl language program, according to six reading and The three-reading frame translation method translates to obtain the protein library file; then uses ProteoWizard to convert the original data into a standard mgf format file; finally configures the search engine search parameters uniformly.
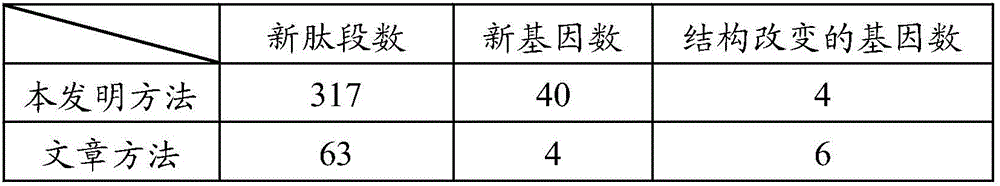
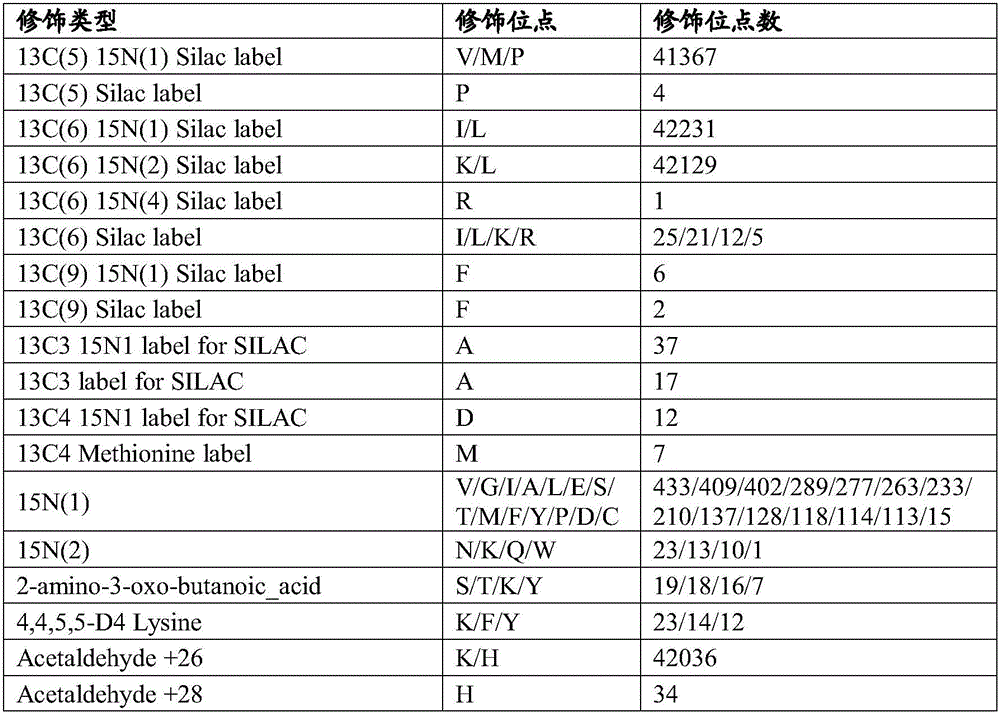
[0067] 2) The search engines of five different algorithms automatically search the database, and carry out the identification of new genes and structurally changed genes, as shown in Table 3, by the method of the present invention, 10 new genes and 9 N The gene with terminal extension includes 559 new unique peptides; t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com