Stable method for preparing boron nitride nanoflake through liquid-phase chemical stripping
A technology of boron nitride and nanosheets, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, nitrogen compounds, etc., can solve the limitations of the preparation and application of boron nitride nanosheets, the time-consuming and high reaction temperature of ultrasonic-assisted solvent stripping Or reaction pressure and other issues, to achieve the effect of favorable peeling, low cost, safety and environmental protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Fully stir 1g of hexagonal boron nitride powder and 60ml of concentrated sulfuric acid and soak for 4 hours, then add 3g of potassium ferrate, continue to stir, and mix evenly;
[0034] (2) The mixture was stirred and reacted at 20° C. for 10 hours, and then the reactants were added dropwise to distilled water for dilution;
[0035] (3) centrifuging the diluted solution to remove bulk unstripped boron nitride powder;
[0036] (4) The reaction product was obtained by suction filtration, washed 2-3 times with hydrochloric acid, and then washed with deionized water until neutral, and dried at 60° C. for 10 hours to obtain boron nitride nanosheets.
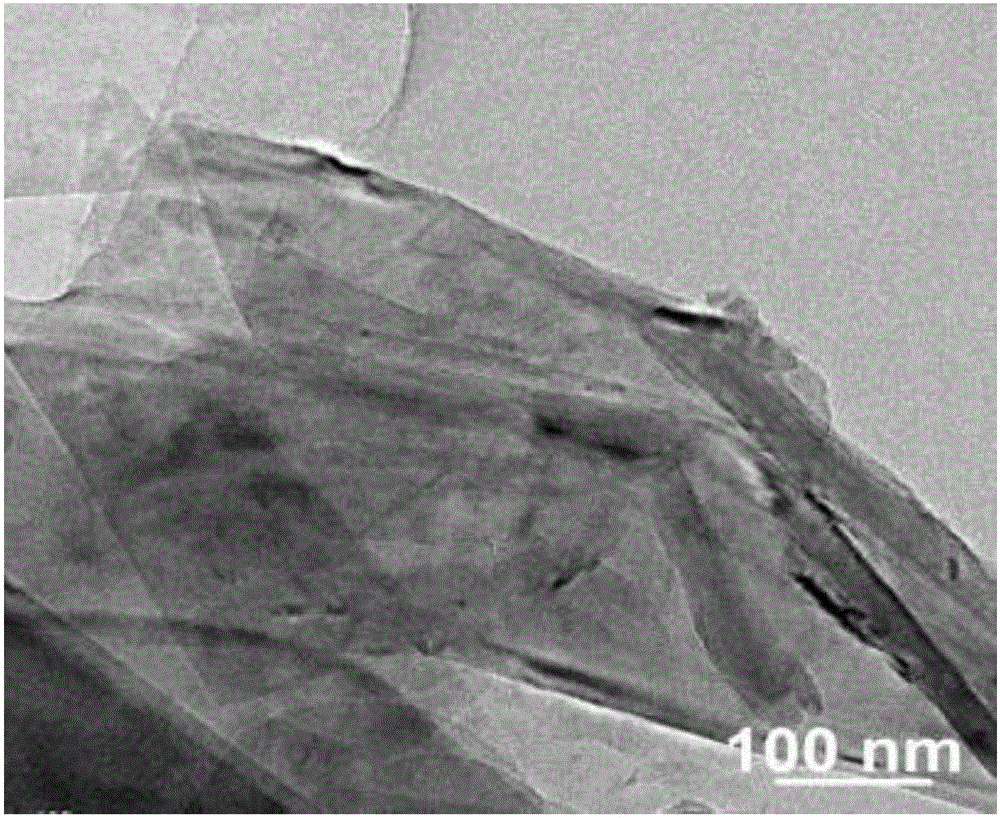
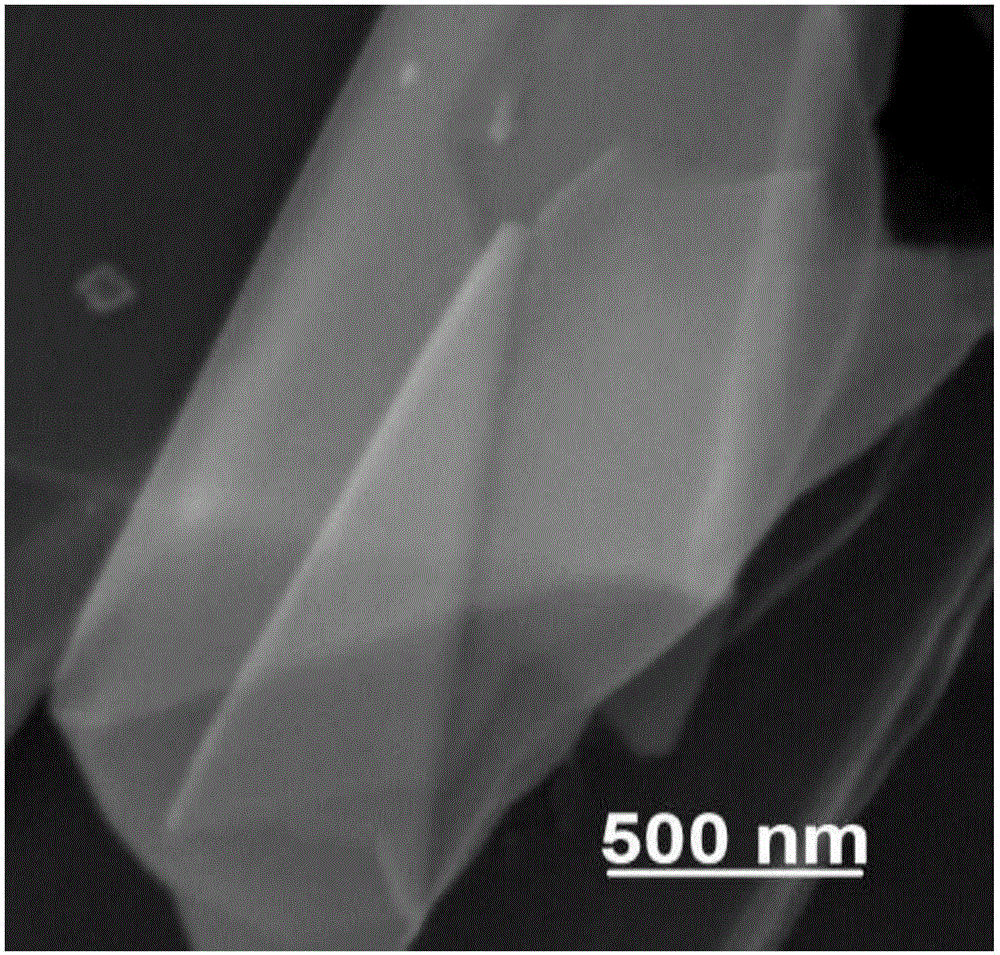
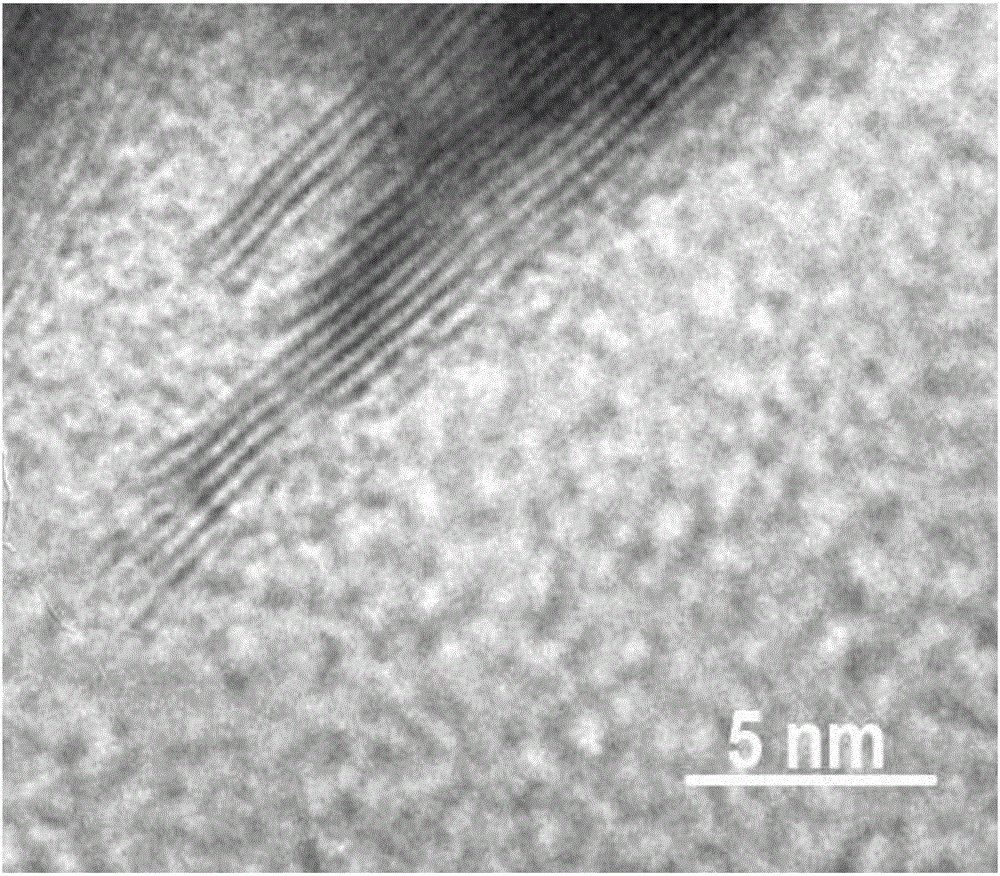
[0037] The scanning electron micrograph of the boron nitride nanosheet prepared in this embodiment is as follows: figure 1 Shown; The low magnification transmission electron microscope photo of the boron nitride nanosheet prepared in the present embodiment is as follows figure 2 Shown; The high magnification transmission...
Embodiment 2
[0039](1) Fully stir 1g of hexagonal boron nitride powder and 100ml of nitric acid and infiltrate for 2 hours, then add 3g of potassium ferrate, continue to stir, and mix evenly;
[0040] (2) The mixture was stirred and reacted at 30° C. for 24 hours, and then the reactant was added dropwise to distilled water for dilution;
[0041] (3) centrifuging the diluted solution to remove bulk unstripped boron nitride powder;
[0042] (4) The reaction product was obtained by suction filtration, washed 2-3 times with hydrochloric acid, and then washed with deionized water until neutral, and dried at 60° C. for 10 hours to obtain boron nitride nanosheets.
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) Fully stir 1g of hexagonal boron nitride powder and 100ml of sulfuric acid and soak for 6 hours, then add 5g of potassium ferrate, continue to stir, and mix evenly;
[0045] (2) The mixture was stirred and reacted at 60° C. for 10 hours, and after cooling, the reactant was added dropwise to distilled water for dilution;
[0046] (3) centrifuging the diluted solution to remove bulk unstripped boron nitride powder;
[0047] (4) The reaction product was obtained by suction filtration, washed 2-3 times with hydrochloric acid, and then washed with deionized water until neutral, and dried at 60° C. for 10 hours to obtain boron nitride nanosheets.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com