Non-ferrous metal smelting slag utilization method
A technology for non-ferrous metals and smelting slag, which is applied in the improvement of process efficiency, cement production and other directions, can solve the problems of low waste conversion rate, low utilization rate of smelting slag, ecological environment pollution, etc. The effect of reducing the protection and process links
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
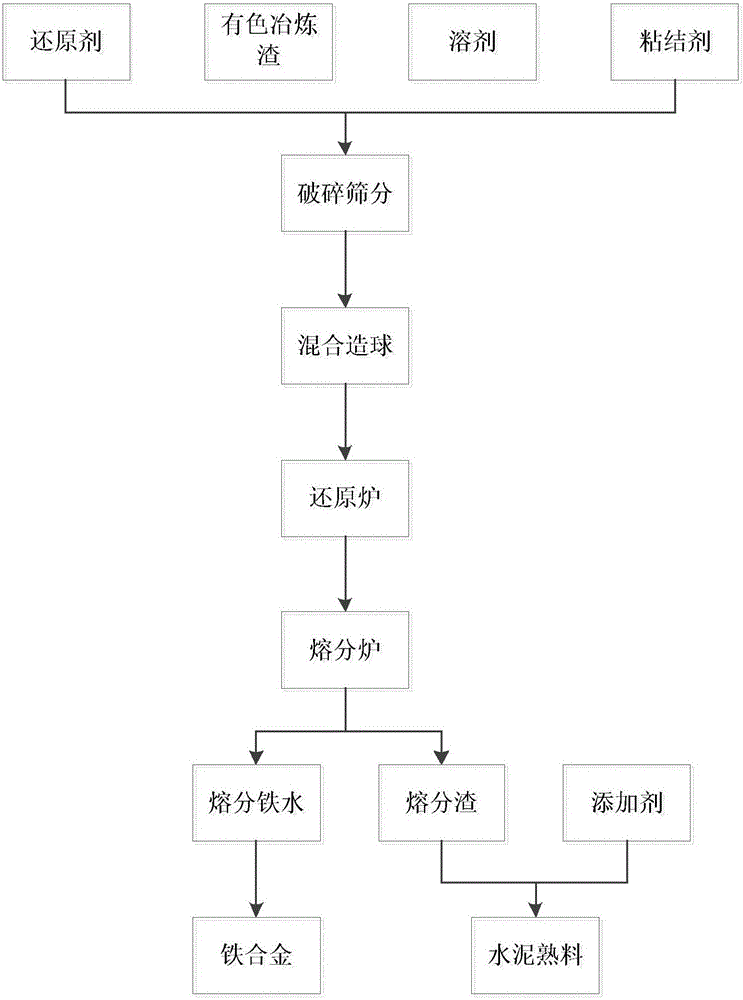
[0022] Raw material preparation:
[0023] Non-ferrous metal smelting slag: Jinchuan copper smelting slag MgO<5%, iron 40%;
[0024] Reducing agent: lignite, anthracite, bituminous coal;
[0025] Solvent: limestone, fluorite, industrial alkali;
[0026] Binder: bentonite;
[0027] Additives: calcium oxide, aluminum oxide.
[0028] (1) Fully mix non-ferrous metal smelting slag, reducing agent, solvent, and binder in a weight ratio of 1:0.2:0.3:0.05 and then pelletize;
[0029] (2) Dry the mixture and then reduce it: put the dried pellets into the reduction furnace, and pass through the inert protective gas, and heat it to 800°C in the furnace for 30 minutes, and the metallization rate can be 85. %~93% of metal pellets, the mixture mainly completes the preheating, heating and reduction processes at this temperature;
[0030] (3) Heat the reduction product of step (2) to the heating furnace, heat to 1500°C, and separate the slag and iron. After smelting, the molten iron enter...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Raw material preparation:
[0033] Non-ferrous metal smelting slag: Jinchuan nickel smelting slag MgO<5%, containing 50% iron;
[0034] Reducing agent: coke powder, lignite, anthracite;
[0035] Solvents: lime, sodium carbonate, fluorite;
[0036] Binder: starch;
[0037] Additives: calcium fluoride and aluminum oxide.
[0038] (1) Fully mix non-ferrous metal smelting slag, reducing agent, solvent, and binder in a weight ratio of 1:0.3:0.3:0.1 and then pelletize;
[0039] (2) Reduction after drying the mixture: put the dried pellets into the reduction furnace, and pass through the inert protective gas, and heat it to 1300°C in the furnace for 10 minutes, and the metallization rate can be 85. %~93% of metal pellets, the mixture mainly completes the preheating, heating and reduction processes at this temperature;
[0040] (3) Heat the reduction product of step (2) to the heating furnace, heat to 1700°C, and separate the slag and iron. After smelting, the molten iron ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Raw material preparation:
[0043] Non-ferrous metal smelting secondary slag: Yunnan copper smelting secondary slag, MgO<5%, iron 45%;
[0044] Reducing agent: coke powder;
[0045] Solvent: limestone;
[0046] Binder: bentonite, starch;
[0047] Additive: calcium fluoride.
[0048] (1) Fully mix the non-ferrous metal smelting slag, reducing agent, solvent and binder according to the weight ratio of 1:0.25:0.2:0.07 and then pelletize;
[0049] (2) Dry the mixture and then reduce it: put the dried pellets into the reduction furnace, and pass through the inert protective gas, and heat it to 1100°C in the furnace for 20 minutes, and the metallization rate of 85 can be obtained. %~93% of metal pellets, the mixture mainly completes the preheating, heating and reduction processes at this temperature;
[0050] (3) Heat the reduction product of step (2) to the heating furnace, heat to 1600°C, and separate the slag and iron. After smelting, the molten iron enters the molten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com