Process for processing microlite slabs
A processing technology and technology of microcrystalline stone, applied in the field of processing technology of microcrystalline stone plate, can solve the problems of unstable color of microcrystalline stone, short service life, low production efficiency, etc., and achieve stable color, long service life, mechanical strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
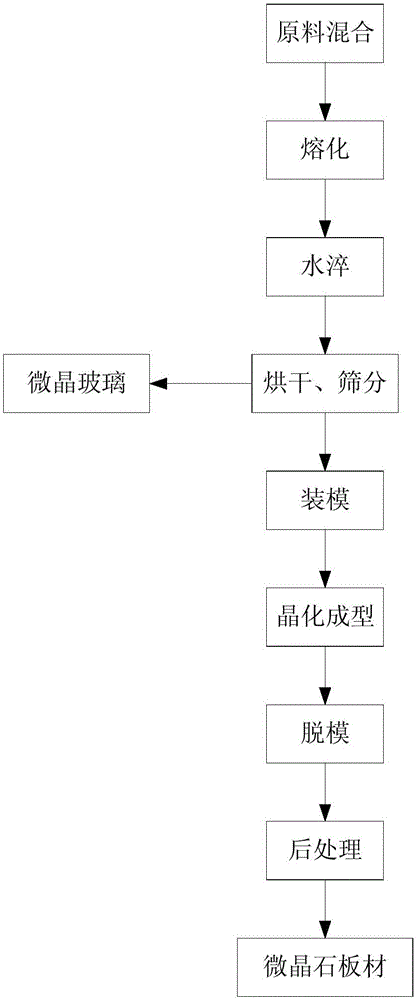
[0019] A processing technology of microcrystalline stone plate, comprising the following steps:
[0020] 1) Mixing of raw materials: tailings slag is transported to the storage tank through the slurry pump, calcium carbonate, quartz sand, borax, zinc oxide, barium carbonate and soda ash enter their respective silos from the raw material warehouse, and the proportion of each material enters through the automatic batching production line. Mix in a mixer, wherein the mass parts of raw materials are 630kg of tailings slag, 30kg of barium carbonate, 210kg of calcium carbonate, 45kg of quartz sand, 35kg of borax, 20kg of soda ash, and 30kg of zinc oxide;
[0021] 2) Melting: After the raw materials are mixed evenly in a certain proportion, they enter the glass melting furnace and are melted at a high temperature of 1500°C to form a liquid substance;
[0022] 3) Water quenching: the liquid substance from the melting furnace enters the water quencher, and is water quenched through wat...
Embodiment 2
[0027] A processing technology of microcrystalline stone plate, comprising the following steps:
[0028] 1) Mixing of raw materials: tailings slag is transported to the storage tank through the slurry pump, calcium carbonate, quartz sand, borax, zinc oxide, barium carbonate and soda ash enter their respective silos from the raw material warehouse, and the proportion of each material enters through the automatic batching production line. Mix in a mixer, wherein the mass parts of raw materials are 600kg of tailings slag, 30kg of barium carbonate, 220kg of calcium carbonate, 40kg of quartz sand, 40kg of borax, 30kg of soda ash, and 40kg of zinc oxide;
[0029] 2) Melting: After the raw materials are mixed evenly in a certain proportion, they enter the glass melting furnace and are melted at a high temperature of 1600°C to form a liquid substance;
[0030] 3) Water quenching: the liquid substance from the melting furnace enters the water quencher, and is water quenched through wat...
Embodiment 3
[0035] A processing technology of microcrystalline stone plate, comprising the following steps:
[0036] 1) Mixing of raw materials: tailings slag is transported to the storage tank through the slurry pump, calcium carbonate, quartz sand, borax, zinc oxide, barium carbonate and soda ash enter their respective silos from the raw material warehouse, and the proportion of each material enters through the automatic batching production line. Mix in a mixer, wherein the mass parts of raw materials are 650kg of tailings slag, 20kg of barium carbonate, 200kg of calcium carbonate, 50kg of quartz sand, 30kg of borax, 20kg of soda ash, and 30kg of zinc oxide;
[0037] 2) Melting: After the raw materials are mixed evenly in a certain proportion, they enter the glass melting furnace and are melted at a high temperature of 1550°C to form a liquid substance;
[0038] 3) Water quenching: the liquid substance from the melting furnace enters the water quencher, and is water quenched through wat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com