Processing method for Liuhe tea
A processing method, the technology of Liuhe tea, which is applied in tea treatment before extraction and adaptation to climate change, etc., can solve the problems of inconsistent product quality and achieve pleasant aroma, reduced leaf area, and bright orange-red soup color
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Construction of Liuhe tea processing method
[0035] A processing method of Liuhe tea, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0036]1) Pick fresh leaves with three to four leaves of a bud (including leaves with the same tenderness) as raw materials. The buds and leaves are required to be complete, uniform, fresh and clean, without heating, and cooled immediately to prevent early fermentation of fresh leaves ;
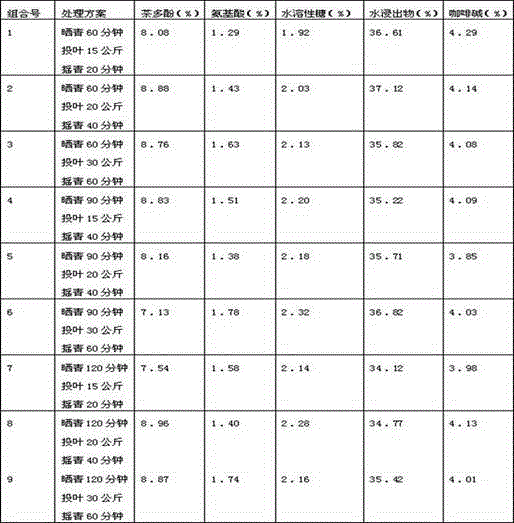
[0037] 2) After cooling, the fresh leaves are subjected to combined treatment of drying and shaking. "Sunning" means dehydrating the fresh leaves of tea trees under sunlight with an appropriate intensity for a certain period of time. Through drying, various hydrolytic enzymes and Oxidase activity, promote the decomposition of nitrogen-containing and carbon-containing compounds in the process of tea making, the formation of small molecular weight phenolic substances, water-soluble sugars, amino acids, and promote the transformation of aromatic oils and th...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The process of sun-drying and shaking green is determined
[0050] The following examples of the present invention are the main kit equipment and instruments;
[0051] Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (analytical pure); Disodium hydrogen phosphate (analytical pure); Ninhydrin (analytical pure); Ferrous sulfate (analytical pure); Potassium sodium tartrate (analytical pure); Methanol (chromatographic pure); Glacial acetic acid (analytically pure); formamide (chromatographically pure); redistilled water; anhydrous ether; anhydrous sodium sulfate; ethyl caprate;
[0052] Analytical balance (1 / 10000); water bath; T-A UV-Vis spectrophotometer; cuvette; thermometer; constant temperature dry box; dry hygrometer; volumetric flask; pipette, etc.; heat extraction device; filter; vacuum evaporator ; Centrifuge; Settling tank; Impurity removal tank; Settling tank; Suction filter; Vacuum dryer, ultrasonic cleaner; 0.45 mm microporous filter;
[0053] LC-2010AHT high performance liqui...
Embodiment 3
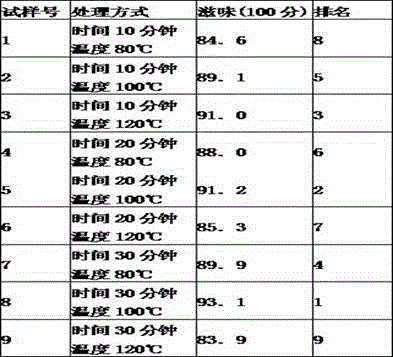
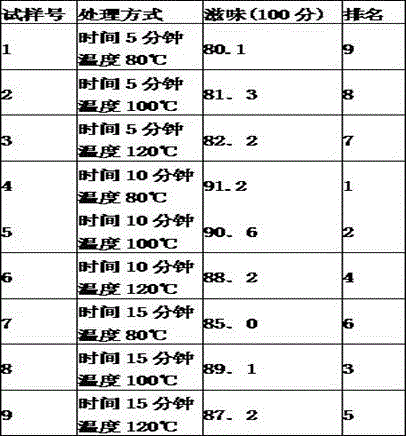
[0089] Research and development of multiple fermentation technology
[0090] 1. Test method
[0091] 1) Determination of the time of the initial compost fermentation
[0092] After kneading, carry out the initial stacking, spread wet cotton cloth on the floor of the fermentation room, put the ventilation and oxygenation device on the cotton cloth, then pile the rolled leaves into a cuboid with a height of 65-70cm, put the thermometer in the pile, and put the wet cotton cloth Cover the tea pile. Observe the temperature and fermentation degree every 2 hours, ventilate and add oxygen according to the temperature of the tea heap and the degree of fermentation, when the temperature reaches 45°C, ventilate and add oxygen for 12 minutes. Wet the piles for 15 hours, 20 hours, and 25 hours respectively to investigate the influence on the color and taste of the finished tea soup, so as to optimize the initial pile fermentation time.
[0093] 2) Determination of the time of composting...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com