A method of using other heavy metal wastewater to strengthen the treatment of chromium-containing wastewater
A technology for heavy metal and chromium wastewater, applied in biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve secondary pollution, unrealistic, unclear effect of reducing electrode passivation, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of strengthening the effect and reducing the impact.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
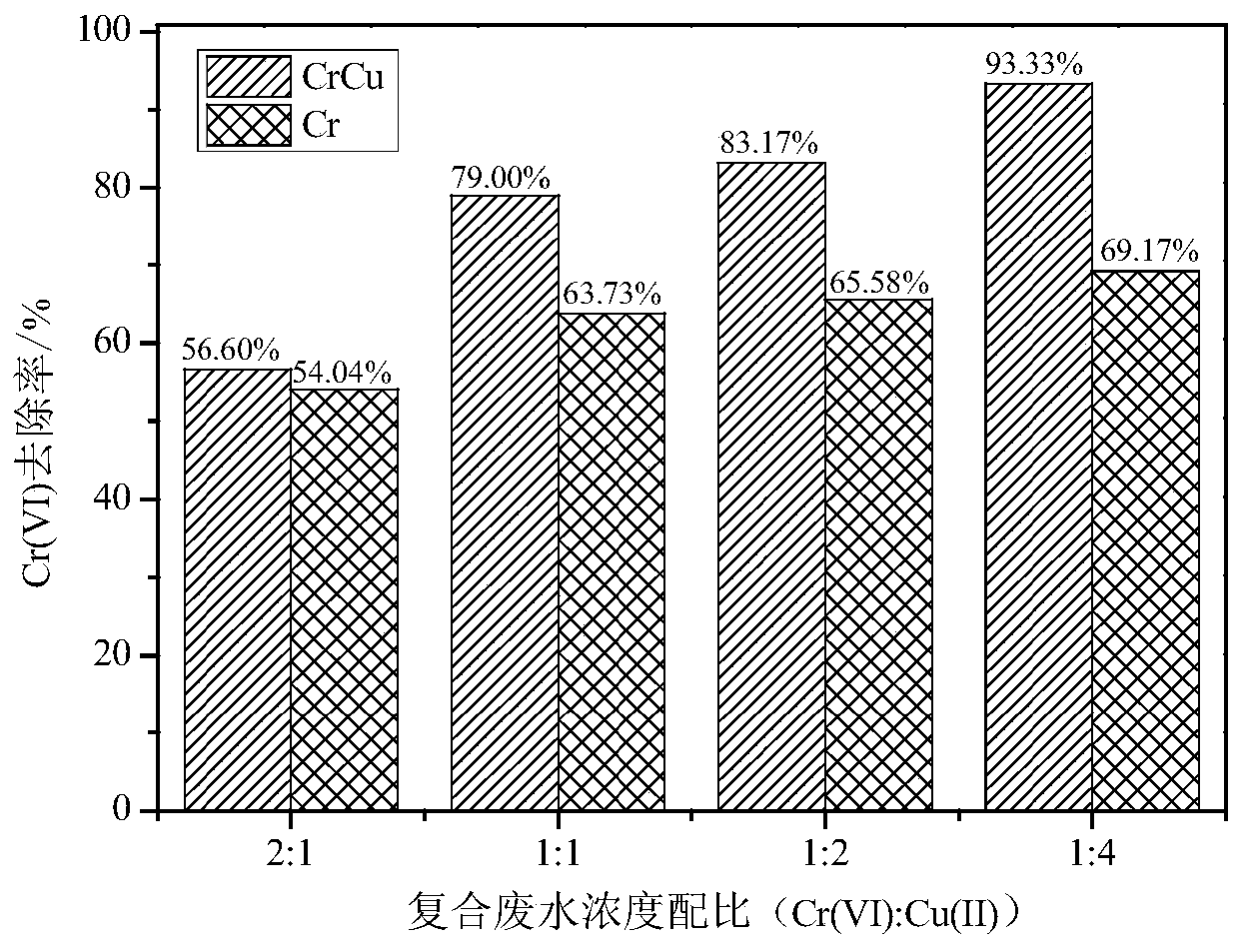
[0027] This example illustrates the effect of different concentration ratios of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) composite wastewater on the removal of chromium by chemical cathode MFC.
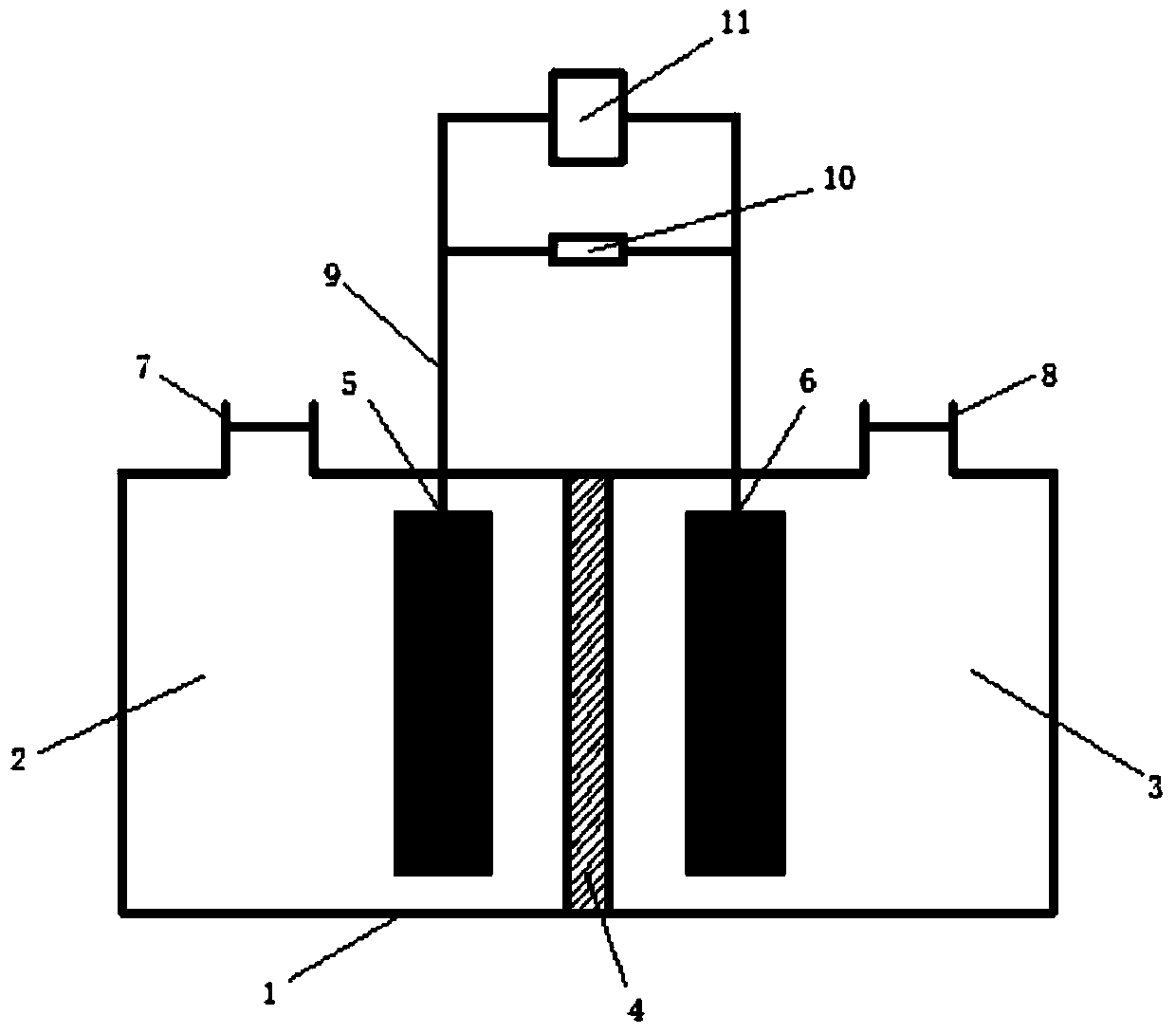
[0028] Such as figure 1 The chemical cathode MFC is constructed as shown, and the MFC anode uses anaerobic digested sludge (taken from Nanjing Jiangbei Sewage Treatment Plant) as the inoculation source, the inoculation ratio is 1:2 (sludge: anolyte), and the anolyte is COD=1000 mg / L artificial organic wastewater (pH=7), and 40mmol / L potassium ferricyanide (pH=7) was used as the catholyte to domesticate the anode electrogenic biofilm. Regularly replace the cathode and anode liquids, and after the MFC has stabilized the power generation for two consecutive cycles, it is regarded as the successful start-up of the MFC anode. Thereafter, the anode chamber was replaced with fresh artificial organic wastewater, and the catholyte was replaced with chromium-copper composite wastewater with a concentration ratio of ...
Embodiment 2
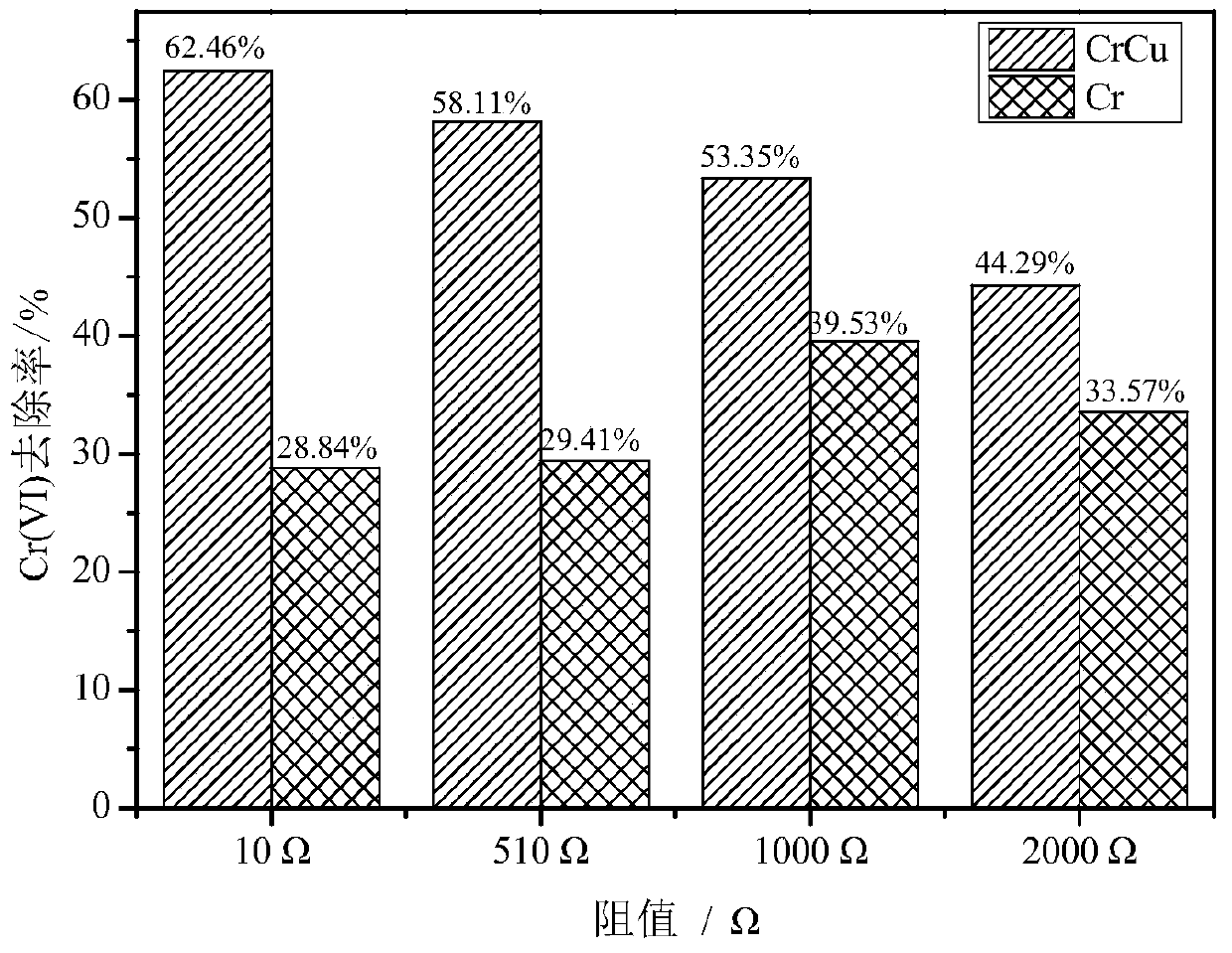
[0031] On the basis of Example 1, this example illustrates the influence of different external resistance conditions on the treatment of Cr(VI), Cu(II) composite wastewater by chemical cathode MFC.
[0032] Such as figure 1 The chemical cathode MFC is constructed as shown, and the domestication of the anode electrogenic bacteria group is the same as that described in Example 1. After the anode is started successfully, the cathode chamber is added with chromium-copper composite wastewater with a concentration ratio of 1:4 of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) (pH=3), at the same time, the chemical cathode MFC with Cr(VI) wastewater added alone was used as the control experiment group, and the cathode and anode chambers were strictly closed with plugs. The external resistance of the experimental group was set to 10 Ω, 510 Ω, 1000 Ω, 2000 Ω respectively, and the circuit was connected. All MFCs were run at 25 °C for 24 h. The cathode and anode materials of the MFC are graphite plates, and the di...
Embodiment 3
[0035] This example illustrates the effect of different aeration conditions on the MFC chemical cathode treatment of Cr(VI), Cu(II) composite wastewater.
[0036] Such as figure 1The chemical cathode MFC is constructed as shown, and the anode start-up is the same as that described in Example 1. The chromium-copper composite wastewater (pH=3) with a concentration ratio of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) of 1:4 is added to the cathode chamber, and at the same time, it is added separately The chemical cathode MFC of Cr(VI) wastewater was used as the control group. The anode chamber is strictly sealed with a stopper, and the cathode chamber is respectively set under anaerobic conditions (dissolved oxygen is about 0.2 mg / L) and aerobic conditions (dissolved oxygen is about 7.03 mg / L). The external resistance is 10 Ω, and the circuit is connected. All MFCs were run at 25 °C for 24 h. The cathode and anode material of the MFC is carbon paper, and the separator is a bipolar membrane.
[0037] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com