Method of whole-cell-biocatalytically producing glutaric acid
A technology of biocatalysis and glutaric acid, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as time-consuming, difficult product separation, and increased production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Construction of overexpressed DavBA and gabDT strains:
[0031] (1) Recombinant strains overexpressing davBA E. coli BL-22AB is provided by our laboratory, the recombinant strain E. coli BL-22AB was made into competent cells.
[0032] (2) gabT was synthesized by Jinweizhi, and the restriction sites were NdeI and XhoI, and it was connected to the pACYC vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pACYC-gabT,
[0033] (3) gabD was synthesized by Jinweiweizhi, with restriction sites NcoI and HindIII, and connected to the pACYC vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pACYC-gabD.
[0034] (4) After the recombinant plasmid pACYC-gabD was recovered by treatment with restriction endonucleases NcoI and HindIII, the fragment gabD with restriction sites of NcoI and HindIII was obtained, and the fragment was combined with the recombinant plasmid treated with the same restriction endonuclease Plasmid pACYC-gabT was ligated using T4 DNA ligase at 25°C for 30min.
[0035] (5) Trans...
Embodiment 2
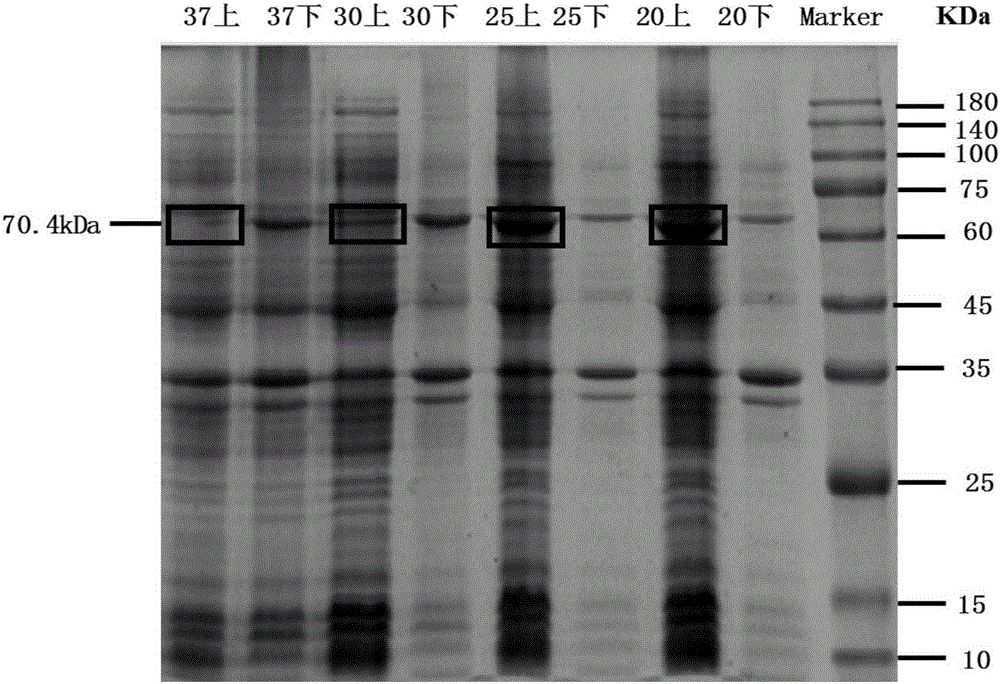
[0041] Optimum temperature screening for inducing LGOX expression
[0042] Pick recombinant strains from the plate E. coli A single colony of 28LGOX was placed in a 5ML LB shake tube containing 50mg / L kanamycin resistance, cultured for 6-8h and then transferred to 100ml LB containing 50mg / L kanamycin resistance until OD 600 =0.6, add 0.5mmol of IPTG, culture in a shaker at 20°C, 25°C, 30°C, and 37°C respectively, after 4h, centrifuge at 6000g for 5min to obtain cells overexpressing LGOX.
[0043] The obtained cells were resuspended with 5ml of 100mmol PBS, crushed using a cell disruptor, the crushing conditions were super 2s, stop 2s, the temperature was 4°C, the power was 30%, the crushing time was 10min, and then centrifuged at 7000g for 20min.
[0044] After measuring the protein concentration of supernatants and precipitates induced under different temperature conditions, the protein concentration was 20ug, and then analyzed by SDS-PAGE to obtain the protein expression a...
Embodiment 3
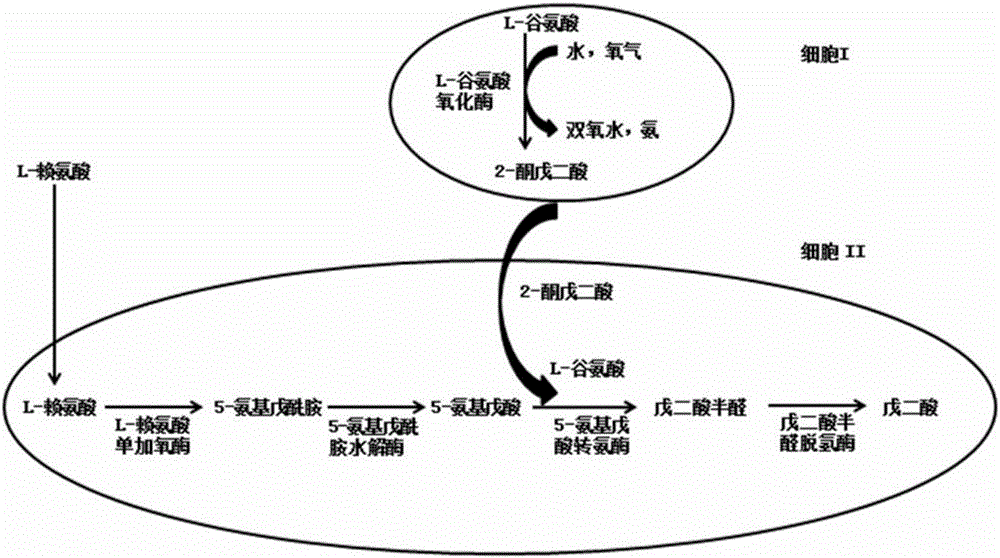
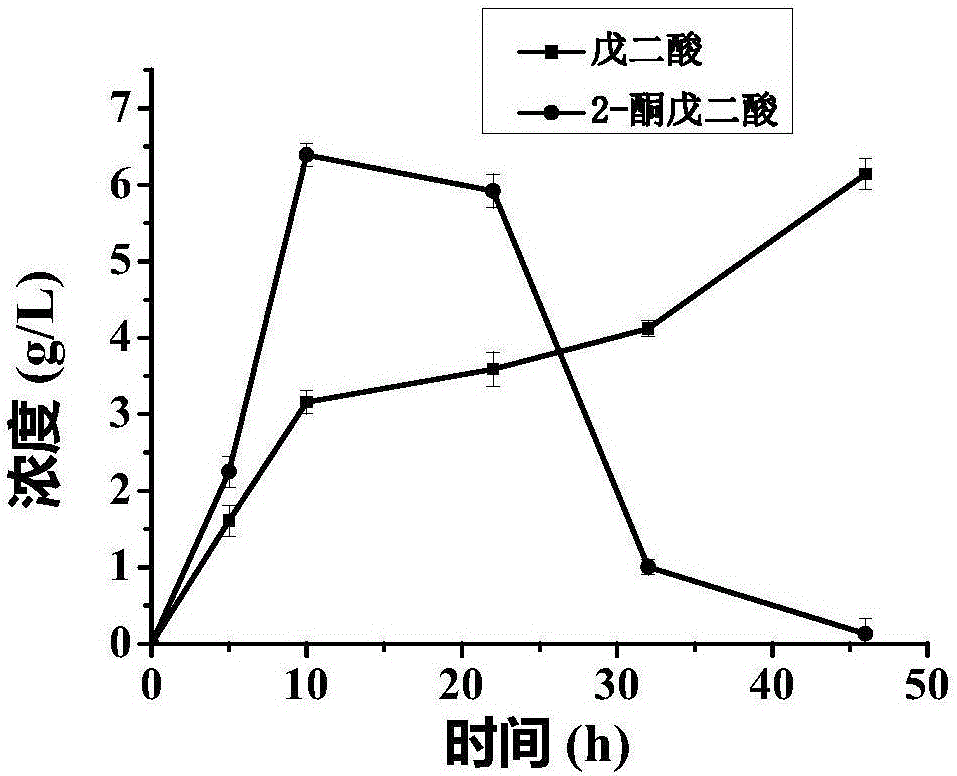
[0046] The whole cell catalyzed process of glutamate to produce 2-oxoglutarate is coupled with the process of whole cell catalyzed conversion of L-lysine to glutarate:
[0047] Cultivate and collect the recombinant bacteria that have overexpressed LGOX according to the mode of Example 2 E. coli 28LGOX cells as a catalyst.
[0048] At the same time, pick the recombinant strains from the plate E. coli A single colony of BL-22AB-YDT was inoculated into a 5ml LB shaking tube containing 100mg / L ampicillin resistance and 35mg / L chloramphenicol resistance. and 35mg / L chloramphenicol resistance in a 100ml shake flask to OD 600 =0.6, add 0.5mmol of IPTG, induce culture at 20°C for 12h, then centrifuge at 7000g for 5min to obtain the recombinant strain E. coli BL-22AB-YDT cells and use it as a catalyst.
[0049] Use 100mmolPBS to resuspend the recombinant bacteria E. coli 28LGOX and E. coli BL-22AB-YDT cells.
[0050] In the reaction system, add recombinant bacteria E. col...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com